A Case Report
... base of the fifth metatarsal along with the peroneus brevis. Further, it also provided small fibrous extensions to the shaft of the fifth metatarsal bone and a large extension to the base of the 4th metatarsal bone. Awareness of such variations in the insertion pattern of this muscle is of importanc ...
... base of the fifth metatarsal along with the peroneus brevis. Further, it also provided small fibrous extensions to the shaft of the fifth metatarsal bone and a large extension to the base of the 4th metatarsal bone. Awareness of such variations in the insertion pattern of this muscle is of importanc ...
Microanatomy and Surgical Approaches to the
... of the temporal bone and greater wing of the sphenoid bone that is sitting deep to the ramus of the mandible. The principal structure to understanding its relationships is the lateral pterygoid muscle. Other important structures are the medial pterygoid muscle, the maxillary artery, the pterygoid ve ...
... of the temporal bone and greater wing of the sphenoid bone that is sitting deep to the ramus of the mandible. The principal structure to understanding its relationships is the lateral pterygoid muscle. Other important structures are the medial pterygoid muscle, the maxillary artery, the pterygoid ve ...
Reconstruction Principles and flaps
... Diagrammatic representation of the Buccal and FAMM flaps. The Buccal flap is supplied by the buccal artery (Ba) of the internal maxillary artery and the posterior buccal branch (Pb) of the facial artery. The FAMM flap is supplied by the distal portion of the facial artery (Fa) through the anterior ...
... Diagrammatic representation of the Buccal and FAMM flaps. The Buccal flap is supplied by the buccal artery (Ba) of the internal maxillary artery and the posterior buccal branch (Pb) of the facial artery. The FAMM flap is supplied by the distal portion of the facial artery (Fa) through the anterior ...
15-Urogenital Traiangle2009-04-20 01:576.7 MB
... The vagina not only is the female genital canal but also serves as the excretory duct for the menstrual blood & forms part of the birth canal. This muscular tube extends upward and backward between the vulva and the uterus. It measures about 3 in. (8 cm) long. The cervix of the uterus pierces its an ...
... The vagina not only is the female genital canal but also serves as the excretory duct for the menstrual blood & forms part of the birth canal. This muscular tube extends upward and backward between the vulva and the uterus. It measures about 3 in. (8 cm) long. The cervix of the uterus pierces its an ...
15-Urogenital Traiangle2009-04-18 05:435.9 MB
... The vagina not only is the female genital canal but also serves as the excretory duct for the menstrual blood & forms part of the birth canal. ...
... The vagina not only is the female genital canal but also serves as the excretory duct for the menstrual blood & forms part of the birth canal. ...
Myology 肌学
... Absent in about 4-5cm below the umbilicus, where aponeuroses of all three muscles form anterior layer the lower free border named arcuate line Below this line rectus abdominis in contact with transverse fascia ...
... Absent in about 4-5cm below the umbilicus, where aponeuroses of all three muscles form anterior layer the lower free border named arcuate line Below this line rectus abdominis in contact with transverse fascia ...
The rectum
... For this reason, surgical ablation of malignant disease concentrates mainly on achieving wide clearance of proximal lymph nodes. However, if the usual upwards routes are blocked, flow can reverse, and it is then possible to find metastatic lymph nodes on the side walls of the pelvis (along the middl ...
... For this reason, surgical ablation of malignant disease concentrates mainly on achieving wide clearance of proximal lymph nodes. However, if the usual upwards routes are blocked, flow can reverse, and it is then possible to find metastatic lymph nodes on the side walls of the pelvis (along the middl ...
Dissection of the Gluteal Region
... The medial sural cutaneous nerve descends between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle and is usually joined by the peroneal communicating branch of the common peroneal nerve to form the sural nerve. ...
... The medial sural cutaneous nerve descends between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle and is usually joined by the peroneal communicating branch of the common peroneal nerve to form the sural nerve. ...
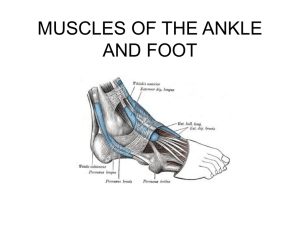
THE ANKLE AND FOOT
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
... • Origin: upper 2/3 of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula • Insertion: posterior surface of the calcaneus via Achilles tendon • Action: – plantar flexion • Superficial posterior compartment ...
Chapter 11, Part 1 Muscles of the head and Neck
... • Anterolateral neck muscles flex the neck • Scalene muscles (anterior, middle, and posterior) • Originate from transverse processes of C2 to C7 • Insert onto ribs 1 and 2 • Elevate ribs 1 and 2 during inhalation ...
... • Anterolateral neck muscles flex the neck • Scalene muscles (anterior, middle, and posterior) • Originate from transverse processes of C2 to C7 • Insert onto ribs 1 and 2 • Elevate ribs 1 and 2 during inhalation ...
Nemertini from the Coasts of Kyusyu (With 18 Text
... frontal organs are ah3E'llL Th2 C:2plialic: fur;'ows arc shallow in transverse section. The dorsal g;UgliOll is cli\'ided i;110 two lobes, of which the small dorsal one immediately ends freely, while the \'entral one extends posteriorly into the cerebral sc~nse organ. The median dorsal nerve extends ...
... frontal organs are ah3E'llL Th2 C:2plialic: fur;'ows arc shallow in transverse section. The dorsal g;UgliOll is cli\'ided i;110 two lobes, of which the small dorsal one immediately ends freely, while the \'entral one extends posteriorly into the cerebral sc~nse organ. The median dorsal nerve extends ...
MORPHOLOGY OF KNEE JOINT-CLASS-AVES-GENUS
... produces extension of the knee joint and also extension of the foot and toes. Similar finding were observed by Vandon Berge and Dye Scoti in chicken. But in the humans beings, it is observed that the origin of the extensor digitorum longus slips down the fermur. It originates from the lateral condyl ...
... produces extension of the knee joint and also extension of the foot and toes. Similar finding were observed by Vandon Berge and Dye Scoti in chicken. But in the humans beings, it is observed that the origin of the extensor digitorum longus slips down the fermur. It originates from the lateral condyl ...
Accessory belly of the first lumbrical – a case report
... Much of the versatility of the human hand depends upon its intrinsic musculature. The lumbrical muscles constitute an important part of the intrinsic musculature of the hands. Lumbricals are the four small intrinsic muscles of the hand. They arise from the four tendons of flexor digitorum profundus ...
... Much of the versatility of the human hand depends upon its intrinsic musculature. The lumbrical muscles constitute an important part of the intrinsic musculature of the hands. Lumbricals are the four small intrinsic muscles of the hand. They arise from the four tendons of flexor digitorum profundus ...
The functional anatomy of the rodent larynx in relation to audible
... The ultrasonic cries of rodents may be of high intensity and are often pure tones varying in frequency from 20-100 kHz or more from species to species. Rapid frequency and amplitude changes may occur during a cry and often instantaneous frequency and amplitude jumps occur with no obvious harmonic re ...
... The ultrasonic cries of rodents may be of high intensity and are often pure tones varying in frequency from 20-100 kHz or more from species to species. Rapid frequency and amplitude changes may occur during a cry and often instantaneous frequency and amplitude jumps occur with no obvious harmonic re ...
An anomalous insertion fascicle of the caput laterale of the triceps
... al to the groove of the radial nerve. The line of origin leads from the insertion of the teres minor as far as the humeral groove for the radial nerve distally and from the aponeurotic arch formed by the lateral intermuscular septum as it crosses the radial groove. The muscle fibers of the caput lat ...
... al to the groove of the radial nerve. The line of origin leads from the insertion of the teres minor as far as the humeral groove for the radial nerve distally and from the aponeurotic arch formed by the lateral intermuscular septum as it crosses the radial groove. The muscle fibers of the caput lat ...
brachial plexus
... the "chimney" effect as local anesthetic is forced to spread up between the anterior and middle scalene muscles, unable to go down because the first rib is in the way. ...
... the "chimney" effect as local anesthetic is forced to spread up between the anterior and middle scalene muscles, unable to go down because the first rib is in the way. ...
anterior trunk
... • The mandibular nerve is formed in the infratemporal fossa by the union of the sensory and motor roots immediately after they leave the skull at the foramen ovale, within the foramen ovale the motor root (or roots) lie posteromedially to the sensory root and these root are accompanied by emissary ...
... • The mandibular nerve is formed in the infratemporal fossa by the union of the sensory and motor roots immediately after they leave the skull at the foramen ovale, within the foramen ovale the motor root (or roots) lie posteromedially to the sensory root and these root are accompanied by emissary ...
Skeletal muscle

Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue which is under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons.Skeletal muscle is made up of individual muscle cells or myocytes, known as muscle fibers. They are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts (a type of embryonic progenitor cell that gives rise to a muscle cell) in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibres are cylindrical, and multinucleated.Muscle fibers are in turn composed of myofibrils. The myofibrils are composed of actin and myosin filaments, repeated in units called sarcomeres, the basic functional units of the muscle fiber. The sarcomere is responsible for the striated appearance of skeletal muscle, and forms the basic machinery necessary for muscle contraction. The term muscle refers to multiple bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. All muscles also contain connective tissue arranged in layers of fasciae. Each muscle is enclosed in a layer of fascia; each fascicle is enclosed by a layer of fascia and each individual muscle fiber is also enclosed in a layer of fascia.