CHEM 210 Chapter 5 Wrap-up
... R impurity will ‘cancel’ the rotation of an equal amount of S: • A sample with an ee of 50% S is actually 50% pure S and 50% racemic R/S. • The total S enantiomer in the sample is actually ...
... R impurity will ‘cancel’ the rotation of an equal amount of S: • A sample with an ee of 50% S is actually 50% pure S and 50% racemic R/S. • The total S enantiomer in the sample is actually ...
Role of Color Interference on the Insect`s Cuticle Coloration
... Abstract: Interference colors result from the reflection of light from a series of neighboring interfaces that are separated by distances comparable with a quarter of the wavelength of light. .Interference colors are common in some adults of Lepidoptera insects. The integument layers producing inter ...
... Abstract: Interference colors result from the reflection of light from a series of neighboring interfaces that are separated by distances comparable with a quarter of the wavelength of light. .Interference colors are common in some adults of Lepidoptera insects. The integument layers producing inter ...
OPTICAL CONSTANTS OF URANIUM NITRIDE IN THE XUV
... March of 2000 the IMAGE (Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration) Satellite was launched carrying three multilayer mirrors made by the XUV optics group at Brigham Young University. These mirrors have been used for imaging the magnetosphere of the earth [1]. Astronomers are also interest ...
... March of 2000 the IMAGE (Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration) Satellite was launched carrying three multilayer mirrors made by the XUV optics group at Brigham Young University. These mirrors have been used for imaging the magnetosphere of the earth [1]. Astronomers are also interest ...
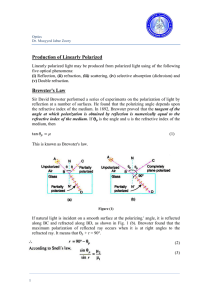
Production of Linearly Polarized Brewster`s Law
... plane polarized light wave is incident on a birefringent crystal such that its electric vector makes an angle with the optic axis, then the polarized wave splits into two polarized waves namely e-ray and o-ray. Let us consider the particular case of a slice of a positive crystal where the optic axis ...
... plane polarized light wave is incident on a birefringent crystal such that its electric vector makes an angle with the optic axis, then the polarized wave splits into two polarized waves namely e-ray and o-ray. Let us consider the particular case of a slice of a positive crystal where the optic axis ...
System for observing interference phenomenon: In the previous
... of amplitude. The parallel light rays from a monochromatic source are incident on beams splitter (glass plate) G1 which is semi silvered on its back surface and mounted at 45° to the axis. Light ray incident ‘O' is refracted into the glass plate and reaches point A , where where it is partially refl ...
... of amplitude. The parallel light rays from a monochromatic source are incident on beams splitter (glass plate) G1 which is semi silvered on its back surface and mounted at 45° to the axis. Light ray incident ‘O' is refracted into the glass plate and reaches point A , where where it is partially refl ...
Modern battlefield and new materials for eyes protection
... factor by which the optical filter reduces light in the specified wavelength range power. For example, eyewear with OD 3 reduces the beam power by a factor of 1000. In addition to the optical density, sufficient to reduce beam power below the maximum permissible exposure, the laser eyewear can be us ...
... factor by which the optical filter reduces light in the specified wavelength range power. For example, eyewear with OD 3 reduces the beam power by a factor of 1000. In addition to the optical density, sufficient to reduce beam power below the maximum permissible exposure, the laser eyewear can be us ...
Display
... Time-sequential method Liquid crystal shutter glass Battery is needed One of lens comes to dark. ...
... Time-sequential method Liquid crystal shutter glass Battery is needed One of lens comes to dark. ...
MINIATURIZED FLUORESCENCE EXCITATION PLATFORM WITH OPTICAL FIBER FOR BIO-DETECTION CHIPS
... into the microchannel by a single-mode fiber guide on top of the microchannel. A fiber terminated waveguide was used to collect fluorescence light. Optical losses between waveguides and fibers may result in low power efficiency. Camou et al. tried to use thick film process and PDMS replication metho ...
... into the microchannel by a single-mode fiber guide on top of the microchannel. A fiber terminated waveguide was used to collect fluorescence light. Optical losses between waveguides and fibers may result in low power efficiency. Camou et al. tried to use thick film process and PDMS replication metho ...
Optics 101 for non-optical engineers
... Abbe Constant (V-Value) = The constant of an optical medium that describes the ratio of its refractivity to it dispersion. A high V-Value indicates more nearly equal refraction at all wavelengths ...
... Abbe Constant (V-Value) = The constant of an optical medium that describes the ratio of its refractivity to it dispersion. A high V-Value indicates more nearly equal refraction at all wavelengths ...
24.1 - 24.4
... Wave reach point P either by a direct path or by reflection The reflected ray can be treated as a ray from the source S’ behind the mirror April 2, 2009 ...
... Wave reach point P either by a direct path or by reflection The reflected ray can be treated as a ray from the source S’ behind the mirror April 2, 2009 ...
Polarization of light on reflection by some natural
... forthwith have been drawn on the basis of the entire set of data. The measured values of the polarization of reflected light corresponding to four different states of polarization of the illuminating radiation are shown in figures 4, 5, 6 and 7. Examples of the variation of the normalized intensity, ...
... forthwith have been drawn on the basis of the entire set of data. The measured values of the polarization of reflected light corresponding to four different states of polarization of the illuminating radiation are shown in figures 4, 5, 6 and 7. Examples of the variation of the normalized intensity, ...
WHAT IS THE OPTICAL COMPUTING?
... Wavelength division multiplexing is a method of sending many different wavelengths down the same optical fiber. ...
... Wavelength division multiplexing is a method of sending many different wavelengths down the same optical fiber. ...
Welcome to BME 495: Advanced Physical and Applied Optics
... This course will provide a rigorous introduction to the theory and applications of the state-of-the-art physical optics. Coverage includes wave optics, Gaussian optics, Fourier optics, light propagation in continuous and turbid media, light scattering, statistical optics, and fiber optics. The cours ...
... This course will provide a rigorous introduction to the theory and applications of the state-of-the-art physical optics. Coverage includes wave optics, Gaussian optics, Fourier optics, light propagation in continuous and turbid media, light scattering, statistical optics, and fiber optics. The cours ...
DOC - math for college
... tend to high albedo. Note that the registered intensity in the image does not depend on the camera location because a Lambertian surface reflects light equally in all directions. This would not be true for specular surfaces and the corresponding image formation equation would involve the viewing dir ...
... tend to high albedo. Note that the registered intensity in the image does not depend on the camera location because a Lambertian surface reflects light equally in all directions. This would not be true for specular surfaces and the corresponding image formation equation would involve the viewing dir ...
Laser Tweezers
... looking through his microscope onto the miniature world below. His sample, which had a laser focused on it, was behaving in a way that he did not expect. To his surprise, he noticed that some of the particles in his sample began to "stick" to the laser beam and follow it around as the laser tracked ...
... looking through his microscope onto the miniature world below. His sample, which had a laser focused on it, was behaving in a way that he did not expect. To his surprise, he noticed that some of the particles in his sample began to "stick" to the laser beam and follow it around as the laser tracked ...
untitled - PhysRevLett.111.243901
... the ensemble averaged intensity distribution at the target arrival time is plotted in Fig. 4(c). The peak intensity after the optimization is about 2 orders of magnitude higher than that before the optimization. Moreover, the observed intensity in the region surrounding the target position also incr ...
... the ensemble averaged intensity distribution at the target arrival time is plotted in Fig. 4(c). The peak intensity after the optimization is about 2 orders of magnitude higher than that before the optimization. Moreover, the observed intensity in the region surrounding the target position also incr ...
VII-I
... mirrors or they seem to come from a virtual focal point behind the mirror, if the mirror is convex. • Optical properties of ideal mirror are described by one parameter only, the focal length f, the distance of the focal point from the mirrors center. ...
... mirrors or they seem to come from a virtual focal point behind the mirror, if the mirror is convex. • Optical properties of ideal mirror are described by one parameter only, the focal length f, the distance of the focal point from the mirrors center. ...
full article pdf
... However, actual inspection for digs was visually performed with reference to a standard, rather than by physical measurement of dig dimensions. Because MIL-O-13830 specified scratch visibility, as opposed to actual physical dimensions, the viewing conditions for testing were also spelled out. These ...
... However, actual inspection for digs was visually performed with reference to a standard, rather than by physical measurement of dig dimensions. Because MIL-O-13830 specified scratch visibility, as opposed to actual physical dimensions, the viewing conditions for testing were also spelled out. These ...
Two-photon ablation with 1278nm laser radiation
... and this can be done by keeping single-photon absorption to a minimum. Hence, it is of great importance to select the wavelength of the laser with care, taking into account single and multi-photon cross sections plus the dispersion characteristics of the optical system. In multi-photon interactions, ...
... and this can be done by keeping single-photon absorption to a minimum. Hence, it is of great importance to select the wavelength of the laser with care, taking into account single and multi-photon cross sections plus the dispersion characteristics of the optical system. In multi-photon interactions, ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... Specimen induced spherical aberrations are known to severely degrade the point spread function (PSF) of high numerical aperture (NA) systems in imaging and focusing applications. A planar refractive index mismatch is introduced by a suspension medium, a glass cover slide or imaging into a thick tran ...
... Specimen induced spherical aberrations are known to severely degrade the point spread function (PSF) of high numerical aperture (NA) systems in imaging and focusing applications. A planar refractive index mismatch is introduced by a suspension medium, a glass cover slide or imaging into a thick tran ...
lecture 7 OPL and interference
... 2t is split into 3t and 3r; at this point, all these rays are in phase (no shift high to low η). 3r reflects back as 4 within polymer, its phase then changes relative to 2t. 3t + 4 = resultant, constructive + or destructive - depends on the λ. So to solve this for max. constructive transmitted inter ...
... 2t is split into 3t and 3r; at this point, all these rays are in phase (no shift high to low η). 3r reflects back as 4 within polymer, its phase then changes relative to 2t. 3t + 4 = resultant, constructive + or destructive - depends on the λ. So to solve this for max. constructive transmitted inter ...
Stopped light with storage times greater than one second using EIT
... are close in frequency, in this configuration, the wavevector mismatch is typically less than 1 cm−1 . A consequence of this co-propagating operation is that it is difficult to separate the probe and the coupling beam. In a solid-state system, where the optical centers are locked in a crystal lattic ...
... are close in frequency, in this configuration, the wavevector mismatch is typically less than 1 cm−1 . A consequence of this co-propagating operation is that it is difficult to separate the probe and the coupling beam. In a solid-state system, where the optical centers are locked in a crystal lattic ...
supporting material
... formation technique not only maintains the SNR when super-resolution photon position measurements are used, but actually increases this parameter. Similar increases in SNR could only be observed in COP images after low-pass filtering, which suppressed noise by smoothing pixel transitions, but also ...
... formation technique not only maintains the SNR when super-resolution photon position measurements are used, but actually increases this parameter. Similar increases in SNR could only be observed in COP images after low-pass filtering, which suppressed noise by smoothing pixel transitions, but also ...
CC_A3_C2_photo2_old
... • Replace the mercury vapor lamp an excimer laser source with shorter wavelength emission – ArF – 193 nM – Shorter wavelength than so-called “deep UV” peak of 248nM – F2 Laser – Low output but at 157nM ...
... • Replace the mercury vapor lamp an excimer laser source with shorter wavelength emission – ArF – 193 nM – Shorter wavelength than so-called “deep UV” peak of 248nM – F2 Laser – Low output but at 157nM ...
Three models of light
... light travels in straight lines. • Each point on an object scatters light, spraying it off in all directions. • A polished surface reflects rays back again according to the rule: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
... light travels in straight lines. • Each point on an object scatters light, spraying it off in all directions. • A polished surface reflects rays back again according to the rule: The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.