Waveguide electro-optic modulation in micro-engineered
... to L , similar to the switching voltage (Vπ ), so that a tradeoff exists between Vπ and BW and the ratio BW/Vπ is used as a figure of merit. To obtain improved efficiency (increase in BW/Vπ ), better coupling between the microwave and optical fields is required. Different solutions have been propose ...
... to L , similar to the switching voltage (Vπ ), so that a tradeoff exists between Vπ and BW and the ratio BW/Vπ is used as a figure of merit. To obtain improved efficiency (increase in BW/Vπ ), better coupling between the microwave and optical fields is required. Different solutions have been propose ...
Damping rates of the atomic velocity in Sisyphus cooling
... have been compared and shown to lead to the same values for the friction coefficients. Also for the present choice of interaction parameters, we found that the two methods lead to values of αj in excellent agreement [23]. These values are shown in Fig. 5 as functions of Γ′0 for different values of t ...
... have been compared and shown to lead to the same values for the friction coefficients. Also for the present choice of interaction parameters, we found that the two methods lead to values of αj in excellent agreement [23]. These values are shown in Fig. 5 as functions of Γ′0 for different values of t ...
Label-free super-resolution imaging of adenoviruses by submerged
... where dmin is the diffraction-limited optical resolution, l is the optical wavelength and NA is the numerical aperture of the microscope lens. For the optical microscopes used in this work, the theoretical diffraction limit resolutions of the light microscopes used in air for white light illuminatio ...
... where dmin is the diffraction-limited optical resolution, l is the optical wavelength and NA is the numerical aperture of the microscope lens. For the optical microscopes used in this work, the theoretical diffraction limit resolutions of the light microscopes used in air for white light illuminatio ...
Confocal Microscopy - Emory Physics
... to drop to a lower energy level (the second black line). If the surrounding molecules are not able to accept the larger energy difference needed to further lower the molecule to its ground state, it may undergo spontaneous emission, thereby losing the remaining energy, by emitting light of a longer ...
... to drop to a lower energy level (the second black line). If the surrounding molecules are not able to accept the larger energy difference needed to further lower the molecule to its ground state, it may undergo spontaneous emission, thereby losing the remaining energy, by emitting light of a longer ...
5377 17paper
... be designed so that it is most sensitive to particular aberration types and order. Rather than spatially, it is convenient to examine this object structure in the frequency domain. The idea is to find the optimum linear combination of features that samples the entire pupil. As an example, Figure 2(a ...
... be designed so that it is most sensitive to particular aberration types and order. Rather than spatially, it is convenient to examine this object structure in the frequency domain. The idea is to find the optimum linear combination of features that samples the entire pupil. As an example, Figure 2(a ...
characterisation of vibration isolators using vibration test data
... number of cycles after ti. If the system is linear, the same modal properties are obtained irrespective of which cycle or how many cycles are used in the evaluation of the above equations. When the system is nonlinear, however, the arguments stated above are no longer valid; the modal properties est ...
... number of cycles after ti. If the system is linear, the same modal properties are obtained irrespective of which cycle or how many cycles are used in the evaluation of the above equations. When the system is nonlinear, however, the arguments stated above are no longer valid; the modal properties est ...
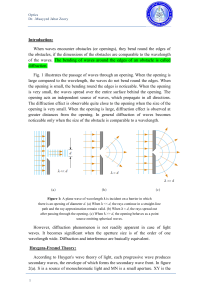
Introduction: When waves encounter obstacles (or openings), they
... screen placed in the path of light. AB is the illuminated portion of the screen and above A and below B is the region of the geometrical shadow. Considering MN as the primary wave front. According to Huygen's construction, if secondary wave fronts are drawn, one would expect encroachment of light in ...
... screen placed in the path of light. AB is the illuminated portion of the screen and above A and below B is the region of the geometrical shadow. Considering MN as the primary wave front. According to Huygen's construction, if secondary wave fronts are drawn, one would expect encroachment of light in ...
Design of a spherical focal surface using close
... control of surface profile, susceptibility to environmental changes, and variability in pixel density along the sensor face prevent this type of sensor from being used for high resolution, diffraction limited imagers where optical tolerances are tight and even coverage of the field is required. Rece ...
... control of surface profile, susceptibility to environmental changes, and variability in pixel density along the sensor face prevent this type of sensor from being used for high resolution, diffraction limited imagers where optical tolerances are tight and even coverage of the field is required. Rece ...
Interferometry
Interferometry is a family of techniques in which waves, usually electromagnetic, are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, and velocimetry.Interferometers are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In analytical science, interferometers are used in continuous wave Fourier transform spectroscopy to analyze light containing features of absorption or emission associated with a substance or mixture. An astronomical interferometer consists of two or more separate telescopes that combine their signals, offering a resolution equivalent to that of a telescope of diameter equal to the largest separation between its individual elements.