introduction to digestive system anatomy
... The oral cavity is inferior to the nasal cavities. It has a roof and floor, and lateral walls, opens onto the face through the oral fissure. It is continuous with the cavity of the pharynx at the oropharyngeal isthmus. Bones that contribute to the skeletal framework of the oral cavity or are related ...
... The oral cavity is inferior to the nasal cavities. It has a roof and floor, and lateral walls, opens onto the face through the oral fissure. It is continuous with the cavity of the pharynx at the oropharyngeal isthmus. Bones that contribute to the skeletal framework of the oral cavity or are related ...
skull - SWAU Department of Geology
... ribs, one on each side. Sacral ribs exist but are fused to the pelvic girdle. Instead of ribs, caudal vertebrae have chevrons, single bones which protect the nerves and blood vessels that run underneath the caudal centra. ...
... ribs, one on each side. Sacral ribs exist but are fused to the pelvic girdle. Instead of ribs, caudal vertebrae have chevrons, single bones which protect the nerves and blood vessels that run underneath the caudal centra. ...
ON UNUSUAL THEROPODS FROM THE UPPER CRETACEOUS
... suggests the possibility that the height of the endocranium may be connected with the double curvature of the elongated brain, which is characteristic for birds. The small pieces preserved of the orbitosphenoid bones carry large foramina for the optic nerves. The orbitosphenods are almost at a right ...
... suggests the possibility that the height of the endocranium may be connected with the double curvature of the elongated brain, which is characteristic for birds. The small pieces preserved of the orbitosphenoid bones carry large foramina for the optic nerves. The orbitosphenods are almost at a right ...
Anatomy and pathology of the aging spine1
... The vertebral column is a complicated anatomical structure which is composed of the intervertebral discs and the vertebrae. Both components develop special degenerative changes and morphologic features during life. This paper first reviews the anatomical fundamentals and then describes the morpholog ...
... The vertebral column is a complicated anatomical structure which is composed of the intervertebral discs and the vertebrae. Both components develop special degenerative changes and morphologic features during life. This paper first reviews the anatomical fundamentals and then describes the morpholog ...
practice quiz chapters7, 8,9
... ethmoid, frontal, lacrimal, maxillary bones lacrimal, vomer, ethmoid, frontal bones sphenoid, frontal, ethmoid, maxillary bones sphenoid, ethmoid, vomer, lacrimal bones ...
... ethmoid, frontal, lacrimal, maxillary bones lacrimal, vomer, ethmoid, frontal bones sphenoid, frontal, ethmoid, maxillary bones sphenoid, ethmoid, vomer, lacrimal bones ...
Outline 8
... The base of the spine of the scapula is level with the third thoracic vertebra and the inferior angle of the scapula is even with the seventh thoracic vertebra The medial and lateral borders are also ______________________ The triangle of auscultation is present on the back It’s the region bor ...
... The base of the spine of the scapula is level with the third thoracic vertebra and the inferior angle of the scapula is even with the seventh thoracic vertebra The medial and lateral borders are also ______________________ The triangle of auscultation is present on the back It’s the region bor ...
Finite element modeling of the U-C6 cervical spine unit
... cervical spine coupled with a rigid head to study the biomechanics of neck injury*. The complex anatomic structures were simplified to a combination of regularly shaped blocks such as cylinders, rectangles, and wedges. The superior and inferior surfaces of the vertebral bodies were flat. All facet a ...
... cervical spine coupled with a rigid head to study the biomechanics of neck injury*. The complex anatomic structures were simplified to a combination of regularly shaped blocks such as cylinders, rectangles, and wedges. The superior and inferior surfaces of the vertebral bodies were flat. All facet a ...
File
... • Frontal/coronal plane: divides into anterior/posterior • Transverse/horizontal plane: divides into superior/inferior • Oblique: diagonal cuts between horizontal & vertical ...
... • Frontal/coronal plane: divides into anterior/posterior • Transverse/horizontal plane: divides into superior/inferior • Oblique: diagonal cuts between horizontal & vertical ...
physicianlecture day 2015
... and intervertebral discs (very wide) ▸ Prevents back hyperextension ...
... and intervertebral discs (very wide) ▸ Prevents back hyperextension ...
diaphragm
... • Ribs acting as lever, fulcrum being just lateral to the tubercle • The anterior end of the rib is lower than the posterior end, therefore, during elevation of the rib, the anterior end also moves forwards • This occurs mostly in the vertebrosternal ribs • The body of the sternum also moves up and ...
... • Ribs acting as lever, fulcrum being just lateral to the tubercle • The anterior end of the rib is lower than the posterior end, therefore, during elevation of the rib, the anterior end also moves forwards • This occurs mostly in the vertebrosternal ribs • The body of the sternum also moves up and ...
Human Anatomy Nervous System
... Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is located within the vertebral canal, it connects to the brain at the level of foramen magnum and extend inferiorly in the vertebral canal to level L1-L2 of the vertebral column. It is considerably shorter than the vertebral column because it doesn’t grow as rapidly as ...
... Spinal Cord: The spinal cord is located within the vertebral canal, it connects to the brain at the level of foramen magnum and extend inferiorly in the vertebral canal to level L1-L2 of the vertebral column. It is considerably shorter than the vertebral column because it doesn’t grow as rapidly as ...
The detailed functional anatomy of the ligaments of the vertebral
... Ligaments of the vertabral bodies and intervertebral discs Anterior longitudinal ligament At first glance, the anterior longitudinal ligament appears to be a uniform structure covering the entire column ventrally from the anterior atlanto-occipital membrane above to the sacrum below. Closer Observat ...
... Ligaments of the vertabral bodies and intervertebral discs Anterior longitudinal ligament At first glance, the anterior longitudinal ligament appears to be a uniform structure covering the entire column ventrally from the anterior atlanto-occipital membrane above to the sacrum below. Closer Observat ...
Surface Anatomy Of Urinary System
... • On the front of the abdomen • line of the ureter runs from the hilum of the kidney to the pubic tubercle; • On the back • From the hilum vertically downward, passing practically through the posterior superior iliac spine. ...
... • On the front of the abdomen • line of the ureter runs from the hilum of the kidney to the pubic tubercle; • On the back • From the hilum vertically downward, passing practically through the posterior superior iliac spine. ...
Anatomy - Beck-Shop
... longitudinal ligament and the longus colli muscles. The posterior arch corresponds to the lamina of the other vertebrae. On its upper surface is a wide groove for the vertebral artery and the first cervical nerve. In 1–15 % of the population, a bony arch may form, thereby converting this groove into ...
... longitudinal ligament and the longus colli muscles. The posterior arch corresponds to the lamina of the other vertebrae. On its upper surface is a wide groove for the vertebral artery and the first cervical nerve. In 1–15 % of the population, a bony arch may form, thereby converting this groove into ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... longitudinal ligament and the longus colli muscles. The posterior arch corresponds to the lamina of the other vertebrae. On its upper surface is a wide groove for the vertebral artery and the first cervical nerve. In 1–15 % of the population, a bony arch may form, thereby converting this groove into ...
... longitudinal ligament and the longus colli muscles. The posterior arch corresponds to the lamina of the other vertebrae. On its upper surface is a wide groove for the vertebral artery and the first cervical nerve. In 1–15 % of the population, a bony arch may form, thereby converting this groove into ...
Anatomy Lecture 5 – Root of the Neck
... process, acromion, clavicle, and manubrium (most superficial) Splits to ensheath trapezius, omohyoid, sternocleidomastoid, parotid, and submandibular glands o Pretracheal Layer Limited to anterior part of the neck. Attaches to cricoid cartilage, fuses with fibrous pericardium, and surrounds th ...
... process, acromion, clavicle, and manubrium (most superficial) Splits to ensheath trapezius, omohyoid, sternocleidomastoid, parotid, and submandibular glands o Pretracheal Layer Limited to anterior part of the neck. Attaches to cricoid cartilage, fuses with fibrous pericardium, and surrounds th ...
spinal conditions in athletes - South Australian Sports Medicine
... Increase in size from cervical to lumbar ...
... Increase in size from cervical to lumbar ...
Chapter 5: The Skeletal System
... Types of joints; http://www.shockfamily.net/skeleton/JOINTS.HTML Plane joint – articular surfaces are flat; slip or glide across; nonaxial movement; intercarpal joints Hinge joint – cylindrical end of one bone fits into a trough of another; angular movement in one plane, elbow, ankle, phalanges; are ...
... Types of joints; http://www.shockfamily.net/skeleton/JOINTS.HTML Plane joint – articular surfaces are flat; slip or glide across; nonaxial movement; intercarpal joints Hinge joint – cylindrical end of one bone fits into a trough of another; angular movement in one plane, elbow, ankle, phalanges; are ...
ANATOMY TEAM Lecture (5) Muscles of the back
... rami of spinal nerves through brachial plexus except Trapezius (eleventh cranial ) Trapezius covered other three muscle connecting vertebral column to scapula "levator scapulae , rhomboid minor & major". Levator scapulae and rhomboid minor & major have the same: Nerve supply, insertion "medial b ...
... rami of spinal nerves through brachial plexus except Trapezius (eleventh cranial ) Trapezius covered other three muscle connecting vertebral column to scapula "levator scapulae , rhomboid minor & major". Levator scapulae and rhomboid minor & major have the same: Nerve supply, insertion "medial b ...
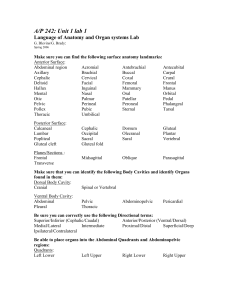
Language of Anatomy and Organ systems Lab
... Make sure that you can identify the following Body Cavities and identify Organs found in them: Dorsal Body Cavity: Cranial Spinal or Vertebral Ventral Body Cavity: Abdominal Pleural ...
... Make sure that you can identify the following Body Cavities and identify Organs found in them: Dorsal Body Cavity: Cranial Spinal or Vertebral Ventral Body Cavity: Abdominal Pleural ...
The functional morphology of the superior articular processes of the
... internal architecture of the spongy bone, and the results of the photoelastic experiment. If one accepts the claim of Pauwels (1965) that the trabeculae of spongy bone align themselves in accordance with the lines of stress, it can be assumed that the superior articular process comes under stress du ...
... internal architecture of the spongy bone, and the results of the photoelastic experiment. If one accepts the claim of Pauwels (1965) that the trabeculae of spongy bone align themselves in accordance with the lines of stress, it can be assumed that the superior articular process comes under stress du ...
MP1300 Posterior Abdominal wa osterior Abdominal wall
... The somatic nerves of the posterior abdominal wall are clearly clearly identifiable and consist of from above downwards – the subcostal, the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves lie on the quadratus lumborum (in this individual they arise together and– this can often occur and they split later in ...
... The somatic nerves of the posterior abdominal wall are clearly clearly identifiable and consist of from above downwards – the subcostal, the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves lie on the quadratus lumborum (in this individual they arise together and– this can often occur and they split later in ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... A) Echinodermata – bilateral symmetry as larvae, coelom present B) Nematoda – roundworms, pseudocoelomate C) Cnidaria – radial symmetry, polyp and medusa body forms D) Platyhelminthes – flatworms, gastrovascular cavity, acoelomate E) Calcarea – gastrovascular cavity, coelom present 22.) Which of the ...
... A) Echinodermata – bilateral symmetry as larvae, coelom present B) Nematoda – roundworms, pseudocoelomate C) Cnidaria – radial symmetry, polyp and medusa body forms D) Platyhelminthes – flatworms, gastrovascular cavity, acoelomate E) Calcarea – gastrovascular cavity, coelom present 22.) Which of the ...
SESSION 15 - Anterior and lateral neck - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... SESSION 15 - Anterior and lateral neck 1. Which nerve running across the posterior triangle of the neck would, when cut, lead to a droopy shoulder? ...
... SESSION 15 - Anterior and lateral neck 1. Which nerve running across the posterior triangle of the neck would, when cut, lead to a droopy shoulder? ...
Terminology
... The intestine is the convoluted membranous tube which extends from the stomach to the anus and which receives the ingested food from the stomach, mixes it with bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal secretions, gives origin to the chyle and delivers the indigestible products from the system. Intestin ...
... The intestine is the convoluted membranous tube which extends from the stomach to the anus and which receives the ingested food from the stomach, mixes it with bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal secretions, gives origin to the chyle and delivers the indigestible products from the system. Intestin ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.