Weekly Science Lesson Plans
... forms of energy (light, sound, heat, electrical, and magnetic) as the ability to cause motion or create change. 4.P.1.2 Explain how electrically charged objects push or pull on other electrically charged objects and produce motion. ...
... forms of energy (light, sound, heat, electrical, and magnetic) as the ability to cause motion or create change. 4.P.1.2 Explain how electrically charged objects push or pull on other electrically charged objects and produce motion. ...
David`s Project - The-Bobcat
... depending on what it is doing. The magnetic field attracts any type of metal or steel objects near it. ...
... depending on what it is doing. The magnetic field attracts any type of metal or steel objects near it. ...
Electricity (1)
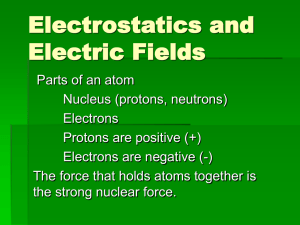
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... located on the outer edges of atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
... located on the outer edges of atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
nature phenomenon of electricity and magnetism
... 1800- Alessandro Volta made a miraculous discovery. By stringing these electrical cells together he was able to create a battery. In his honor battery power is measured in volts. 1879- Thomas Edison experimented by soaking cotton thread in carbon and used a small wire, known as a filament to conduct ...
... 1800- Alessandro Volta made a miraculous discovery. By stringing these electrical cells together he was able to create a battery. In his honor battery power is measured in volts. 1879- Thomas Edison experimented by soaking cotton thread in carbon and used a small wire, known as a filament to conduct ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.