Roots and Soil Wildlife Trading Cards
... salmon emerge, they shelter in pools and eddies formed by fallen logs. Conservation Status: Climate change and damming of rivers threaten salmon survival. ...
... salmon emerge, they shelter in pools and eddies formed by fallen logs. Conservation Status: Climate change and damming of rivers threaten salmon survival. ...
weathering_erosion_soils_1327072876
... – For example, quartz is more resistant (harder) than calcite ...
... – For example, quartz is more resistant (harder) than calcite ...
Lecture1
... Value units range between 0 and 10. The numbers ascend vertically on the page from the lowest to highest numbers, indicating dark to light values. Chroma units are arranged horizontally across the page from 0 to 10, increasing in numbers from left to right. Low numbers indicate an increase in grayne ...
... Value units range between 0 and 10. The numbers ascend vertically on the page from the lowest to highest numbers, indicating dark to light values. Chroma units are arranged horizontally across the page from 0 to 10, increasing in numbers from left to right. Low numbers indicate an increase in grayne ...
FACTORS OF SOIL FORMATION There are five soil forming factors
... Value units range between 0 and 10. The numbers ascend vertically on the page from the lowest to highest numbers, indicating dark to light values. Chroma units are arranged horizontally across the page from 0 to 10, increasing in numbers from left to right. Low numbers indicate an increase in grayne ...
... Value units range between 0 and 10. The numbers ascend vertically on the page from the lowest to highest numbers, indicating dark to light values. Chroma units are arranged horizontally across the page from 0 to 10, increasing in numbers from left to right. Low numbers indicate an increase in grayne ...
Mollusk & Segmented Worms
... Crop: holds soil before it is passed to the gizzard Gizzard: grinds food into small pieces so it can be absorbed. Setae: helps earthworm move by providing a way to anchor their bodies in the soil Circulatory system: closed Nervous system: nerve fibers connected by ventral nerve cord to a simple brai ...
... Crop: holds soil before it is passed to the gizzard Gizzard: grinds food into small pieces so it can be absorbed. Setae: helps earthworm move by providing a way to anchor their bodies in the soil Circulatory system: closed Nervous system: nerve fibers connected by ventral nerve cord to a simple brai ...
The challenges of innovative soil erosion control and management
... • Impacts on ecosystem goods and services (Millennium Development Goals) • Environmental Impact Assessments throughout the supply chain ...
... • Impacts on ecosystem goods and services (Millennium Development Goals) • Environmental Impact Assessments throughout the supply chain ...
Assessing Nitrogen Loss after Soil Saturation
... Individual results may vary, and performance may vary from location to location and from year to year. This result may not be an indicator of results you may obtain as local growing, soil and weather conditions may vary. Growers should evaluate data from multiple locations and years whenever possibl ...
... Individual results may vary, and performance may vary from location to location and from year to year. This result may not be an indicator of results you may obtain as local growing, soil and weather conditions may vary. Growers should evaluate data from multiple locations and years whenever possibl ...
Lecture 19, April 5, 2017 - EPSc 413 Introduction to Soil Science
... • Key types of sediment materials: – Sand & Silt: Typically composed of quartz [SiO2] – Clay: Dominated by microscopic aluminosilicate minerals – Loess: Wind-blown silt produced by glaciers; “rock flour” ...
... • Key types of sediment materials: – Sand & Silt: Typically composed of quartz [SiO2] – Clay: Dominated by microscopic aluminosilicate minerals – Loess: Wind-blown silt produced by glaciers; “rock flour” ...
5M Science Handbook
... Plants need light, carbon dioxide and water to make food for themselves. Plants need the right amount of light, carbon dioxide and water. If they do not get enough of any of them they will not be able to make enough food and will die. ...
... Plants need light, carbon dioxide and water to make food for themselves. Plants need the right amount of light, carbon dioxide and water. If they do not get enough of any of them they will not be able to make enough food and will die. ...
SPRING BREAK PACKET 2013.
... removing which of these from the body? A. urea B. feces C. oxygen D. carbon dioxide 56. Which of these describes a mutually beneficial relationship between two organisms? A. a dog with worms in its intestines B. a turtle and a snail that both eat grass live in a river C. a honeybee pollinating a pla ...
... removing which of these from the body? A. urea B. feces C. oxygen D. carbon dioxide 56. Which of these describes a mutually beneficial relationship between two organisms? A. a dog with worms in its intestines B. a turtle and a snail that both eat grass live in a river C. a honeybee pollinating a pla ...
Role play activity with the Nitrogen Cycle
... The nitrogen cycle occurs as nitrogen moves from air, to the soil, into living things, and then back into the air again. As gaseous nitrogen moves into the soil, bacteria fix the nitrogen into compounds that living things can use. INQUIRY FOCUS Make Models ...
... The nitrogen cycle occurs as nitrogen moves from air, to the soil, into living things, and then back into the air again. As gaseous nitrogen moves into the soil, bacteria fix the nitrogen into compounds that living things can use. INQUIRY FOCUS Make Models ...
Identification of exogenous growth stimulants or N
... isolated from the root surface between 28 and 56 DAS and there were no differences in the population sizes of either nif- or nif+ bacteria. Bacterial numbers declined from 28 to 56 DAS and by 77 DAS there were no live bacteria on the root surface. Possible causes of this lack of longevity were that ...
... isolated from the root surface between 28 and 56 DAS and there were no differences in the population sizes of either nif- or nif+ bacteria. Bacterial numbers declined from 28 to 56 DAS and by 77 DAS there were no live bacteria on the root surface. Possible causes of this lack of longevity were that ...
Erosion - Cloudfront.net
... What are the two types of weathering? How are they different? What affects the rate (how fast or slow) at which weathering occurs? What examples have you seen of each type of weathering around the school, your home, or community? ...
... What are the two types of weathering? How are they different? What affects the rate (how fast or slow) at which weathering occurs? What examples have you seen of each type of weathering around the school, your home, or community? ...
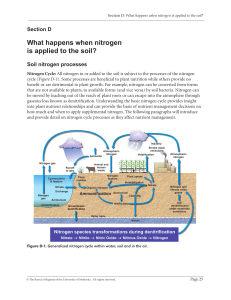
What happens when nitrogen is applied to the soil?
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
Growing Soft Fruits - Spryfield Urban Farm
... For fruiting shrubs and vines planting holes should be twice as wide as the pot they came in, and only little deeper than the pot. Spread out roots horizontally, to their full extent. If the roots are pot bound and growing in circles, be sure to loosen the roots at planting time. Soak the root ball ...
... For fruiting shrubs and vines planting holes should be twice as wide as the pot they came in, and only little deeper than the pot. Spread out roots horizontally, to their full extent. If the roots are pot bound and growing in circles, be sure to loosen the roots at planting time. Soak the root ball ...
Soils
... Although soils can be grouped together in various categories according to characteristics, no two soils are truly identical. This is partly a function of the fact that no two parent materials (e.g. rocks) are truly identical. Also, the amounts and types of organic material contained in soils differ ...
... Although soils can be grouped together in various categories according to characteristics, no two soils are truly identical. This is partly a function of the fact that no two parent materials (e.g. rocks) are truly identical. Also, the amounts and types of organic material contained in soils differ ...
PDF file
... according to characteristics, no two soils are truly identical. This is partly a function of the fact that no two parent materials (e.g. rocks) are truly identical. Also, the amounts and types of organic material contained in soils differ according to climate and vegetation type ...
... according to characteristics, no two soils are truly identical. This is partly a function of the fact that no two parent materials (e.g. rocks) are truly identical. Also, the amounts and types of organic material contained in soils differ according to climate and vegetation type ...
Githae.pmd
... responses to moisture stress allow this species to produce a high biomass even under extremely dry environments (Gaafar et al., 2006). Nitrogen is the nutrient that is most commonly deficient contributing to reduced agricultural yields throughout the world. Nitrogen- fixing species hence have larger ...
... responses to moisture stress allow this species to produce a high biomass even under extremely dry environments (Gaafar et al., 2006). Nitrogen is the nutrient that is most commonly deficient contributing to reduced agricultural yields throughout the world. Nitrogen- fixing species hence have larger ...
a ax280e
... Research Institute. About 12 500 soil samples originating from the Ministry’s archive have been analysed since 2012 to assess their fertility, texture, salinity, organic carbon and bulk density. The Ministry’s research staff have been trained in soil organic carbon analysis, digital soil mapping and ...
... Research Institute. About 12 500 soil samples originating from the Ministry’s archive have been analysed since 2012 to assess their fertility, texture, salinity, organic carbon and bulk density. The Ministry’s research staff have been trained in soil organic carbon analysis, digital soil mapping and ...
Rock PPT - Mrs Blanks APES
... • Erosion-process by which earth particles are moved from one place & deposited in another ...
... • Erosion-process by which earth particles are moved from one place & deposited in another ...
Sahelian Africa
... In Niger in West Africa desertification has led to increased food shortages in an area where food is already scarce. One of the projects combating desertification encourages farmers to plant edible, drought-resistant perennial species that do not need watering or fertilisers. The continued presence ...
... In Niger in West Africa desertification has led to increased food shortages in an area where food is already scarce. One of the projects combating desertification encourages farmers to plant edible, drought-resistant perennial species that do not need watering or fertilisers. The continued presence ...
Soil food web

The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how it interacts with the environment, plants, and animals. Food webs describe the transfer of energy between species in an ecosystem. While a food chain examines one, linear, energy pathway through an ecosystem, a food web is more complex and illustrates all of the potential pathways. Much of this transferred energy comes from the sun. Plants use the sun’s energy to convert inorganic compounds into energy-rich, organic compounds, turning carbon dioxide and minerals into plant material by photosynthesis. Plants are called autotrophs because they make their own energy; they are also called producers because they produce energy available for other organisms to eat. Heterotrophs are consumers that cannot make their own food. In order to obtain energy they eat plants or other heterotrophs.