Document
... b. digestive – releases bile into canaliculi, to common hepatic duct, joins cystic duct (from gallbladder) to bile duct to duodenum. Regulated by sphincter of Oddi. (B) Gallbladder and Bile Gallbladder stores and concentrates bile- contains minerals, cholesterol, bile pigments (mostly bilirubin) fro ...
... b. digestive – releases bile into canaliculi, to common hepatic duct, joins cystic duct (from gallbladder) to bile duct to duodenum. Regulated by sphincter of Oddi. (B) Gallbladder and Bile Gallbladder stores and concentrates bile- contains minerals, cholesterol, bile pigments (mostly bilirubin) fro ...
Slide 1
... (most medicines, alcohol, harmful substances from the body) 1. Production of blood clotting factors 2. Storage of glycogen 3. Storage of vitamins and minerals 4. Destruction of old non-functional red blood cells 5. Removal of hormones 6. Removal of ammonia from the body (urea formation) 7. Formation ...
... (most medicines, alcohol, harmful substances from the body) 1. Production of blood clotting factors 2. Storage of glycogen 3. Storage of vitamins and minerals 4. Destruction of old non-functional red blood cells 5. Removal of hormones 6. Removal of ammonia from the body (urea formation) 7. Formation ...
4/19
... • Biliary Calculi (aka Gall stones) Cholelithiasis and lithotripsy • In contrast to kidney stones • Duct Blockages and jaundice! • If the Gallbladder is removed the bile is dumped into the small intestine at a constant rate, not bad bud bile isn’t available for handling meals with lots of fat. ...
... • Biliary Calculi (aka Gall stones) Cholelithiasis and lithotripsy • In contrast to kidney stones • Duct Blockages and jaundice! • If the Gallbladder is removed the bile is dumped into the small intestine at a constant rate, not bad bud bile isn’t available for handling meals with lots of fat. ...
Digestive System
... Small Intestine: 6 meters long, enzymatic digestion, most absorption of nutrients. Duodenum: chyme goes through pyloric sphincter into first segment of the s. intestine Helper organs: they secrete enzymes that digest macromolecules in the duodenum Pancreas: Chymotrypsin and trypsin, which breaks dow ...
... Small Intestine: 6 meters long, enzymatic digestion, most absorption of nutrients. Duodenum: chyme goes through pyloric sphincter into first segment of the s. intestine Helper organs: they secrete enzymes that digest macromolecules in the duodenum Pancreas: Chymotrypsin and trypsin, which breaks dow ...
Liver, Gallbladder and Bile Quick Notes
... • Low-fat diet or bad fats will not signal the gallbladder to release bile, causing the bile to become viscous within the gallbladder or throughout the bile duct. • The body begins to suffer the effects of poor assimilation of fat-soluble nutrients, that may play a role in: o Eczema, psoriasis, dry ...
... • Low-fat diet or bad fats will not signal the gallbladder to release bile, causing the bile to become viscous within the gallbladder or throughout the bile duct. • The body begins to suffer the effects of poor assimilation of fat-soluble nutrients, that may play a role in: o Eczema, psoriasis, dry ...
Digestive enzymes - Univerzita Karlova v Praze
... Their N-terminus contains a signal sequence that anchors ribosome to the membrane of ER → release of the protein into ER; then, the signal ...
... Their N-terminus contains a signal sequence that anchors ribosome to the membrane of ER → release of the protein into ER; then, the signal ...
The Digestive System - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • Bile acids not reabsorbed in ileum may be deconjugated by bacteria in colon – deconjugated bile acids form secondary bile acids • cholic acid is converted to deoxycholic acid which may be reabsorbed • chenodeoxycholic acid is converted to lithocholic acid which is excreted in feces ...
... • Bile acids not reabsorbed in ileum may be deconjugated by bacteria in colon – deconjugated bile acids form secondary bile acids • cholic acid is converted to deoxycholic acid which may be reabsorbed • chenodeoxycholic acid is converted to lithocholic acid which is excreted in feces ...
Digestive System - Miss Gleason`s Science
... used in digestion; liver, gall bladder and ducts LIVER- large right lobe and small left lobe Hepatic portal vein – delivers blood to the liver ...
... used in digestion; liver, gall bladder and ducts LIVER- large right lobe and small left lobe Hepatic portal vein – delivers blood to the liver ...
Activity 2 Answer Key
... easily. This may leave a person wanting/needing to consume more proteins just to get the vital materials that they provide. ...
... easily. This may leave a person wanting/needing to consume more proteins just to get the vital materials that they provide. ...
DOWNLOAD The Digestive Dysfunction Map
... The principle functions of the stomach are the initiation of protein digestion and the breakdown of minerals for absorption in the small intestine. The most important elements in the stomach are hydrochloric acid and pepsin. Without these two elements, in sufficient quantity, protein digestion and m ...
... The principle functions of the stomach are the initiation of protein digestion and the breakdown of minerals for absorption in the small intestine. The most important elements in the stomach are hydrochloric acid and pepsin. Without these two elements, in sufficient quantity, protein digestion and m ...
Human Digestion
... • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it passes on its way to the intestine. ...
... • Bile duct – a long tube that carries BILE. The top half of the common bile duct is associated with the liver, while the bottom half of the common bile duct is associated with the pancreas, through which it passes on its way to the intestine. ...
PROCESS OF NUTRITION Nutrition involves five steps. 1
... The walls of the intestine contain glands that secrete intestinal juice. The enzymes present in it finally convert proteins to amino acids, complex carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acid and glycerol. 3. Absorption: It is the process of mixing of digested food in the body fluid. The int ...
... The walls of the intestine contain glands that secrete intestinal juice. The enzymes present in it finally convert proteins to amino acids, complex carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acid and glycerol. 3. Absorption: It is the process of mixing of digested food in the body fluid. The int ...
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior
... Chyme – A slushy acidic mixture of food and digestive juices. Enzymes – Protein molecules that increase the speed of chemical reactions in the body. They work by combining with and altering the molecules of other chemical substances. The digestive enzymes split large molecules of food into smaller u ...
... Chyme – A slushy acidic mixture of food and digestive juices. Enzymes – Protein molecules that increase the speed of chemical reactions in the body. They work by combining with and altering the molecules of other chemical substances. The digestive enzymes split large molecules of food into smaller u ...
bio intestine paper
... bile contains no enzymes but helps to digest fats by breaking up the large fat drops into smaller ones (emulsification). this is done by salts in the bile called bile salts. ...
... bile contains no enzymes but helps to digest fats by breaking up the large fat drops into smaller ones (emulsification). this is done by salts in the bile called bile salts. ...
The Liver Notes - Northern Highlands
... 4. Remove and store heavy metals Bile flow: -bile secreted by hepatocytes -flows through bile canaliculi between cells Canaliculi Bile ducts of triads merge into common hepatic duct Hepatic duct exits liver, joins cystic duct from gallbladder creating common bile duct Common bile duct connects t ...
... 4. Remove and store heavy metals Bile flow: -bile secreted by hepatocytes -flows through bile canaliculi between cells Canaliculi Bile ducts of triads merge into common hepatic duct Hepatic duct exits liver, joins cystic duct from gallbladder creating common bile duct Common bile duct connects t ...
Biochemistry of Gastrointestinal Fluid and Enzymes
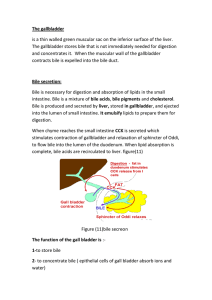
... 1. Flows toward bile duct branches in portal triads 2. Constantly made by hepatocytes 3. List of contents but bile salts and phospholipids important in digestion 4. Bile cholesterol is important because it is one of the few ways in which cholesterol stores can be regulated ...
... 1. Flows toward bile duct branches in portal triads 2. Constantly made by hepatocytes 3. List of contents but bile salts and phospholipids important in digestion 4. Bile cholesterol is important because it is one of the few ways in which cholesterol stores can be regulated ...
Digestive system and Nutrition
... enzymes, and fluids to aid in the breakdown of ingested food. But each has its own important function Liver: Makes bile, oxidizes fatty acids, Gallbladder: stores bile Pancreas:pancreatic juices, proteolytic enzymes ...
... enzymes, and fluids to aid in the breakdown of ingested food. But each has its own important function Liver: Makes bile, oxidizes fatty acids, Gallbladder: stores bile Pancreas:pancreatic juices, proteolytic enzymes ...
chapter_17_powerpoint_l
... • converts noncarbohydrates to glucose • oxidizes fatty acids • synthesizes lipoproteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol • converts carbohydrates and proteins into fats • deaminates amino acids • forms urea • synthesizes plasma proteins • converts some amino acids to other amino acids • stores glyco ...
... • converts noncarbohydrates to glucose • oxidizes fatty acids • synthesizes lipoproteins, phospholipids, and cholesterol • converts carbohydrates and proteins into fats • deaminates amino acids • forms urea • synthesizes plasma proteins • converts some amino acids to other amino acids • stores glyco ...
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Different molecular forms of bile acids can be synthesized in the liver by different species. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine in the liver, forming bile salts.Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts in bile and are roughly equal in concentration. The conjugated salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids.Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids produces an increase in bile flow. The main function of bile acids is to facilitate the formation of micelles, which promotes digestion and absorption of dietary fat, but they are increasingly being shown to have hormonal actions throughout the body.