5E-2
... (1) Definitions. The following definitions shall apply to this rule: (a) “Available water capacity” means the ability of the soil to hold water available for use by most plants and commonly expressed as inches of water per inch of soil. (b) “Bedrock” means the solid rock that underlies the soil and ...
... (1) Definitions. The following definitions shall apply to this rule: (a) “Available water capacity” means the ability of the soil to hold water available for use by most plants and commonly expressed as inches of water per inch of soil. (b) “Bedrock” means the solid rock that underlies the soil and ...
Mollusks, Worms, Arthropods, Echinoderms
... – Largest group of animals – Have jointed appendages which include legs, antennae, claws, wings, and pincers – Have bilateral symmetry, segmented bodies, exoskeletons, a body cavity, a digestive system with two openings and a nervous system – Most have separate sexes and reproduce sexually ...
... – Largest group of animals – Have jointed appendages which include legs, antennae, claws, wings, and pincers – Have bilateral symmetry, segmented bodies, exoskeletons, a body cavity, a digestive system with two openings and a nervous system – Most have separate sexes and reproduce sexually ...
Soils - sabresocials.com
... • Light colour of the A horizon indicates a very dry climate and little or no humus content ...
... • Light colour of the A horizon indicates a very dry climate and little or no humus content ...
Reducing mobility of arsenic in a brownfield soil using stabilized
... Arsenic is a trace element which is naturally found in the environment, but anthropogenic activities (e.g. mining, industrial wastes, application of agricultural pesticides, and military activities), have increased its concentration in soils and groundwater. It is one of the most toxic contaminants. ...
... Arsenic is a trace element which is naturally found in the environment, but anthropogenic activities (e.g. mining, industrial wastes, application of agricultural pesticides, and military activities), have increased its concentration in soils and groundwater. It is one of the most toxic contaminants. ...
File
... layers, that can be either aquatic, terrestrial or parasitic They have 2 body openings, therefore have complete one way digestive system food is digested extracellularly They reproduce sexually with species having either opposite sex or in some cases species can be hermaphroditic fertilization is in ...
... layers, that can be either aquatic, terrestrial or parasitic They have 2 body openings, therefore have complete one way digestive system food is digested extracellularly They reproduce sexually with species having either opposite sex or in some cases species can be hermaphroditic fertilization is in ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
Soil Testing for South Dakota Vineyards
... hole 3-feet deep. Then fill the hole with water and wait 72 hours. If water is still present in the hole after that time, the site is not well-drained enough for grapes, which are deep-rooted and not tolerant of “wet feet.” If you are using well or surface water for irrigation, it’s also a good idea ...
... hole 3-feet deep. Then fill the hole with water and wait 72 hours. If water is still present in the hole after that time, the site is not well-drained enough for grapes, which are deep-rooted and not tolerant of “wet feet.” If you are using well or surface water for irrigation, it’s also a good idea ...
Animals: - This is just a sample and may not include all topics or may
... a. extending the arm straight out b. bending the forearm toward the shoulder c. opening and closing the hand d. rotating the thumb What would result if the heart were made of skeletal muscle? a. It would beat according to its own pacemaker. b. It would not contain any striations when dissected. c. Y ...
... a. extending the arm straight out b. bending the forearm toward the shoulder c. opening and closing the hand d. rotating the thumb What would result if the heart were made of skeletal muscle? a. It would beat according to its own pacemaker. b. It would not contain any striations when dissected. c. Y ...
CHAPTER 33
... The members of the Phylum Nemertea, proboscis worms or ribbon worms, have bodies much like those of flatworms. ° However, they have a small fluid-filled sac that may be a reduced version of a true coelom. ° The sac and fluid hydraulics operate an extensible proboscis, which the worm uses to capture ...
... The members of the Phylum Nemertea, proboscis worms or ribbon worms, have bodies much like those of flatworms. ° However, they have a small fluid-filled sac that may be a reduced version of a true coelom. ° The sac and fluid hydraulics operate an extensible proboscis, which the worm uses to capture ...
Vomarine Teeth: Used for holding prey Maxillary Teeth: used to bite
... Mesentery: Holds coils of the small intestine together Large Intestine: Collects waste, absorbs water Cloaca: "Sewer": eggs, sperm, urine and feces enter this area Spleen: Part of circulatory system, stores blood, filters out dead blood cells Kidneys: Filter Blood Ureters: Carry urine from kidneys t ...
... Mesentery: Holds coils of the small intestine together Large Intestine: Collects waste, absorbs water Cloaca: "Sewer": eggs, sperm, urine and feces enter this area Spleen: Part of circulatory system, stores blood, filters out dead blood cells Kidneys: Filter Blood Ureters: Carry urine from kidneys t ...
Exercises unit 2. Digestive system
... 6.b. Excretion is the process of collecting and expelling outside waste substances produced by cellular metabolism, such as CO2 and urea. These waste substances come from the interior of cells. Kidneys and other similar structures and respiratory systems play a role in excretion. Urine is produced b ...
... 6.b. Excretion is the process of collecting and expelling outside waste substances produced by cellular metabolism, such as CO2 and urea. These waste substances come from the interior of cells. Kidneys and other similar structures and respiratory systems play a role in excretion. Urine is produced b ...
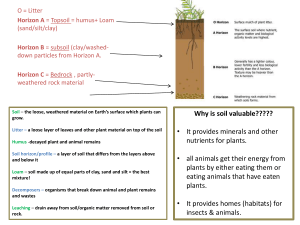
soil study guide 2015
... Soil – the loose, weathered material on Earth’s surface which plants can grow. Litter – a loose layer of leaves and other plant material on top of the soil Humus -decayed plant and animal remains Soil horizon/profile – a layer of soil that differs from the layers above and below it ...
... Soil – the loose, weathered material on Earth’s surface which plants can grow. Litter – a loose layer of leaves and other plant material on top of the soil Humus -decayed plant and animal remains Soil horizon/profile – a layer of soil that differs from the layers above and below it ...
Nematoda
... blood through the body. 30. Carnivorous birds have hooked bills and talons on their feet. 31. Annelids have a closed circulatory system, hydrostatic skeleton, and nephridia. 32. A gastrovascular cavity is a digestive sac with one opening. A complete digestive tract has 2 openings in between its dige ...
... blood through the body. 30. Carnivorous birds have hooked bills and talons on their feet. 31. Annelids have a closed circulatory system, hydrostatic skeleton, and nephridia. 32. A gastrovascular cavity is a digestive sac with one opening. A complete digestive tract has 2 openings in between its dige ...
Digestive and Excretory Systems
... ingested food into particles small enough to be absorbed into the blood. 2. Metabolism (the breakdown of food) produces cellular energy and accounts for all cellular activities. ...
... ingested food into particles small enough to be absorbed into the blood. 2. Metabolism (the breakdown of food) produces cellular energy and accounts for all cellular activities. ...
Annelida
... Annelida Characteristics Metamerism The body is made up of serially repeating, coordinated segments called metameres that are separated from one another by septa. •Each metamere contains sets of repeating organs e.g. gut, blood vessels, nerve cord, excretory organs ...
... Annelida Characteristics Metamerism The body is made up of serially repeating, coordinated segments called metameres that are separated from one another by septa. •Each metamere contains sets of repeating organs e.g. gut, blood vessels, nerve cord, excretory organs ...
Invertebrates Animal Kingdom Characteristics Body Plans
... Either sexual or asexual Asexual- fragmentation- each piece of sponge will grow into a complete new sponge Sexual- hermaphrodite- produce both eggs and sperm- release into water at different times-sperm from one enters pores of other to fertilize eggs- External fertilization ...
... Either sexual or asexual Asexual- fragmentation- each piece of sponge will grow into a complete new sponge Sexual- hermaphrodite- produce both eggs and sperm- release into water at different times-sperm from one enters pores of other to fertilize eggs- External fertilization ...
Inverterates - Grafton School District
... Either sexual or asexual Asexual- fragmentation- each piece of sponge will grow into a complete new sponge Sexual- hermaphrodite- produce both eggs and sperm- release into water at different times-sperm from one enters pores of other to fertilize eggs- External fertilization ...
... Either sexual or asexual Asexual- fragmentation- each piece of sponge will grow into a complete new sponge Sexual- hermaphrodite- produce both eggs and sperm- release into water at different times-sperm from one enters pores of other to fertilize eggs- External fertilization ...
Soil The loose mixture of small mineral fragments, organic material
... most plants grow. Leaves and other organic material fall to the ground becoming litter. This litter eventually breaks down and becomes humus. Humus is the decayed organic material that makes the soil so fertile. The layer directly below Horizon A and is also known as subsoil. Subsoil could eventuall ...
... most plants grow. Leaves and other organic material fall to the ground becoming litter. This litter eventually breaks down and becomes humus. Humus is the decayed organic material that makes the soil so fertile. The layer directly below Horizon A and is also known as subsoil. Subsoil could eventuall ...
Soils Part One: What`s in soil
... Next, place several of the soil samples on paper towels and let sit for several minutes Dump of the soil from each paper towel, and place each onto a lit overhead projector Ask the students to rank the soil samples by moisture content. Is there a relationship between soil components and moistu ...
... Next, place several of the soil samples on paper towels and let sit for several minutes Dump of the soil from each paper towel, and place each onto a lit overhead projector Ask the students to rank the soil samples by moisture content. Is there a relationship between soil components and moistu ...
How do Arthropods maintain homeostasis?
... Introduction to Arthropoda The arthropods are the most successful phylum of animals, both in diversity of distribution and in numbers of species and individuals. They have adapted successfully to life in water, on land and in the air. ...
... Introduction to Arthropoda The arthropods are the most successful phylum of animals, both in diversity of distribution and in numbers of species and individuals. They have adapted successfully to life in water, on land and in the air. ...
TYPES OF SOIL Mansi Jain B.Ed VDIT SOIL
... Residual soils are those that remain at the place of their formation as result of the weathering of the parent rocks. The depth of residual soils depends primarily on climatic conditions and the time of espouser. In temperate zones residual soils are commonly stiff and stable. An important charact ...
... Residual soils are those that remain at the place of their formation as result of the weathering of the parent rocks. The depth of residual soils depends primarily on climatic conditions and the time of espouser. In temperate zones residual soils are commonly stiff and stable. An important charact ...
Digestion
... chyme that enters the small intestine – Releases proteases to help with further digestion of proteins ...
... chyme that enters the small intestine – Releases proteases to help with further digestion of proteins ...
The Human Body System
... red blood cells. Red blood cells pick up oxygen and deliver it to the rest of the body. Circulatory/Muscular Smooth muscle helps move materials throughout the body. Found in arteries and veins to control blood flow through the blood vessel. ...
... red blood cells. Red blood cells pick up oxygen and deliver it to the rest of the body. Circulatory/Muscular Smooth muscle helps move materials throughout the body. Found in arteries and veins to control blood flow through the blood vessel. ...
Earthworm

An earthworm is a tube-shaped, segmented worm found in the phylum Annelida. They are commonly found living in soil, feeding on live and dead organic matter. Its digestive system runs through the length of its body. It conducts respiration through its skin. An earthworm has a double transport system composed of coelomic fluid that moves within the fluid-filled coelom and a simple, closed blood circulatory system. It has a central and a peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve cord running back along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each segment. Large numbers of chemoreceptors are concentrated near its mouth. Circumferential and longitudinal muscles on the periphery of each segment enable the worm to move. Similar sets of muscles line the gut, and their actions move the digesting food toward the worm's anus.Earthworms are hermaphrodites—each individual carries both male and female sex organs. They lack either an internal skeleton or exoskeleton, but maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelom chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.""Earthworm"" is the common name for the largest members of Oligochaeta (which is either a class or a subclass depending on the author). In classical systems, they were placed in the order Opisthopora, on the basis of the male pores opening posterior to the female pores, though the internal male segments are anterior to the female. Theoretical cladistic studies have placed them, instead, in the suborder Lumbricina of the order Haplotaxida, but this may again soon change. Folk names for the earthworm include ""dew-worm"", ""rainworm"", ""night crawler"", and ""angleworm"" (due to its use as fishing bait).Larger terrestrial earthworms are also called megadriles (or big worms), as opposed to the microdriles (or small worms) in the semiaquatic families Tubificidae, Lumbriculidae, and Enchytraeidae, among others. The megadriles are characterized by having a distinct clitellum (which is more extensive than that of microdriles) and a vascular system with true capillaries.Earthworms are far less abundant in disturbed environments and are typically active only if water is present.