Skeletal System
... through the birth canal Vertebral Column Composed of vertebrae (bones) separated by intervertebral disks (fibrocartilage) A Typical Vertebra ...
... through the birth canal Vertebral Column Composed of vertebrae (bones) separated by intervertebral disks (fibrocartilage) A Typical Vertebra ...
Organs
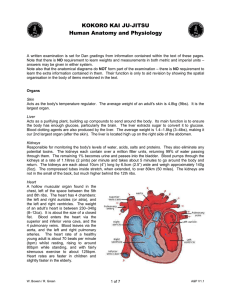
... A hollow muscular organ found in the chest, left of the space between the 5th and 8th ribs. The heart has 4 chambers: the left and right auricles (or atria), and the left and right ventricles. The weight of an adult’s heart is between 230–340g (8–12oz). It is about the size of a closed fist. Blood e ...
... A hollow muscular organ found in the chest, left of the space between the 5th and 8th ribs. The heart has 4 chambers: the left and right auricles (or atria), and the left and right ventricles. The weight of an adult’s heart is between 230–340g (8–12oz). It is about the size of a closed fist. Blood e ...
CM 5- Cervical Spine Trauma Spinal Injuries 11,000 New injuries
... Ligament Injury • Occipitoatlantal dissociation: skull may be displaced anteriorly or posteriorly or distracted from the cervical spine • Frequently results in death Transverse Ligament Disruption • Located anteriorly on the inside of the ring of C1 and runs along the posterior surface of the dens • ...
... Ligament Injury • Occipitoatlantal dissociation: skull may be displaced anteriorly or posteriorly or distracted from the cervical spine • Frequently results in death Transverse Ligament Disruption • Located anteriorly on the inside of the ring of C1 and runs along the posterior surface of the dens • ...
a glossary of terms related to oral
... sternum at the sternal angle; the largest part of the sternum is the body or corpus with its long, narrow shape as it articulates with the costal cartilages of ribs 2 through 7 laterally and with the most inferior aspect of the sternum called the xiphoid (ensiform) process. SUPRASTERNAL NOTCH Depres ...
... sternum at the sternal angle; the largest part of the sternum is the body or corpus with its long, narrow shape as it articulates with the costal cartilages of ribs 2 through 7 laterally and with the most inferior aspect of the sternum called the xiphoid (ensiform) process. SUPRASTERNAL NOTCH Depres ...
TOPICAL ANATOMY I Anatomical Terms of
... Movements (effects of muscle contraction on the joints of the body) NOTE: The body is in ANATOMICAL POSITION Flexion: bending (decrease in the angle between two bones) Extension: increase in angle between two bones Abduction: movement away from the midline Adduction: movement towards the midline ANA ...
... Movements (effects of muscle contraction on the joints of the body) NOTE: The body is in ANATOMICAL POSITION Flexion: bending (decrease in the angle between two bones) Extension: increase in angle between two bones Abduction: movement away from the midline Adduction: movement towards the midline ANA ...
Skeletal System Notes
... Cranium = top portion of the skull which protects the brain Vertebral column = vertebrae that collectively form the flexible spine Scapula = flat, triangular bone at the back of the shoulder, also called shoulder blade Sternum = long flat bone in the middle of the upper chest; chest bone Clavicle = ...
... Cranium = top portion of the skull which protects the brain Vertebral column = vertebrae that collectively form the flexible spine Scapula = flat, triangular bone at the back of the shoulder, also called shoulder blade Sternum = long flat bone in the middle of the upper chest; chest bone Clavicle = ...
Chapter 7 PPT 3 - Blair Community Schools
... Vertebral Column 1. Cervical vertebrae – 7 bones of the neck 2. Thoracic vertebrae – 12 bones of the torso ...
... Vertebral Column 1. Cervical vertebrae – 7 bones of the neck 2. Thoracic vertebrae – 12 bones of the torso ...
Thorax
... • Slope – ant. Part 1.5 cm below than post. Part ant. Part lies at T3(U) • Obliquity approx 45 degree ...
... • Slope – ant. Part 1.5 cm below than post. Part ant. Part lies at T3(U) • Obliquity approx 45 degree ...
Foundations Palpation Lab #1
... Palpation of the Spinous Processes (SP’s) Patient seated, Dr. stands to the side of the patient Step #1 - Palpate Spinous Processes of C2 through C7 (Note bifed structure) Flex the patients head forward to separate the SP’s as you palpate. This makes them easier to distinguish. As your skills improv ...
... Palpation of the Spinous Processes (SP’s) Patient seated, Dr. stands to the side of the patient Step #1 - Palpate Spinous Processes of C2 through C7 (Note bifed structure) Flex the patients head forward to separate the SP’s as you palpate. This makes them easier to distinguish. As your skills improv ...
fracture type Malgenya
... The mechanism of injury-line. Complaints: pain in the pubic area, in the crotch on the side of injury. Symptom-Gabai when turning from back to side-step the patient maintains a damaged side of the pelvis lower legs or feet healthy side, turning from a lateral position on the back of the patient keep ...
... The mechanism of injury-line. Complaints: pain in the pubic area, in the crotch on the side of injury. Symptom-Gabai when turning from back to side-step the patient maintains a damaged side of the pelvis lower legs or feet healthy side, turning from a lateral position on the back of the patient keep ...
Jeopardy Game, Axial Skeleton
... b. form synovial joints at the angle of the ribs c. form the sternal angle d. do all of the above BACK TO GAME ...
... b. form synovial joints at the angle of the ribs c. form the sternal angle d. do all of the above BACK TO GAME ...
Anterior (Transperitoneal) Approach to the Lumbar Spine
... Divide the latissimus dorsi muscle posteriorly in line with the skin incision ...
... Divide the latissimus dorsi muscle posteriorly in line with the skin incision ...
PDF Lecture 6 - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... Unilateral – bend spine to same side, rotate to opposite side Multifidus Origin & Insertion: Between transverse and spinous processes (skipping two to four vertebrae) of C2-sacrum. Innervation: Segmental spinal nerves Function: Bilateral – extend spine; Unilateral – bend spine to same side, rotate t ...
... Unilateral – bend spine to same side, rotate to opposite side Multifidus Origin & Insertion: Between transverse and spinous processes (skipping two to four vertebrae) of C2-sacrum. Innervation: Segmental spinal nerves Function: Bilateral – extend spine; Unilateral – bend spine to same side, rotate t ...
Upper Cross System Head Injuries & Neck Injuries
... – Small bodies with large vertebral foramen – bifed spinous process – foramen in each transverse process – articular facets lie at 45° in transverse plane ...
... – Small bodies with large vertebral foramen – bifed spinous process – foramen in each transverse process – articular facets lie at 45° in transverse plane ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... The cervical region of the spinal column contains two unique vertebrae, the Atlas C1 and the Axis C2. The occipital bone of the skull rests on and communicates with the first cervical vertebra C1. The arrangement of these first two vertebrae allows the rotation of the head on the spinal column. The ...
... The cervical region of the spinal column contains two unique vertebrae, the Atlas C1 and the Axis C2. The occipital bone of the skull rests on and communicates with the first cervical vertebra C1. The arrangement of these first two vertebrae allows the rotation of the head on the spinal column. The ...
Lecture 8: Bone Organs
... D. temporal: the temple, or side of the head above the ear E. occipital: the back of the head ...
... D. temporal: the temple, or side of the head above the ear E. occipital: the back of the head ...
A NEW LAGOSUCHIDAE (THECODONTIA
... projections that can be interpreted as processes for the articulation of sacral ribs. Caudals: They have an elongate body, markedly laterally compressed and anteroposteriorly expanded (Fig. 2). The prezygapophyses are well developed and project away from the vertebral body, over the adjacent vertebr ...
... projections that can be interpreted as processes for the articulation of sacral ribs. Caudals: They have an elongate body, markedly laterally compressed and anteroposteriorly expanded (Fig. 2). The prezygapophyses are well developed and project away from the vertebral body, over the adjacent vertebr ...
Lumbar Hypermobility - therapyinmotion.net
... Lumbar Hypermobility Anatomy: The spine is composed of 33 vertebrae- 7 cervical (neck), 12 thoracic (mid-back), and 5 lumbar (low back), 5 fused to form the sacrum, and 4 fused to form the coccyx (tailbone). These vertebrae are shaped to accommodate the movements and the forces imposed on the spine ...
... Lumbar Hypermobility Anatomy: The spine is composed of 33 vertebrae- 7 cervical (neck), 12 thoracic (mid-back), and 5 lumbar (low back), 5 fused to form the sacrum, and 4 fused to form the coccyx (tailbone). These vertebrae are shaped to accommodate the movements and the forces imposed on the spine ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
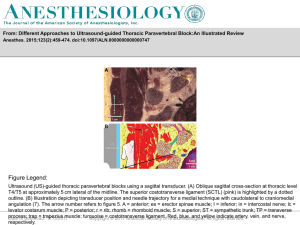
... Ultrasound (US)-guided thoracic paravertebral blocks using a sagittal transducer. (A) Oblique sagittal cross-section at thoracic level T4/T5 at approximately 5 cm lateral of the midline. The superior costotransverse ligament (SCTL) (pink) is highlighted by a dotted outline. (B) Illustration depictin ...
... Ultrasound (US)-guided thoracic paravertebral blocks using a sagittal transducer. (A) Oblique sagittal cross-section at thoracic level T4/T5 at approximately 5 cm lateral of the midline. The superior costotransverse ligament (SCTL) (pink) is highlighted by a dotted outline. (B) Illustration depictin ...
Vertebrae
... There are three atypical cervical vertebrae (C1, C2, and C7): • The C1 vertebra or atlas: a ring-like, kidney-shaped bone lacking a spinous process or body and consis]ng of two lateral masses connected by anterior and posterior arches. Its concave superior ar]cular facets receive the occipital ...
... There are three atypical cervical vertebrae (C1, C2, and C7): • The C1 vertebra or atlas: a ring-like, kidney-shaped bone lacking a spinous process or body and consis]ng of two lateral masses connected by anterior and posterior arches. Its concave superior ar]cular facets receive the occipital ...
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 5: The vertebrate skeleton Axial
... bearing the weight of the animal. There may be as few as one or over a dozen in a given species. - Caudal vertebrae: The vertebrae of the tail. Other components of the axial skeleton include: - Ribs: Ribs are associated with and connect to most types of vertebrae. Depending upon their location along ...
... bearing the weight of the animal. There may be as few as one or over a dozen in a given species. - Caudal vertebrae: The vertebrae of the tail. Other components of the axial skeleton include: - Ribs: Ribs are associated with and connect to most types of vertebrae. Depending upon their location along ...
the link
... side with the palms facing forwards and feet pointing straight ahead. The sagittal plane is vertical and extends from front to back. The coronal plane or frontal plane is vertical and extends from side to side. The transverse plane is a horizontal plane and divides the body into upper and lower comp ...
... side with the palms facing forwards and feet pointing straight ahead. The sagittal plane is vertical and extends from front to back. The coronal plane or frontal plane is vertical and extends from side to side. The transverse plane is a horizontal plane and divides the body into upper and lower comp ...
Color Atlas of Neuroscience
... Three membranes surround both spinal cord and brain: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. The dura mater is a tough, fibrous coat that encloses the spinal column and cauda equina, which is a bundle of nerve roots from the lumbar, sacral and coccygeal spinal nerves. The dura mater runs rostral ...
... Three membranes surround both spinal cord and brain: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. The dura mater is a tough, fibrous coat that encloses the spinal column and cauda equina, which is a bundle of nerve roots from the lumbar, sacral and coccygeal spinal nerves. The dura mater runs rostral ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.