Document
... or extensions from the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris to the fourth or more commonly the fifth metacarpal bone; duplication of the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon; a fibrous or muscular extension from the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris to the carpal ligaments; the flexor carpi ulnaris diving ori ...
... or extensions from the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris to the fourth or more commonly the fifth metacarpal bone; duplication of the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon; a fibrous or muscular extension from the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris to the carpal ligaments; the flexor carpi ulnaris diving ori ...
Trajectory of the main sensory and motor branches of the lumbar
... Object. The minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach is increasingly used to treat various spinal disorders. Accessing the retroperitoneal space and traversing the abdominal wall poses a risk of injury to the major nervous structures and adds significant morbidity to the proced ...
... Object. The minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas approach is increasingly used to treat various spinal disorders. Accessing the retroperitoneal space and traversing the abdominal wall poses a risk of injury to the major nervous structures and adds significant morbidity to the proced ...
Bones and Muscles - An Illustrated Anatomy
... the kind used to harness oxen. Maxilla is from the Latin mala meaning jaw, particularly the upper jaw. Mandible derives from the Latin mandibula, which stems from mandare meaning to chew and pertains particularly to the lower jaw, which has most of the chewing motion. Parietal is from the Latin pari ...
... the kind used to harness oxen. Maxilla is from the Latin mala meaning jaw, particularly the upper jaw. Mandible derives from the Latin mandibula, which stems from mandare meaning to chew and pertains particularly to the lower jaw, which has most of the chewing motion. Parietal is from the Latin pari ...
SKELETON, LATERAL VIEW
... Plate 14: MUSCULATURE OF BACK, POSTERIOR VIEW 3rd occipital nerve dorsal ramus of greater occipital nerve (C2) lesser occipital nerve (C2,C3) greater auricular nerve (C2,C3) medial cutaneous branches of dorsal rami of C4–C8, spinal nerves medial cutaneous branches of dorsal rami of T1–T6 spinal ner ...
... Plate 14: MUSCULATURE OF BACK, POSTERIOR VIEW 3rd occipital nerve dorsal ramus of greater occipital nerve (C2) lesser occipital nerve (C2,C3) greater auricular nerve (C2,C3) medial cutaneous branches of dorsal rami of C4–C8, spinal nerves medial cutaneous branches of dorsal rami of T1–T6 spinal ner ...
ARTICULAR SYSTEM
... The temporomandibular joint, articulatio temporomandibularis, is paired and formed by the articulation of the head of the mandible (ellipsoid in shape) with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone. It belongs to the group of the bicondylar, combined joints. The articular surfaces are incongruent. ...
... The temporomandibular joint, articulatio temporomandibularis, is paired and formed by the articulation of the head of the mandible (ellipsoid in shape) with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone. It belongs to the group of the bicondylar, combined joints. The articular surfaces are incongruent. ...
Laryngeal Anatomy - Dr.Hani Shaker`s Website
... 1) Thyrohyoid approximation, 2) Hyoid protraction and 3) Hyolaryngeal elevation. The muscles responsible for shortening the pharynx mentioned above (Salpingopharyngeus, Palatopharyngeus and Stylopharyngeus) partly contribute to hyolaryngeal excursion, but the primary movers for this movement are t ...
... 1) Thyrohyoid approximation, 2) Hyoid protraction and 3) Hyolaryngeal elevation. The muscles responsible for shortening the pharynx mentioned above (Salpingopharyngeus, Palatopharyngeus and Stylopharyngeus) partly contribute to hyolaryngeal excursion, but the primary movers for this movement are t ...
Thoracic wall, abdominal region, muscles
... The diaphragm is a shared wall (actually floor/ceiling) separating the thorax and abdomen. Although it has functions related to both compartments of the trunk, its most important (vital) function is serving as the primary muscle of inspiration. Accessory muscles of respiration The movement of the di ...
... The diaphragm is a shared wall (actually floor/ceiling) separating the thorax and abdomen. Although it has functions related to both compartments of the trunk, its most important (vital) function is serving as the primary muscle of inspiration. Accessory muscles of respiration The movement of the di ...
The mandibular nerve
... mandibular molar and in the buccal mucosa , these being post-ganglionic fibres from the otic ganglion. The buccal branch of the mandibular nerve may be seen to 'anastomose' with the buccal branches of the facial nerve. The auriculotemporal nerve This is the first branch of the posterior of the mand ...
... mandibular molar and in the buccal mucosa , these being post-ganglionic fibres from the otic ganglion. The buccal branch of the mandibular nerve may be seen to 'anastomose' with the buccal branches of the facial nerve. The auriculotemporal nerve This is the first branch of the posterior of the mand ...
- Nottingham SCRUBS
... B? – Pyramidalis What is the innervation of the rectus abdominis? Anterior rami of T6T12 spinal nerves ...
... B? – Pyramidalis What is the innervation of the rectus abdominis? Anterior rami of T6T12 spinal nerves ...
Submandibular gland excision - Vula
... behind the posterior belly of digastric (removed), and gives rise to a few branches including the submental artery The submental flap is based on the submental branch of the facial artery which courses along the inferior, inner margin of the mandible (Figures 8). The mylohyoid artery and vein are en ...
... behind the posterior belly of digastric (removed), and gives rise to a few branches including the submental artery The submental flap is based on the submental branch of the facial artery which courses along the inferior, inner margin of the mandible (Figures 8). The mylohyoid artery and vein are en ...
- European Journal of Radiology
... The high resolution and dynamic capability of ultrasound make it an excellent tool for assessment of superficial structures. The ligaments, tendons, and nerves about the elbow can be fully evaluated with ultrasound. The medial collateral ligament consists of an anterior and posterior band that can ea ...
... The high resolution and dynamic capability of ultrasound make it an excellent tool for assessment of superficial structures. The ligaments, tendons, and nerves about the elbow can be fully evaluated with ultrasound. The medial collateral ligament consists of an anterior and posterior band that can ea ...
A sensate lateral sural artery muscle perforator flap
... in either case at about the level of the knee joint (21,22). Anomalies are not uncommon, as for example Potparic found a double medial sural artery in 15% of cadavers, and sometimes even more (21). The external diameter of either artery at its origin is approximately 3 mm.; and there are usually 2 v ...
... in either case at about the level of the knee joint (21,22). Anomalies are not uncommon, as for example Potparic found a double medial sural artery in 15% of cadavers, and sometimes even more (21). The external diameter of either artery at its origin is approximately 3 mm.; and there are usually 2 v ...
- Wiley Online Library
... portion of the temporalis insertion (Fig. 3B,D). In lateral view, the distal-most portion of the deep masseter insertion occurs immediately dorsal to the insertion for the superficial masseter, and follows a similar, but dorsally placed, curvilinear path (Figs. 2 and 3H). Unlike the superficial mass ...
... portion of the temporalis insertion (Fig. 3B,D). In lateral view, the distal-most portion of the deep masseter insertion occurs immediately dorsal to the insertion for the superficial masseter, and follows a similar, but dorsally placed, curvilinear path (Figs. 2 and 3H). Unlike the superficial mass ...
Transversus Abdominis Plane (TAP) block - e-safe
... INDICATIONS FOR TAP BLOCK The TAP block can be used as part of an analgesic regimen for abdominal surgery. Initial studies were able to demonstrate blocks extending from T7-L1 using bilateral injections[4]. Subsequent studies have been unable to reproduce these findings with most studies achieving u ...
... INDICATIONS FOR TAP BLOCK The TAP block can be used as part of an analgesic regimen for abdominal surgery. Initial studies were able to demonstrate blocks extending from T7-L1 using bilateral injections[4]. Subsequent studies have been unable to reproduce these findings with most studies achieving u ...
Femoral nerve.
... Action: The iliopsoas flexes the thigh on the trunk at the hip joint; or if the thigh is fixed, it flexes the trunk on the thigh; it also medially rotates the thigh. ...
... Action: The iliopsoas flexes the thigh on the trunk at the hip joint; or if the thigh is fixed, it flexes the trunk on the thigh; it also medially rotates the thigh. ...
Some features in the anatomy and later development of the head of
... is continued back to suture with the lateral-down-turned edge of the basiocCipital bone. The pterygoid plates, as they extend upward and backward from the hamular process and palatine lamina, arch inward, medially. This is more marked in the internal plate than in the external, and more pronounced p ...
... is continued back to suture with the lateral-down-turned edge of the basiocCipital bone. The pterygoid plates, as they extend upward and backward from the hamular process and palatine lamina, arch inward, medially. This is more marked in the internal plate than in the external, and more pronounced p ...
PDF - Florida Museum of Natural History
... IV-1.-The fibers of this series begin near the, medio-anterior dorsal surface of the ~ projected anterior upper edge of the neural arch. The fibers thence continue anteriorly, connecting to the posterior surface of the entire length of each of the arms of the V-shaped alliform processes (Figure 1). ...
... IV-1.-The fibers of this series begin near the, medio-anterior dorsal surface of the ~ projected anterior upper edge of the neural arch. The fibers thence continue anteriorly, connecting to the posterior surface of the entire length of each of the arms of the V-shaped alliform processes (Figure 1). ...
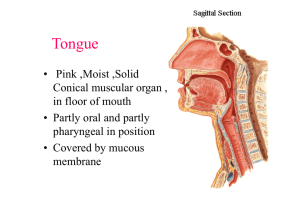
Tongue
... • Utilised in gestures and postures of facial expression • Thermo – regulation in lower animals ...
... • Utilised in gestures and postures of facial expression • Thermo – regulation in lower animals ...
Tongue
... • Utilised in gestures and postures of facial expression • Thermo – regulation in lower animals ...
... • Utilised in gestures and postures of facial expression • Thermo – regulation in lower animals ...
Selective Neck Dissection - Vula
... retropharyngeal) or non-lymphatic structures (skin, muscle, nerve, blood vessels etc.) not usually included in a comprehensive neck dissection. It has been proposed that neck dissections be more logically and precisely described and classified by naming the structures and the nodal levels that have ...
... retropharyngeal) or non-lymphatic structures (skin, muscle, nerve, blood vessels etc.) not usually included in a comprehensive neck dissection. It has been proposed that neck dissections be more logically and precisely described and classified by naming the structures and the nodal levels that have ...
Skeletal muscle

Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue which is under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons.Skeletal muscle is made up of individual muscle cells or myocytes, known as muscle fibers. They are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts (a type of embryonic progenitor cell that gives rise to a muscle cell) in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibres are cylindrical, and multinucleated.Muscle fibers are in turn composed of myofibrils. The myofibrils are composed of actin and myosin filaments, repeated in units called sarcomeres, the basic functional units of the muscle fiber. The sarcomere is responsible for the striated appearance of skeletal muscle, and forms the basic machinery necessary for muscle contraction. The term muscle refers to multiple bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. All muscles also contain connective tissue arranged in layers of fasciae. Each muscle is enclosed in a layer of fascia; each fascicle is enclosed by a layer of fascia and each individual muscle fiber is also enclosed in a layer of fascia.