Voltage/Current PowerPoint
... Q is doing something to the “space” around it…the force on q depends on where you put it in this “space”. If we know what a point in “space” is like, we can describe the force on some charge q in that space. As q is moved further away, what happens to the force? ...
... Q is doing something to the “space” around it…the force on q depends on where you put it in this “space”. If we know what a point in “space” is like, we can describe the force on some charge q in that space. As q is moved further away, what happens to the force? ...
Document
... a. Draw a set of plates and the field between them. b. Calculate the electric field between the plates. c. How much energy would a proton gain if it is released at the positive plate and allowed to move to the negative plate? d. How fast is the proton moving? ...
... a. Draw a set of plates and the field between them. b. Calculate the electric field between the plates. c. How much energy would a proton gain if it is released at the positive plate and allowed to move to the negative plate? d. How fast is the proton moving? ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... • The electric force between two charged particles varies directly as the product of their charges and inversely as the square of the separation distances. • force (newtons) = k x 1st charge x 2nd charge / distance2 ...
... • The electric force between two charged particles varies directly as the product of their charges and inversely as the square of the separation distances. • force (newtons) = k x 1st charge x 2nd charge / distance2 ...
Task 1
... potential energy – arise from the ____________ positions or configurations of objects. The potential energy may then be defined as the ____________ that must be done against a particular force – in these examples, gravitational, electrical or ____________ force – so as to achieve that configuration. ...
... potential energy – arise from the ____________ positions or configurations of objects. The potential energy may then be defined as the ____________ that must be done against a particular force – in these examples, gravitational, electrical or ____________ force – so as to achieve that configuration. ...
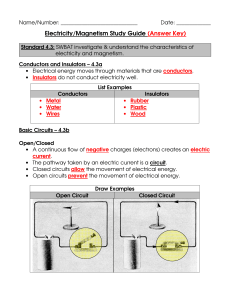
Electricity/Magnetism Study Guide (Answer Key)
... • A continuous flow of negative charges (electrons) creates an electric current. • The pathway taken by an electric current is a circuit. • Closed circuits allow the movement of electrical energy. • Open circuits prevent the movement of electrical energy. Draw Examples Open Circuit ...
... • A continuous flow of negative charges (electrons) creates an electric current. • The pathway taken by an electric current is a circuit. • Closed circuits allow the movement of electrical energy. • Open circuits prevent the movement of electrical energy. Draw Examples Open Circuit ...
File
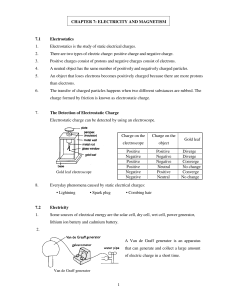
... (1) Positive charge is established by the absence of electrons, not an abundance of protons IV) Conservation and Charge Diagrams A) Charge is neither created nor destroyed B) As one object looses electrons the other in contact will have to gain the same number of electrons as lost by the first ...
... (1) Positive charge is established by the absence of electrons, not an abundance of protons IV) Conservation and Charge Diagrams A) Charge is neither created nor destroyed B) As one object looses electrons the other in contact will have to gain the same number of electrons as lost by the first ...
Unit 8: Electricity and Magnetism
... Unit Description This unit thoroughly examines the properties of static electricity, electric circuits, magnetic fields, and the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Enduring Understandings All particles of matter contain energy. Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric fo ...
... Unit Description This unit thoroughly examines the properties of static electricity, electric circuits, magnetic fields, and the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Enduring Understandings All particles of matter contain energy. Magnetic forces are very closely related to electric fo ...
Chemistry 221
... a) For the ionic compound, if the negative ion has a –1 charge, what is the charge of the positive ion? b) Suggest two ions that might form this compound and draw a microscopic sketch of several formula units of this compound. c) How would a sketch representing the molecular compound differ from the ...
... a) For the ionic compound, if the negative ion has a –1 charge, what is the charge of the positive ion? b) Suggest two ions that might form this compound and draw a microscopic sketch of several formula units of this compound. c) How would a sketch representing the molecular compound differ from the ...
Electricity - WordPress.com
... In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produ ...
... In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produ ...
Electric Energy and Current Chapter 17
... done to move a charge. Many different names- Potential, Potential Difference, Voltage, Emf. Symbol is V, units are V = J/C. DV = DPE/q ...
... done to move a charge. Many different names- Potential, Potential Difference, Voltage, Emf. Symbol is V, units are V = J/C. DV = DPE/q ...
Static electricity - Ms. Chelsea Gaudet
... will be asked to rub the balloon against their hair for 30 seconds and then to put the balloon close to the can. Students, before this experiment, will write a prediction in their science journal. After completing the experiment, students will then record their observations. Did the can roll when yo ...
... will be asked to rub the balloon against their hair for 30 seconds and then to put the balloon close to the can. Students, before this experiment, will write a prediction in their science journal. After completing the experiment, students will then record their observations. Did the can roll when yo ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.