How do the circulatory system digestive system and respiratory
... the colon—rectum, and anus. Inside these hollow organs is a lining called the mucosa. In the mouth, stomach, and small intestine, the mucosa contains tiny glands that produce juices to help digest food. The digestive tract also contains a layer of smooth muscle that helps break down food and move it ...
... the colon—rectum, and anus. Inside these hollow organs is a lining called the mucosa. In the mouth, stomach, and small intestine, the mucosa contains tiny glands that produce juices to help digest food. The digestive tract also contains a layer of smooth muscle that helps break down food and move it ...
Digestive and excretory systems
... The enzymes are the molecules in the body that break down all the food. Any enzyme that digest proteins are called protease. ...
... The enzymes are the molecules in the body that break down all the food. Any enzyme that digest proteins are called protease. ...
Lecture 2: Insect Morphology - Introduction to Applied Entomology
... different forms of mandibles in insects. Analogous = structures with similar functions but different evolutionary origins, such as the wings in birds versus insects.) Inside the insect: Digestive System: A tube that extends from the mouth to the anus; there are 3 sections: Foregut: Pharynx (throat) ...
... different forms of mandibles in insects. Analogous = structures with similar functions but different evolutionary origins, such as the wings in birds versus insects.) Inside the insect: Digestive System: A tube that extends from the mouth to the anus; there are 3 sections: Foregut: Pharynx (throat) ...
Chapter 12 Molluscan Success
... Some snails have a operculum that closes the opening of the shell and prevents dessication 2. Allows clean water from the front of the snail to enter the mantle cavity 3. It makes the snail more sensitive to stimuli coming from the direction in which it moves ...
... Some snails have a operculum that closes the opening of the shell and prevents dessication 2. Allows clean water from the front of the snail to enter the mantle cavity 3. It makes the snail more sensitive to stimuli coming from the direction in which it moves ...
Read Article - Equinox Landscape
... our feet billions of organisms, some microscopic, some much larger, are busy decomposing today’s dead material, turning it into tomorrow’s living nutrients. They are the most efficient recyclers on the planet, with next to nothing being wasted. For the last billion years the soil food web, as these ...
... our feet billions of organisms, some microscopic, some much larger, are busy decomposing today’s dead material, turning it into tomorrow’s living nutrients. They are the most efficient recyclers on the planet, with next to nothing being wasted. For the last billion years the soil food web, as these ...
small intestine
... region. Using a probe, trace follow the esophagus to thestomach. Identify the small intestine and large intestine. Find the posterior part of the large intestine called the rectum and observe that it leads to the anus. Locate the cecum, a blind pouch where the small intestine joins the large intesti ...
... region. Using a probe, trace follow the esophagus to thestomach. Identify the small intestine and large intestine. Find the posterior part of the large intestine called the rectum and observe that it leads to the anus. Locate the cecum, a blind pouch where the small intestine joins the large intesti ...
Lecture 4
... thus easily transported. The five materials and plant nutrients are removed. Seeds may be separated and washed out of the soil. ...
... thus easily transported. The five materials and plant nutrients are removed. Seeds may be separated and washed out of the soil. ...
Cho - Chordate Practice
... KEY 12.) The notochord is replaced with ___backbone or vertebral column__ in vertebrates and is made up of individual segments called ___vertebrae___. 13.) A vertebrate's backbone is part of an ___endoskeleton___. 14.) Look at pgs. 724/725. To which other vertebrate group are birds most closely rel ...
... KEY 12.) The notochord is replaced with ___backbone or vertebral column__ in vertebrates and is made up of individual segments called ___vertebrae___. 13.) A vertebrate's backbone is part of an ___endoskeleton___. 14.) Look at pgs. 724/725. To which other vertebrate group are birds most closely rel ...
Chapter 30 - Digestive System
... Tissue Types • Muscle Tissue- can contract and shorten for movement • Connective Tissue- provides support and connects all parts of the body • Nerve Tissue- carries messages back and forth from body to brain and spinal cord • Epithelial Tissue- forms a protective surface inside and outside of the b ...
... Tissue Types • Muscle Tissue- can contract and shorten for movement • Connective Tissue- provides support and connects all parts of the body • Nerve Tissue- carries messages back and forth from body to brain and spinal cord • Epithelial Tissue- forms a protective surface inside and outside of the b ...
PS Final Project
... After watering, measuring, and recording data about our plants over a period of time, we found results and came to a conclusion. We averaged the heights of the plants and stalks of each category, with the categories being control group, plants with worms in the soil, plants with bacteria added to th ...
... After watering, measuring, and recording data about our plants over a period of time, we found results and came to a conclusion. We averaged the heights of the plants and stalks of each category, with the categories being control group, plants with worms in the soil, plants with bacteria added to th ...
Soil Layers - Harperclass
... • The main difference between sand, silt, and clay soils is their grain size. They are also made up of different minerals. • Smallest to largest rock particles. clay, silt, sand ...
... • The main difference between sand, silt, and clay soils is their grain size. They are also made up of different minerals. • Smallest to largest rock particles. clay, silt, sand ...
Soil formation
... some bacteria produce carbon dioxide, ammonia, nitric acid, sulphurous acid. All these substances react with minerals and favour their alteration ...
... some bacteria produce carbon dioxide, ammonia, nitric acid, sulphurous acid. All these substances react with minerals and favour their alteration ...
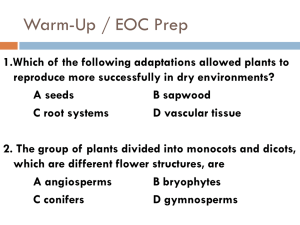
Biology B
... and kill the hydra’s food (chemical thrown at fish) Hydra reproduce sexually and asexually They reproduce asexually by budding They also reproduce sexually during winter. One hydra makes and release eggs(female). These eggs are met by sperm from a diffect hydra and become a new hydra ...
... and kill the hydra’s food (chemical thrown at fish) Hydra reproduce sexually and asexually They reproduce asexually by budding They also reproduce sexually during winter. One hydra makes and release eggs(female). These eggs are met by sperm from a diffect hydra and become a new hydra ...
verticillium soil assay for determination of colony forming units per
... Communicated by Sharon Kirkpatrick, Gordon Lab, Department of Plant Pathology, UC Davis Version October 21, 2014 ...
... Communicated by Sharon Kirkpatrick, Gordon Lab, Department of Plant Pathology, UC Davis Version October 21, 2014 ...
3.4 ANIMALS, Invertebrates
... species, such as flukes and tapeworms. Flatworms are named because their bodies are thin; the smallest are nearly microscopic, while some tapeworms can be over 20 m long. Flatworms have no anus, but have a highly branched gastrovascular cavity with only one opening. Although there are four classes o ...
... species, such as flukes and tapeworms. Flatworms are named because their bodies are thin; the smallest are nearly microscopic, while some tapeworms can be over 20 m long. Flatworms have no anus, but have a highly branched gastrovascular cavity with only one opening. Although there are four classes o ...
VERT-EXPERT “TRADITION”: Organic Mineral “Slow Release
... (following the NFU 42-001 standard), specifically designed for use in hydroseeding operations, and completely different from any known organic mineral products currently used. Their “PREMIUM” ingredients are chosen to provide maximum efficiency while ensuring optimal environmental protection. ...
... (following the NFU 42-001 standard), specifically designed for use in hydroseeding operations, and completely different from any known organic mineral products currently used. Their “PREMIUM” ingredients are chosen to provide maximum efficiency while ensuring optimal environmental protection. ...
Animals: Annelids and Insects
... are mostly land earthworms. The size of annelids can range from as small as 1 mm to as big as 3 meters. ...
... are mostly land earthworms. The size of annelids can range from as small as 1 mm to as big as 3 meters. ...
Animal Structure and Function
... insect’s nervous system is composed of neurons within the body. These cells are grouped in bundles called ganglia and nerves. Insects have a relatively simple central nervous system with a “brain” linked to nerve cord that consists of paired ganglia. Insects use special cells in the body to produce ...
... insect’s nervous system is composed of neurons within the body. These cells are grouped in bundles called ganglia and nerves. Insects have a relatively simple central nervous system with a “brain” linked to nerve cord that consists of paired ganglia. Insects use special cells in the body to produce ...
ARTHROPODS
... B. Digestion: inject prey with digestive enzymes and suck up the partially digested animal tissue with a pharynx, water reabsorption done in the hindgut (intestine) ...
... B. Digestion: inject prey with digestive enzymes and suck up the partially digested animal tissue with a pharynx, water reabsorption done in the hindgut (intestine) ...
6.5 Multicellular Organisms Meeting Their Needs
... together. For example, oxygen and nutrients are materials that cells need to survive. The respiratory, digestive, and circulatory systems work together to meet this need. The respiratory system supplies oxygen to blood cells and the digestive system supplies nutrients. The circulatory system then pu ...
... together. For example, oxygen and nutrients are materials that cells need to survive. The respiratory, digestive, and circulatory systems work together to meet this need. The respiratory system supplies oxygen to blood cells and the digestive system supplies nutrients. The circulatory system then pu ...
Multicellular Organisms Meeting Their Needs
... together. For example, oxygen and nutrients are materials that cells need to survive. The respiratory, digestive, and circulatory systems work together to meet this need. The respiratory system supplies oxygen to blood cells and the digestive system supplies nutrients. The circulatory system then pu ...
... together. For example, oxygen and nutrients are materials that cells need to survive. The respiratory, digestive, and circulatory systems work together to meet this need. The respiratory system supplies oxygen to blood cells and the digestive system supplies nutrients. The circulatory system then pu ...
soil makeup
... • Solid portions (50 percent of soil volume) ▫ Mineral matter 45 percent of the soil Inorganic material originating from rock. Determine the soil’s ability to hold water and provide nutrients Sand, silt, and clay ...
... • Solid portions (50 percent of soil volume) ▫ Mineral matter 45 percent of the soil Inorganic material originating from rock. Determine the soil’s ability to hold water and provide nutrients Sand, silt, and clay ...
Earthworm

An earthworm is a tube-shaped, segmented worm found in the phylum Annelida. They are commonly found living in soil, feeding on live and dead organic matter. Its digestive system runs through the length of its body. It conducts respiration through its skin. An earthworm has a double transport system composed of coelomic fluid that moves within the fluid-filled coelom and a simple, closed blood circulatory system. It has a central and a peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve cord running back along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each segment. Large numbers of chemoreceptors are concentrated near its mouth. Circumferential and longitudinal muscles on the periphery of each segment enable the worm to move. Similar sets of muscles line the gut, and their actions move the digesting food toward the worm's anus.Earthworms are hermaphrodites—each individual carries both male and female sex organs. They lack either an internal skeleton or exoskeleton, but maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelom chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.""Earthworm"" is the common name for the largest members of Oligochaeta (which is either a class or a subclass depending on the author). In classical systems, they were placed in the order Opisthopora, on the basis of the male pores opening posterior to the female pores, though the internal male segments are anterior to the female. Theoretical cladistic studies have placed them, instead, in the suborder Lumbricina of the order Haplotaxida, but this may again soon change. Folk names for the earthworm include ""dew-worm"", ""rainworm"", ""night crawler"", and ""angleworm"" (due to its use as fishing bait).Larger terrestrial earthworms are also called megadriles (or big worms), as opposed to the microdriles (or small worms) in the semiaquatic families Tubificidae, Lumbriculidae, and Enchytraeidae, among others. The megadriles are characterized by having a distinct clitellum (which is more extensive than that of microdriles) and a vascular system with true capillaries.Earthworms are far less abundant in disturbed environments and are typically active only if water is present.