Phylum Mollusca - MissReidClasses
... mantle cavity) to extract dissolved oxygen from the water • Land molluscs breathe via an adapted mantle cavity lined with blood vessels. Must be kept moist for oxygen to enter the cells ...
... mantle cavity) to extract dissolved oxygen from the water • Land molluscs breathe via an adapted mantle cavity lined with blood vessels. Must be kept moist for oxygen to enter the cells ...
Worms - Cloudfront.net
... Flatworm Parasites • Tapeworms – Larvae enter through undercooked meat – Hooks attach to inner walls of intestines – Food absorbed through skin – Grow up to 12 meters ...
... Flatworm Parasites • Tapeworms – Larvae enter through undercooked meat – Hooks attach to inner walls of intestines – Food absorbed through skin – Grow up to 12 meters ...
animal kingdom - Biology Junction
... • Capture prey using stinging cells to inject venom - paralyzes prey • Pull prey into mouth, digest in body cavity digestive system: 1 opening - expel food from mouths also. ...
... • Capture prey using stinging cells to inject venom - paralyzes prey • Pull prey into mouth, digest in body cavity digestive system: 1 opening - expel food from mouths also. ...
Zoology Semester Exam Chapters 26-34 Unlike plant cells, animal
... 4. Only 5 % of all animals have _______________ columns. 5. Aquatic animals that strain floating plants and animals from the water they take in are _______________ feeders. 6. Many small aquatic organisms move oxygen and carbon dioxide through their skin by the process of _______________. 7. An anim ...
... 4. Only 5 % of all animals have _______________ columns. 5. Aquatic animals that strain floating plants and animals from the water they take in are _______________ feeders. 6. Many small aquatic organisms move oxygen and carbon dioxide through their skin by the process of _______________. 7. An anim ...
Subphylum Crustacea
... – Paste mixed with enzymes secreted by a digestive gland – Move to intestine for digestion and absorption. – Indigestible material is excreted through the anus ...
... – Paste mixed with enzymes secreted by a digestive gland – Move to intestine for digestion and absorption. – Indigestible material is excreted through the anus ...
Worms - Cloudfront.net
... digestions – Completely surrounded by muscle • Several organ systems – Complex digestive system – Circulatory sys: 2 blood vessels – Nervous sys: Primitive brain and nerve cord – Muscular sys: Circular & longitudinal muscles • Gas exchange through skin • Eat organic waste ...
... digestions – Completely surrounded by muscle • Several organ systems – Complex digestive system – Circulatory sys: 2 blood vessels – Nervous sys: Primitive brain and nerve cord – Muscular sys: Circular & longitudinal muscles • Gas exchange through skin • Eat organic waste ...
Reproductive
... Right and left side Top (dorsal) and bottom (ventral) triploblastic -ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm. Protostomia - a group of animals whose mouth develops from the blastopore, and the mesoderm forms from an area near the blastopore. Acoelomata - They have a true mesoderm which fills the original blast ...
... Right and left side Top (dorsal) and bottom (ventral) triploblastic -ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm. Protostomia - a group of animals whose mouth develops from the blastopore, and the mesoderm forms from an area near the blastopore. Acoelomata - They have a true mesoderm which fills the original blast ...
Insecta
... structures that remove metabolic wastes from blood and return water to the cells • Exoskeleton—prevents water evaporation • Book Lungs—gas exchange without water loss (also used in respiration) ...
... structures that remove metabolic wastes from blood and return water to the cells • Exoskeleton—prevents water evaporation • Book Lungs—gas exchange without water loss (also used in respiration) ...
Worms at Work - Prairie`s Edge Organics
... * Teeming with beneficial enzymes, microorganisms, humic acids, and other growth factors. * Provide an organic energy source for biological activity in the soil. * Stimulate root system development and activity •Promote plant health, stress tolerance, pest and disease resistant. What microbes are fo ...
... * Teeming with beneficial enzymes, microorganisms, humic acids, and other growth factors. * Provide an organic energy source for biological activity in the soil. * Stimulate root system development and activity •Promote plant health, stress tolerance, pest and disease resistant. What microbes are fo ...
Science Chapter 5 Study Sheet
... When you hold your breath, hour brain sends a message to the diaphragm and rib muscles telling them to breathe. This message is sent to the brain when carbon dioxide builds up in the blood. ...
... When you hold your breath, hour brain sends a message to the diaphragm and rib muscles telling them to breathe. This message is sent to the brain when carbon dioxide builds up in the blood. ...
Roundworms
... • Elongated, cylindrical, threadlike body which is pointed at both ends and covered by a tough, flexible cuticle • Cuticle gives nematode body shape and protection • Epidermis not composed of distinct cells • Beneath epidermis is a layer of longitudinal muscles • No circular muscles present in the b ...
... • Elongated, cylindrical, threadlike body which is pointed at both ends and covered by a tough, flexible cuticle • Cuticle gives nematode body shape and protection • Epidermis not composed of distinct cells • Beneath epidermis is a layer of longitudinal muscles • No circular muscles present in the b ...
Human Body Systems
... Muscles pull the bones to produce movement. There are voluntary, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Circulatory System The circulatory system transports oxygen, nutrients, and wastes through the body in the blood. Parts of the system: blood, heart, veins, and arteries Respiratory System In the res ...
... Muscles pull the bones to produce movement. There are voluntary, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Circulatory System The circulatory system transports oxygen, nutrients, and wastes through the body in the blood. Parts of the system: blood, heart, veins, and arteries Respiratory System In the res ...
Science Chapter 5 Study Sheet Name: My child studied for this test
... When you hold your breath, your brain sends a message to the diaphragm and rib muscles telling them to breathe. This message is sent to the brain when carbon dioxide builds up in the blood. ...
... When you hold your breath, your brain sends a message to the diaphragm and rib muscles telling them to breathe. This message is sent to the brain when carbon dioxide builds up in the blood. ...
Phylum Nematoda: Roundworms
... Slender, unsegmented, with tapering ends Most microscopic, but can be more than 1 meter in length Free-living or parasitic ...
... Slender, unsegmented, with tapering ends Most microscopic, but can be more than 1 meter in length Free-living or parasitic ...
NOTES: Simple Invertebrates
... STINGING CELLS, part of a NERVE “NET” (a primitive nervous system, a de-centralized nerve cord), NO BRAIN but sensors TWO LAYERS of cells (epidermis & gastrodermis)…no body cavity ...
... STINGING CELLS, part of a NERVE “NET” (a primitive nervous system, a de-centralized nerve cord), NO BRAIN but sensors TWO LAYERS of cells (epidermis & gastrodermis)…no body cavity ...
Accumulation of heavy metals by earthworms in boron
... Boron enters the environment mainly through the weathering of rocks, boric acid volatilization from seawater, and volcanic activity. Boron is also released from anthropogenic sources to a lesser extent. Anthropogenic sources include agricultural, refuse, and fuel wood burning, power generation using ...
... Boron enters the environment mainly through the weathering of rocks, boric acid volatilization from seawater, and volcanic activity. Boron is also released from anthropogenic sources to a lesser extent. Anthropogenic sources include agricultural, refuse, and fuel wood burning, power generation using ...
Human Body Systems Review answers
... 9. Transports nutrients and oxygen to cells circulatory 10. Exchanges gases between body and environment respiratory 11. Responds to external and internal stimuli nervous 12. Produces sex cells reproductive 13. Includes skin, hair, nails integumentary 14. Transports nutrients to body digestive ...
... 9. Transports nutrients and oxygen to cells circulatory 10. Exchanges gases between body and environment respiratory 11. Responds to external and internal stimuli nervous 12. Produces sex cells reproductive 13. Includes skin, hair, nails integumentary 14. Transports nutrients to body digestive ...
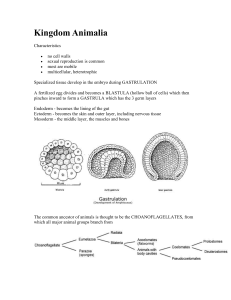
Kingdom Animalia
... Ectoderm - becomes the skin and outer layer, including nervous tissue Mesoderm - the middle layer, the muscles and bones ...
... Ectoderm - becomes the skin and outer layer, including nervous tissue Mesoderm - the middle layer, the muscles and bones ...
Black Castings - Prairie`s Edge Organics
... * Teeming with beneficial enzymes, microorganisms, humic acids, and other growth factors. * Provide an organic energy source for biological activity in the soil. * Stimulate root system development and activity •Promote plant health, stress tolerance, pest and disease resistant. What microbes are fo ...
... * Teeming with beneficial enzymes, microorganisms, humic acids, and other growth factors. * Provide an organic energy source for biological activity in the soil. * Stimulate root system development and activity •Promote plant health, stress tolerance, pest and disease resistant. What microbes are fo ...
Phylum Aschelminthes Learning Outcomes
... • Have a ‘tube within a tube’ arrangement called a pseudocoelom ...
... • Have a ‘tube within a tube’ arrangement called a pseudocoelom ...
Ecology and Adaptations - Madison County Schools
... Simple nervous system sensitive to light, touch, and vibrations Reproduction1. Asexual makes an identical copy of itself without mating. 2. Sexual-some species have both sex organs in an individual. ...
... Simple nervous system sensitive to light, touch, and vibrations Reproduction1. Asexual makes an identical copy of itself without mating. 2. Sexual-some species have both sex organs in an individual. ...
100
... Two pairs of bristles located on each segment that are used to anchor worm and increase traction ...
... Two pairs of bristles located on each segment that are used to anchor worm and increase traction ...
Earthworm

An earthworm is a tube-shaped, segmented worm found in the phylum Annelida. They are commonly found living in soil, feeding on live and dead organic matter. Its digestive system runs through the length of its body. It conducts respiration through its skin. An earthworm has a double transport system composed of coelomic fluid that moves within the fluid-filled coelom and a simple, closed blood circulatory system. It has a central and a peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve cord running back along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each segment. Large numbers of chemoreceptors are concentrated near its mouth. Circumferential and longitudinal muscles on the periphery of each segment enable the worm to move. Similar sets of muscles line the gut, and their actions move the digesting food toward the worm's anus.Earthworms are hermaphrodites—each individual carries both male and female sex organs. They lack either an internal skeleton or exoskeleton, but maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelom chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.""Earthworm"" is the common name for the largest members of Oligochaeta (which is either a class or a subclass depending on the author). In classical systems, they were placed in the order Opisthopora, on the basis of the male pores opening posterior to the female pores, though the internal male segments are anterior to the female. Theoretical cladistic studies have placed them, instead, in the suborder Lumbricina of the order Haplotaxida, but this may again soon change. Folk names for the earthworm include ""dew-worm"", ""rainworm"", ""night crawler"", and ""angleworm"" (due to its use as fishing bait).Larger terrestrial earthworms are also called megadriles (or big worms), as opposed to the microdriles (or small worms) in the semiaquatic families Tubificidae, Lumbriculidae, and Enchytraeidae, among others. The megadriles are characterized by having a distinct clitellum (which is more extensive than that of microdriles) and a vascular system with true capillaries.Earthworms are far less abundant in disturbed environments and are typically active only if water is present.