lecture 36 - waves in 3 dimensions, optical devices
... Exam 3 review session today, 5-6 pm, room C258 Lab 10 due tomorrow Exam 3 starts Monday after break, goes through Saturday Final exam: in Testing Center, M-Th week of finals ...
... Exam 3 review session today, 5-6 pm, room C258 Lab 10 due tomorrow Exam 3 starts Monday after break, goes through Saturday Final exam: in Testing Center, M-Th week of finals ...
Characterisation of the Humidity and Temperature Responses of a
... Novel sensors utilising a hologram recorded in an analyte sensitive medium have been attracting increasing interest in recent years [1-4]. The operation of such sensors is based on the fact that when the properties of the holographic recording medium are changed due to the presence of an analyte the ...
... Novel sensors utilising a hologram recorded in an analyte sensitive medium have been attracting increasing interest in recent years [1-4]. The operation of such sensors is based on the fact that when the properties of the holographic recording medium are changed due to the presence of an analyte the ...
Interference 1 - schoolphysics
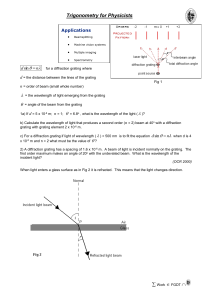
... 11. Draw a graph that shows the variation of intensity with position for the double slit experiment. 12. A laser beam of wavelength 620 nm is shone along a rod of glass so that part of the beam reflects from the near end and part from the far end. When the two beams combine they show interference d ...
... 11. Draw a graph that shows the variation of intensity with position for the double slit experiment. 12. A laser beam of wavelength 620 nm is shone along a rod of glass so that part of the beam reflects from the near end and part from the far end. When the two beams combine they show interference d ...
PPT
... Wghat fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polarizer, the light is now vertically polarized. Then, I2=I1cos26o = 1/4 I1 =1/8 I0. • Now the light ...
... Wghat fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polarizer, the light is now vertically polarized. Then, I2=I1cos26o = 1/4 I1 =1/8 I0. • Now the light ...
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
... • Ground-based FTIR spectrometers also used for various applications ...
... • Ground-based FTIR spectrometers also used for various applications ...
Fabrication and Application of Phase only Holograms for High
... leads to test sample destruction. Cooling of the samples with compressed air allowed them not to be destroyed at least for 60 seconds. 4. Beam shaping with binary phase only holograms Although the ability of ITO coatings to withstand high cw power levels is crucial for the envisioned applications it ...
... leads to test sample destruction. Cooling of the samples with compressed air allowed them not to be destroyed at least for 60 seconds. 4. Beam shaping with binary phase only holograms Although the ability of ITO coatings to withstand high cw power levels is crucial for the envisioned applications it ...
Optics - Tensors for Tots
... separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted twice, when it enters the prism and when it leaves. Refraction is the change i ...
... separating white light into components of different wavelength (different colors). The different colors refract at different angles, splitting white light into a rainbow. When light passes through a prism, it is refracted twice, when it enters the prism and when it leaves. Refraction is the change i ...
Optics and Optoelectronics
... 2. Light reflection and refraction at a spherical surfaces. Convex and concave mirrors. Formation of images by spherical mirrors. Thin lenses, focus, optical power. Aberrations of lenses. 3. Combinations of lenses, magnification. Optical instruments: human eye, magnifying glass, eyepiece, telescopes ...
... 2. Light reflection and refraction at a spherical surfaces. Convex and concave mirrors. Formation of images by spherical mirrors. Thin lenses, focus, optical power. Aberrations of lenses. 3. Combinations of lenses, magnification. Optical instruments: human eye, magnifying glass, eyepiece, telescopes ...
Week7-animations
... fusion energy. Pellets of hydrogen of fused using intense laser pulses. July 5th, 2012: 192 laser beams delivered 1.85MJ and 500 trillion watts of power (short time period). 1000 times more power than used by US at any instant of time. ...
... fusion energy. Pellets of hydrogen of fused using intense laser pulses. July 5th, 2012: 192 laser beams delivered 1.85MJ and 500 trillion watts of power (short time period). 1000 times more power than used by US at any instant of time. ...
Michelson Lab Guide UTSA
... The beam splitter is a glass plate with a thin film on one surface that partially reflects and partially transmits light. For definiteness, we will assume that it is a few-nanometer-thick aluminum film. In Physics II, you studied thin films and learned that light was phase shifted by when reflecte ...
... The beam splitter is a glass plate with a thin film on one surface that partially reflects and partially transmits light. For definiteness, we will assume that it is a few-nanometer-thick aluminum film. In Physics II, you studied thin films and learned that light was phase shifted by when reflecte ...
exam solutions
... (c) If you reflect an unpolarized beam from a glass plate at the polarization angle, the reflected light is linearly polarized. (d) In an optically dense material, interference between an incoming beam and the secondary wave it creates is constructive in the forward direction. (e) In specular reflec ...
... (c) If you reflect an unpolarized beam from a glass plate at the polarization angle, the reflected light is linearly polarized. (d) In an optically dense material, interference between an incoming beam and the secondary wave it creates is constructive in the forward direction. (e) In specular reflec ...
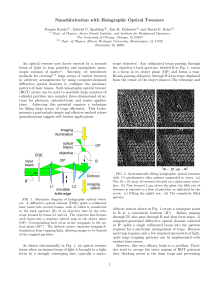
Nanofabrication with Holographic Optical Tweezers
... (OP∗ ) to OP in which each trapping beam comes to a separate focus. Their separation in OP∗ , moreover, is magnified by the ratio of L2’s focal length to the objective’s. Blocking an individual beam in OP∗ extinguishes the corresponding trap in OP. A simple knife edge can block all but one row of a ...
... (OP∗ ) to OP in which each trapping beam comes to a separate focus. Their separation in OP∗ , moreover, is magnified by the ratio of L2’s focal length to the objective’s. Blocking an individual beam in OP∗ extinguishes the corresponding trap in OP. A simple knife edge can block all but one row of a ...
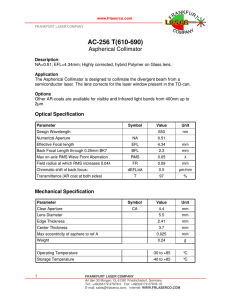
AC-256 T(610-690) - Frankfurt Laser Company
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...
Computer-generated holograms of three
... images can be classified into several main types: stereoscopic display,1 volumetric system,2 integral photography3 (also known as integral imaging), and holography.4 Each of these technologies has particular advantages and disadvantages. However, holography seems to be a more attractive method of di ...
... images can be classified into several main types: stereoscopic display,1 volumetric system,2 integral photography3 (also known as integral imaging), and holography.4 Each of these technologies has particular advantages and disadvantages. However, holography seems to be a more attractive method of di ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.