Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... The cervical region of the spinal column contains two unique vertebrae, the Atlas C1 and the Axis C2. The occipital bone of the skull rests on and communicates with the first cervical vertebra C1. The arrangement of these first two vertebrae allows the rotation of the head on the spinal column. The ...
... The cervical region of the spinal column contains two unique vertebrae, the Atlas C1 and the Axis C2. The occipital bone of the skull rests on and communicates with the first cervical vertebra C1. The arrangement of these first two vertebrae allows the rotation of the head on the spinal column. The ...
Subrata Kumar Banerjea B.H.M.S Solved Papers on Anatomy
... (i) Posterior ramus of 1st cervical nerve or sub-occipital nerve, (ii) Anterior rami of 1st cervical nerve. Artery (iii) 3rd part of of vertebra? artery. Distinguishing Points (i) It has no body and no spine. (ii) It consists of— (A) 2 arches : anterior and posterior. (B) 2 lateral masses. Descripti ...
... (i) Posterior ramus of 1st cervical nerve or sub-occipital nerve, (ii) Anterior rami of 1st cervical nerve. Artery (iii) 3rd part of of vertebra? artery. Distinguishing Points (i) It has no body and no spine. (ii) It consists of— (A) 2 arches : anterior and posterior. (B) 2 lateral masses. Descripti ...
Anatomical Planes Transverse plane
... The Hyoid Bone The only bone that does not articulate with another bone ...
... The Hyoid Bone The only bone that does not articulate with another bone ...
Ca Ba V - VCOMcc
... These cells are no longer influenced by the AER (they stop dividing and are left behind) and begin to differentiate into skeletal components of limbs therefore, limbs grow proximal to distal (cells are left behind along the way forming the bones of arms) ...
... These cells are no longer influenced by the AER (they stop dividing and are left behind) and begin to differentiate into skeletal components of limbs therefore, limbs grow proximal to distal (cells are left behind along the way forming the bones of arms) ...
MUSCLES OF BACK
... Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial group, as well as, its nerve supply and action. Describe ...
... Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial group, as well as, its nerve supply and action. Describe ...
The Skeletal System
... role in respiratory movement. The sacral vertebrae “cement” the two halves of the pelvic girdle together, in the midline, and thus, contribute to the foundation of the respiratory system. The coccygeal vertebrae -- our vestigial tails -- may well be useless. We could probably lose them, like tadpole ...
... role in respiratory movement. The sacral vertebrae “cement” the two halves of the pelvic girdle together, in the midline, and thus, contribute to the foundation of the respiratory system. The coccygeal vertebrae -- our vestigial tails -- may well be useless. We could probably lose them, like tadpole ...
HuP 191B – Advanced Assessment of Upper Extremity Injuries
... – Small vertebral body with superior projection called the dens (odontoid process) – Dens articulates with atlas at atlanto-axial joint – Allows for “no” movements ...
... – Small vertebral body with superior projection called the dens (odontoid process) – Dens articulates with atlas at atlanto-axial joint – Allows for “no” movements ...
anatomylab4
... Subclavian artery divided by Scalenus anterior into (3) parts, the 1st part gives : 1. internal thoracic artery . 2. vertebral artery. 3. thyrocervical trunk(it gives 3 branches:) - Inferior thyroid artery. - suprascapular artery. -transverse cervical artery. How to distinguish between them in the l ...
... Subclavian artery divided by Scalenus anterior into (3) parts, the 1st part gives : 1. internal thoracic artery . 2. vertebral artery. 3. thyrocervical trunk(it gives 3 branches:) - Inferior thyroid artery. - suprascapular artery. -transverse cervical artery. How to distinguish between them in the l ...
SESSION 11 - Posterior Mediastinum, Diaphragm, Thoracic Wall
... 9. What vertebral level does the oesophagus pass through the diaphragm? What three other structures pass through with it? ...
... 9. What vertebral level does the oesophagus pass through the diaphragm? What three other structures pass through with it? ...
The Skeleton
... arch. • Spinous process: posterior projection arising from the junction of 2 lamina (posterior projection of the arch). • Transverse process: extends laterally from each side of the arch. • Intervertebral foramina: the spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord pass through these holes. ebneshahidi ...
... arch. • Spinous process: posterior projection arising from the junction of 2 lamina (posterior projection of the arch). • Transverse process: extends laterally from each side of the arch. • Intervertebral foramina: the spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord pass through these holes. ebneshahidi ...
Psoas Major Technique
... Psoas Major Patient supine. Operator stands on the same side as tender point. Flexion – of hips from 90-110 degrees Rotation – of hips toward the tender point side. (Knee toward) Side-bend – of hips away from the tender point side. (Feet away) Traction – lift with hand under knees to traction. Psoas ...
... Psoas Major Patient supine. Operator stands on the same side as tender point. Flexion – of hips from 90-110 degrees Rotation – of hips toward the tender point side. (Knee toward) Side-bend – of hips away from the tender point side. (Feet away) Traction – lift with hand under knees to traction. Psoas ...
Temporal Bone Landmarks cont..
... • C1 is called the atlas. – Supports the skull. – It lacks a body and a spinous process. ...
... • C1 is called the atlas. – Supports the skull. – It lacks a body and a spinous process. ...
Temporal Bone Landmarks cont..
... • C1 is called the atlas. – Supports the skull. – It lacks a body and a spinous process. ...
... • C1 is called the atlas. – Supports the skull. – It lacks a body and a spinous process. ...
Lecture (1) Parts: 1. Thoracic cage. 2. Thoracic wall. 3. Thoracic cavity.
... Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan ...
... Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan ...
Digital Necropsy of a Bottlenose Dolphin
... This picture of the external features of a dolphin also shows their well-designed, streamlined bodies. All cetaceans have a smooth, tear-shaped body that is propelled through the water by horizontal tail flukes, as well as fore flippers and a dorsal fin. Streamlining has made these animals faster by ...
... This picture of the external features of a dolphin also shows their well-designed, streamlined bodies. All cetaceans have a smooth, tear-shaped body that is propelled through the water by horizontal tail flukes, as well as fore flippers and a dorsal fin. Streamlining has made these animals faster by ...
BONY PELVIS
... The apex is directed downward, and presents an oval facet for articulation with the coccyx. The pelvic surface of the sacrum is concave from above downward. The dorsal surface of the sacrum is convex and narrower than the pelvic. The lateral surface of the sacrum is broad above, but narrowed into a ...
... The apex is directed downward, and presents an oval facet for articulation with the coccyx. The pelvic surface of the sacrum is concave from above downward. The dorsal surface of the sacrum is convex and narrower than the pelvic. The lateral surface of the sacrum is broad above, but narrowed into a ...
Mediastinum
... 3- Thoracic duct (left lymphatic) starts at the abdomen and then it will go up. 4- Sympathetic trunks (extending from the base of the skull then on both sides of the vertebral column and end at the tip of the coccyx). - Sympathetic trunk is beaded these beads are ganglions which gives the code to th ...
... 3- Thoracic duct (left lymphatic) starts at the abdomen and then it will go up. 4- Sympathetic trunks (extending from the base of the skull then on both sides of the vertebral column and end at the tip of the coccyx). - Sympathetic trunk is beaded these beads are ganglions which gives the code to th ...
- Catalyst
... O: Medial-upper part of the anterior surface of the manubrium sterni--runs superiorly, laterally, and posteriorly Lateral-superior border and anterior surface of the medial third of the clavicle; it is directed almost vertically upward. I: lateral surface of the mastoid process, ...
... O: Medial-upper part of the anterior surface of the manubrium sterni--runs superiorly, laterally, and posteriorly Lateral-superior border and anterior surface of the medial third of the clavicle; it is directed almost vertically upward. I: lateral surface of the mastoid process, ...
Answer Key: What Did You Learn
... with prominent muscle markings. The external surface of the occipital bone in a female is relatively smooth, with no major bony projections, while the male skull has well-demarcated nuchal lines and a prominent bump for the external occipital protuberances. The mastoid process in a female is smaller ...
... with prominent muscle markings. The external surface of the occipital bone in a female is relatively smooth, with no major bony projections, while the male skull has well-demarcated nuchal lines and a prominent bump for the external occipital protuberances. The mastoid process in a female is smaller ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
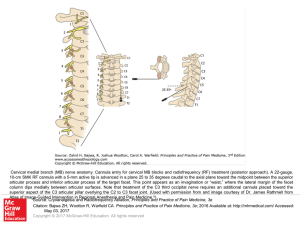
... Cervical medial branch (MB) nerve anatomy. Cannula entry for cervical MB blocks and radiofrequency (RF) treatment (posterior approach). A 22-gauge, 10-cm SMK RF cannula with a 5-mm active tip is advanced in a plane 25 to 35 degrees caudal to the axial plane toward the midpoint between the superior a ...
... Cervical medial branch (MB) nerve anatomy. Cannula entry for cervical MB blocks and radiofrequency (RF) treatment (posterior approach). A 22-gauge, 10-cm SMK RF cannula with a 5-mm active tip is advanced in a plane 25 to 35 degrees caudal to the axial plane toward the midpoint between the superior a ...
Slide 1
... The anterior oblique position may be more comfortable for the patient and may allow the natural lumbar curvature of the spine to coincide with the divergence of the x-ray beam. An anterior oblique visualizes the upside joint. ...
... The anterior oblique position may be more comfortable for the patient and may allow the natural lumbar curvature of the spine to coincide with the divergence of the x-ray beam. An anterior oblique visualizes the upside joint. ...
session-10-v2
... greater height anteriorly compared with posteriorly • The spinous process is smaller • The transverse processes are large and directed superiorly and posteriorly • The inferior facets are adapted for articulation with the sacrum and are widely spaced ...
... greater height anteriorly compared with posteriorly • The spinous process is smaller • The transverse processes are large and directed superiorly and posteriorly • The inferior facets are adapted for articulation with the sacrum and are widely spaced ...
SUMMARY OF SPINAL CURVATURES
... Note: Herniation of Nucleus pulposus = ‘Slipped Disc’ - Nucleus pulposus bulges out through Annulus fibrosus; usually in a Posterolateral direction (lateral to the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament); Most common at levels L4-L5 or L5-S1. Note: Cervical Intervertebral Disc Herniation - Second most comm ...
... Note: Herniation of Nucleus pulposus = ‘Slipped Disc’ - Nucleus pulposus bulges out through Annulus fibrosus; usually in a Posterolateral direction (lateral to the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament); Most common at levels L4-L5 or L5-S1. Note: Cervical Intervertebral Disc Herniation - Second most comm ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.