r - Personal.psu.edu
... same as the field and potential obtained from a point charge that has the same charge ...
... same as the field and potential obtained from a point charge that has the same charge ...
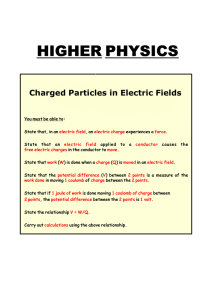
charged particles in electric fields
... charged particle (such as a proton) would accelerate if it was placed in the electric field. A negatively charged particle (such as an electron) would accelerate in the opposite direction to the arrow heads. ...
... charged particle (such as a proton) would accelerate if it was placed in the electric field. A negatively charged particle (such as an electron) would accelerate in the opposite direction to the arrow heads. ...
p. 119 Energy 7th Grade ISN
... Static Electricity notes Static electricity—the build up of charges on an object that do not flow continuously. Charges: 1. like charges---repel (+ & + or - & -) 2. unlike charges—attract (+ & -) 3. When negatively charged object and positively charged object are brought together, electrons transfer ...
... Static Electricity notes Static electricity—the build up of charges on an object that do not flow continuously. Charges: 1. like charges---repel (+ & + or - & -) 2. unlike charges—attract (+ & -) 3. When negatively charged object and positively charged object are brought together, electrons transfer ...
Static Electric Fields
... 1. Define Scalar and Vector and give examples. A scalar is a quantity that is completely characterized by its magnitude and algebraic sign. Eg. Mass, Work, etc. A Vector is a quantity that is completely characterized by its magnitude and direction. Eg. Force, Displacement, etc 2. Give the types of v ...
... 1. Define Scalar and Vector and give examples. A scalar is a quantity that is completely characterized by its magnitude and algebraic sign. Eg. Mass, Work, etc. A Vector is a quantity that is completely characterized by its magnitude and direction. Eg. Force, Displacement, etc 2. Give the types of v ...
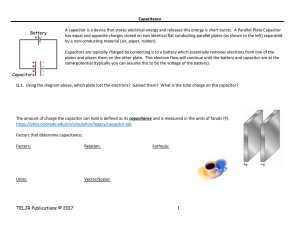
Gauss`s law
... For which of these closed surfaces (a, b, c, d), will the flux of the electric field, produced by the charge +2q, be zero? ...
... For which of these closed surfaces (a, b, c, d), will the flux of the electric field, produced by the charge +2q, be zero? ...
Physics in the Enlightenment
... "I am going to tell you about a new but terrible experiment which I advise you not to try yourself, nor would I, who have experienced it and survived by the grace of God, do it again for all the kingdom of France. I was making some investigations on the force of electricity; for this purpose I had ...
... "I am going to tell you about a new but terrible experiment which I advise you not to try yourself, nor would I, who have experienced it and survived by the grace of God, do it again for all the kingdom of France. I was making some investigations on the force of electricity; for this purpose I had ...
nvest ig at io n - Creation Studies Institute
... Static electricity and magnetism had long been suspected as being connected in some way. They both had invisible fields around them. They both obeyed the rule of “likes repel and unalikes attract.” Until 1820, no one had found a way in which electricity and magnetism were connected. The discovery th ...
... Static electricity and magnetism had long been suspected as being connected in some way. They both had invisible fields around them. They both obeyed the rule of “likes repel and unalikes attract.” Until 1820, no one had found a way in which electricity and magnetism were connected. The discovery th ...
Teacher Guide: UDL Electricity
... a piece of wool you change the charge of the balloon. You can see the results when you take the charged balloon and put it next to some ones hair and their hair will stick out. Another property of charged objects is how they attract or repel. If two objects have the same charge (+ +; - -) they will ...
... a piece of wool you change the charge of the balloon. You can see the results when you take the charged balloon and put it next to some ones hair and their hair will stick out. Another property of charged objects is how they attract or repel. If two objects have the same charge (+ +; - -) they will ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.