electrostatic potential and capacitance
... Thus in the case of metallic conductor, placed in an external electric field (1) A steady electric charge distribution is induced on the surface of the conductor (2) The net electric field inside the conductor is zero (3) The net electric charge inside the conductor is zero (4) On the outer surface ...
... Thus in the case of metallic conductor, placed in an external electric field (1) A steady electric charge distribution is induced on the surface of the conductor (2) The net electric field inside the conductor is zero (3) The net electric charge inside the conductor is zero (4) On the outer surface ...
PPTX - University of Toronto Physics
... This implies that the units of electric field are volts per meter, or V/m. Previously, we have been using electric field units of newtons per coulomb. In fact, as you can show as a homework problem, these units are equivalent to each other: 1 N/C 1 V/m ...
... This implies that the units of electric field are volts per meter, or V/m. Previously, we have been using electric field units of newtons per coulomb. In fact, as you can show as a homework problem, these units are equivalent to each other: 1 N/C 1 V/m ...
R - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... The Electric Field inside a Hollow Sphere Conclusion: the static electric field inside a hollow charged sphere with a spherically symmetric charge distribution must be zero. ...
... The Electric Field inside a Hollow Sphere Conclusion: the static electric field inside a hollow charged sphere with a spherically symmetric charge distribution must be zero. ...
Chapter 24
... motion of charge within a conductor, explain why excess charge on an isolated conductor must reside on its surface. 9. A common demonstration involves charging a rubber balloon, which is an insulator, by rubbing it on your hair and then touching the balloon to a ceiling or wall, which is also an ins ...
... motion of charge within a conductor, explain why excess charge on an isolated conductor must reside on its surface. 9. A common demonstration involves charging a rubber balloon, which is an insulator, by rubbing it on your hair and then touching the balloon to a ceiling or wall, which is also an ins ...
11 - HCC Learning Web
... motion of charge within a conductor, explain why excess charge on an isolated conductor must reside on its surface. 9. A common demonstration involves charging a rubber balloon, which is an insulator, by rubbing it on your hair and then touching the balloon to a ceiling or wall, which is also an ins ...
... motion of charge within a conductor, explain why excess charge on an isolated conductor must reside on its surface. 9. A common demonstration involves charging a rubber balloon, which is an insulator, by rubbing it on your hair and then touching the balloon to a ceiling or wall, which is also an ins ...
Maxwell`s equations with Complex electric and magnetic fields due
... ⃗ . Recall that the two states can’t be measured at same state but with −E, the same time. The energy conservation equation in this state reveals a new charge state moving in opposite direction. It is like the motion of an antiparticle with opposite charge. This may urge us to identify the magnetic ...
... ⃗ . Recall that the two states can’t be measured at same state but with −E, the same time. The energy conservation equation in this state reveals a new charge state moving in opposite direction. It is like the motion of an antiparticle with opposite charge. This may urge us to identify the magnetic ...
Static and Kinetic Friction
... 2.1 Static vs. Kinetic: There are two types of frictional forces, static and kinetic. Static friction is what keeps a resting body at rest. Kinetic friction is what slows down an object when slid on a surface. Any two materials have a static and kinetic coefficient of friction which represents how m ...
... 2.1 Static vs. Kinetic: There are two types of frictional forces, static and kinetic. Static friction is what keeps a resting body at rest. Kinetic friction is what slows down an object when slid on a surface. Any two materials have a static and kinetic coefficient of friction which represents how m ...
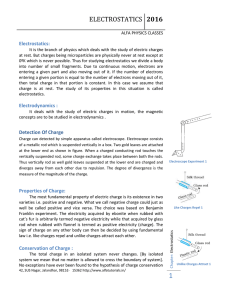
Gauss* Law
... Let’s assume we have a closed container, e.g., a sphere of an imaginary material that doesn’t interact with an electric field ...
... Let’s assume we have a closed container, e.g., a sphere of an imaginary material that doesn’t interact with an electric field ...
Grade 7 Physics Kit
... Grade 7 students will be moving on to high school in grade 8. Understanding electricity and magnetism allows students to explore electives (and possible careers) based on these fundamental forces. This science topic, more than any other, serves as a clear pathway to careers in the trades. An electro ...
... Grade 7 students will be moving on to high school in grade 8. Understanding electricity and magnetism allows students to explore electives (and possible careers) based on these fundamental forces. This science topic, more than any other, serves as a clear pathway to careers in the trades. An electro ...
The Two Kinds of Electric Charge
... differential centrifugal pressure from the tiny vortices, pressing unevenly on an object or an element of electric current. There can be no other possible explanation for a force which only acts when motion occurs, and which acts at right angles to the motion. The v×H form is the basis of the convec ...
... differential centrifugal pressure from the tiny vortices, pressing unevenly on an object or an element of electric current. There can be no other possible explanation for a force which only acts when motion occurs, and which acts at right angles to the motion. The v×H form is the basis of the convec ...
electrostatics - Alfa Tutorials
... on insulating stands. When a negatively charged rod is brought near one of the spheres but without touching it, as in [b], the free electrons from the metal are repelled and drift slightly away from the rod, towards the right. This leaves a positive charge on the left sphere. This negative charge on ...
... on insulating stands. When a negatively charged rod is brought near one of the spheres but without touching it, as in [b], the free electrons from the metal are repelled and drift slightly away from the rod, towards the right. This leaves a positive charge on the left sphere. This negative charge on ...
Chapter 3 GAUSS` LAW
... that depend on the position. Vector fields can be characterized using two important concepts, namely, flux and circulation. For example, the rate of loss of water out of a draining bath tub can be related to the litres/sec flowing down the drain and the circulation or angular momentum carried away b ...
... that depend on the position. Vector fields can be characterized using two important concepts, namely, flux and circulation. For example, the rate of loss of water out of a draining bath tub can be related to the litres/sec flowing down the drain and the circulation or angular momentum carried away b ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.