Beam Splitters A beam splitter is a device that`s used to divide an
... light aluminum is better, and gold may be preferred at longer wavelengths. ...
... light aluminum is better, and gold may be preferred at longer wavelengths. ...
Chapter 1 - Liceo Crespi
... Light travels through an optical medium with a lower speed than c, as atoms in the medium absorb, reemit, and scatter the light. For example, the refractive index for diamond is n = 2.419, so the speed of ligth in diamond = c/n c 3.00 × 10 8 m/s ...
... Light travels through an optical medium with a lower speed than c, as atoms in the medium absorb, reemit, and scatter the light. For example, the refractive index for diamond is n = 2.419, so the speed of ligth in diamond = c/n c 3.00 × 10 8 m/s ...
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
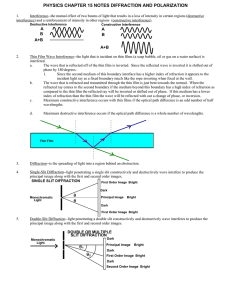
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
doc
... color. This has limited their usefulness. A number of different types of lasers have been created that produce light at a number of different wavelengths ranging through much of the electromagnetic spectrum. Also, researchers have found ways to alter their output frequencies by using lenses made of ...
... color. This has limited their usefulness. A number of different types of lasers have been created that produce light at a number of different wavelengths ranging through much of the electromagnetic spectrum. Also, researchers have found ways to alter their output frequencies by using lenses made of ...
Confocal microscopy with a volume holographic filter
... The pinhole preceding the detector in a confocal microscope is a shift-variant optical element. On-axis in-focus point-source objects are imaged exactly inside the pinhole and give maximal intensity. An out-offocus object, even when it is on axis, is equivalent to an extended source on the input foc ...
... The pinhole preceding the detector in a confocal microscope is a shift-variant optical element. On-axis in-focus point-source objects are imaged exactly inside the pinhole and give maximal intensity. An out-offocus object, even when it is on axis, is equivalent to an extended source on the input foc ...
Optics Review
... Light & Optics Review 1. Define the law of reflection. Using diagrams, explain how diffuse reflection is different from regular reflection. 2. Explain the difference between transparent, translucent and opaque. 3. Light can be produced many different ways – explain incandescence, chemiluminescence, ...
... Light & Optics Review 1. Define the law of reflection. Using diagrams, explain how diffuse reflection is different from regular reflection. 2. Explain the difference between transparent, translucent and opaque. 3. Light can be produced many different ways – explain incandescence, chemiluminescence, ...
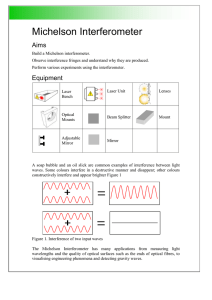
Michelson Interferometer - Research School of Physics and
... Explain how the lenses might change the interference pattern given the speed of light in air and these media is different. Tap the laser bench or table with your hand. Note how sensitive the pattern is to vibrations. This isn’t surprising as the interference pattern is generated from light waves 650 ...
... Explain how the lenses might change the interference pattern given the speed of light in air and these media is different. Tap the laser bench or table with your hand. Note how sensitive the pattern is to vibrations. This isn’t surprising as the interference pattern is generated from light waves 650 ...
lecture22
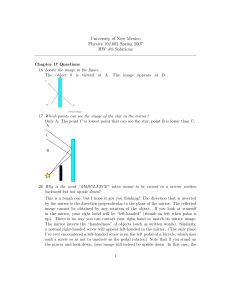
... adjacent maxima on a remote screen is 1.0 cm. What happens to the distance between adjacent maxima when the slit separation is cut in half? A) It increases to 2.0 cm. B) It increases to 4.0 cm. C) It decreases to 0.50 cm. D) It decreases to 0.25 cm. ...
... adjacent maxima on a remote screen is 1.0 cm. What happens to the distance between adjacent maxima when the slit separation is cut in half? A) It increases to 2.0 cm. B) It increases to 4.0 cm. C) It decreases to 0.50 cm. D) It decreases to 0.25 cm. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... refractive index of a thin transparent sheet? 18. (a) Discuss Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of a straight edge. ...
... refractive index of a thin transparent sheet? 18. (a) Discuss Fraunhofer diffraction pattern of a straight edge. ...
Two laser wavelength Thomson Scattering for high electron
... relativistic blue shift of the spectrum are the causes of inadmissible error bars. Due to background radiation (line emission and Bremsstrahlung) it is not advisable to extend the interference filters of the polychromators to much shorter wavelength. As an alternative method an additional Nd:YAG las ...
... relativistic blue shift of the spectrum are the causes of inadmissible error bars. Due to background radiation (line emission and Bremsstrahlung) it is not advisable to extend the interference filters of the polychromators to much shorter wavelength. As an alternative method an additional Nd:YAG las ...
PHYS4014 - Lasers and Nonlinear Optics
... Nonlinear optics: Physical origin of non-linear polarisation, birefringence, o- and e- rays, index ellipsoid for uniaxial crystals, second harmonic generation, phase-matching condition in SHG, optical parametric oscillation (OPO), phase-matching condition in OPO, frequency tuning in OPO. Holography: ...
... Nonlinear optics: Physical origin of non-linear polarisation, birefringence, o- and e- rays, index ellipsoid for uniaxial crystals, second harmonic generation, phase-matching condition in SHG, optical parametric oscillation (OPO), phase-matching condition in OPO, frequency tuning in OPO. Holography: ...
Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani and Elite School of Optometry
... UV-B, UV-C; IR - far and near IR radiations; X-rays ...
... UV-B, UV-C; IR - far and near IR radiations; X-rays ...
Fourier Optics Laboratory Manual - McGill Undergraduate Physics Lab
... image. High and low frequencies occupy different positions on the transform plane, which gives the freedom to filter out some components of an image. The origin of the transform plane, where the zero frequency can be found, is on the axis of the optical system, at the centre of the plane. This fact ...
... image. High and low frequencies occupy different positions on the transform plane, which gives the freedom to filter out some components of an image. The origin of the transform plane, where the zero frequency can be found, is on the axis of the optical system, at the centre of the plane. This fact ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.