Super Size Me - Fort Bend ISD
... into your cells for metabolizing No insulin means diabetes mellitus ...
... into your cells for metabolizing No insulin means diabetes mellitus ...
Mouth - Wsimg.com
... absorb (including undigested material) -Absorption of water Rectum (short term storage which holds feces before it is expelled). ...
... absorb (including undigested material) -Absorption of water Rectum (short term storage which holds feces before it is expelled). ...
Digestion in the Small and Large Intestine (9.5) File
... • bile breaks down large fat globules • lipases secreted by pancreas break down fats into smaller molecules • digested fats are absorbed through lacteals ...
... • bile breaks down large fat globules • lipases secreted by pancreas break down fats into smaller molecules • digested fats are absorbed through lacteals ...
Digestive system
... protects epithelial tissues and neutralizes acids produced by bacterial metabolism. • Water, salts, and vitamins are absorbed, the remaining contents in the lumen form feces (mostly cellulose, bacteria, bilirubin). • Bacteria in the large intestine, such as E. coli, produce vitamins (including vitam ...
... protects epithelial tissues and neutralizes acids produced by bacterial metabolism. • Water, salts, and vitamins are absorbed, the remaining contents in the lumen form feces (mostly cellulose, bacteria, bilirubin). • Bacteria in the large intestine, such as E. coli, produce vitamins (including vitam ...
Gastro04-RvwGIPhysioPt2
... bile ducts. 600-1200 ml/day Secreted in two stages: Hepatocytes secrete bile This is the bile-dependent fraction Bile ducts secrete water/electrolyte This is the bile-independent fraction high concentration of HCO3-, water, other electrolytes stimulated by secretin Cholesterol primary bi ...
... bile ducts. 600-1200 ml/day Secreted in two stages: Hepatocytes secrete bile This is the bile-dependent fraction Bile ducts secrete water/electrolyte This is the bile-independent fraction high concentration of HCO3-, water, other electrolytes stimulated by secretin Cholesterol primary bi ...
Mouth - Net Start Class
... fiber. Vitamins B and K are also produced here by bacteria and absorbed into the blood. Cellulose from the cracker provides fiber for peristalsis to work. The large intestine is often called the colon. ...
... fiber. Vitamins B and K are also produced here by bacteria and absorbed into the blood. Cellulose from the cracker provides fiber for peristalsis to work. The large intestine is often called the colon. ...
BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #9: Chs. 24
... 15) Increased secretion by all the salivary glands results from A) sympathetic stimulation. B) parasympathetic stimulation. C) hormonal stimulation. D) hunger. E) myenteric reflexes. 16) This organ is primarily responsible for water absorption. A) esophagus B) anus C) stomach D) large intestine E) ...
... 15) Increased secretion by all the salivary glands results from A) sympathetic stimulation. B) parasympathetic stimulation. C) hormonal stimulation. D) hunger. E) myenteric reflexes. 16) This organ is primarily responsible for water absorption. A) esophagus B) anus C) stomach D) large intestine E) ...
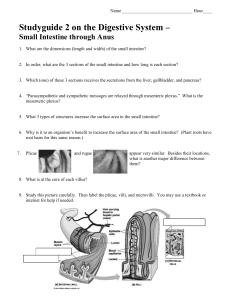
Studyguide 2 on the Digestive System
... 29. Make a diagram listing the following structures and showing how the blood flows in and out of the liver. Use arrows ( ) and the following terms but no pictures in your diagram: descending aorta, hepatic artery, branch of the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, branch of the hepatic portal vei ...
... 29. Make a diagram listing the following structures and showing how the blood flows in and out of the liver. Use arrows ( ) and the following terms but no pictures in your diagram: descending aorta, hepatic artery, branch of the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, branch of the hepatic portal vei ...
Functions of the Liver The liver performs important digestive and
... Distention of the rectal wall by feces acts as a stimulus that initiates the defecation reftex. Local reflexes cause weak contractions of the rectum and relaxation of the internal anal sphincter. Parasympathetic reflexes cause strong contractions of the rectum and are normally responsible for most o ...
... Distention of the rectal wall by feces acts as a stimulus that initiates the defecation reftex. Local reflexes cause weak contractions of the rectum and relaxation of the internal anal sphincter. Parasympathetic reflexes cause strong contractions of the rectum and are normally responsible for most o ...
Digestion1 - MrsGorukhomework
... Balanced diet - contains all the right nutrients and in right amount - carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, fibre, (water) vitamins and minerals. Need to satisfy 3 needs - fuel, raw materials for synthesis and essential nutrients that the body can't make. An equilibrium between food intake and energy us ...
... Balanced diet - contains all the right nutrients and in right amount - carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, fibre, (water) vitamins and minerals. Need to satisfy 3 needs - fuel, raw materials for synthesis and essential nutrients that the body can't make. An equilibrium between food intake and energy us ...
Digestion and Absorption Part 2
... i. C, B1, B2, niacin, B6, biotin, folic acid, B12 b. * Vitamin B12 requires intrinsic factor (IF); terminal ileum (only mechanism to worry about) 1. binds to IF in lumen which aids in absorption into epithelium 2. taken up by mitochondria then released to be taken into the portal blood c. Fat solubl ...
... i. C, B1, B2, niacin, B6, biotin, folic acid, B12 b. * Vitamin B12 requires intrinsic factor (IF); terminal ileum (only mechanism to worry about) 1. binds to IF in lumen which aids in absorption into epithelium 2. taken up by mitochondria then released to be taken into the portal blood c. Fat solubl ...
Slides on Digestion 1
... - secreted in active form but requires colipase for activity - secreted in active form ...
... - secreted in active form but requires colipase for activity - secreted in active form ...
Digestive System Worksheet
... In the mouth food is chewed and mixed with __________________. Food contains ___________________ which all living things need for survival. From the stomach food then passes to the _______________________________________. When digestion occurs the food is being ___________________ down. In the stoma ...
... In the mouth food is chewed and mixed with __________________. Food contains ___________________ which all living things need for survival. From the stomach food then passes to the _______________________________________. When digestion occurs the food is being ___________________ down. In the stoma ...
5B/C - Digestive Part 2 Worksheet KEY
... digesting itself. Whereas, the glands of stomach which are the gastric glands of fundus and body contain mucous neck cells that secrete acid mucus, and the parietal cells that secrete HCl and intrinsic factor for Vitamin B12 absorption along with chief cells that produce pepsinogen which is activate ...
... digesting itself. Whereas, the glands of stomach which are the gastric glands of fundus and body contain mucous neck cells that secrete acid mucus, and the parietal cells that secrete HCl and intrinsic factor for Vitamin B12 absorption along with chief cells that produce pepsinogen which is activate ...
Name - Missouri State University
... The _______________________ is the functional unit of the kidney. __________________ blood enters the kidney through the renal artery. These blood vessels then divide into microscopic _______________________ arterioles which deliver blood into the _____________________ where filtration occurs. Filtr ...
... The _______________________ is the functional unit of the kidney. __________________ blood enters the kidney through the renal artery. These blood vessels then divide into microscopic _______________________ arterioles which deliver blood into the _____________________ where filtration occurs. Filtr ...
to PRINT OUT the Digestion Topics
... statins; HMG-CoA-Reductase; lipogenesis; ketogenesis; fat for storage; fat for ATP; Glucose into fat; amino acids into fat; structure of cholesterol ester; bile salts; emulsification. ...
... statins; HMG-CoA-Reductase; lipogenesis; ketogenesis; fat for storage; fat for ATP; Glucose into fat; amino acids into fat; structure of cholesterol ester; bile salts; emulsification. ...
Digestive Quiz17studyquide
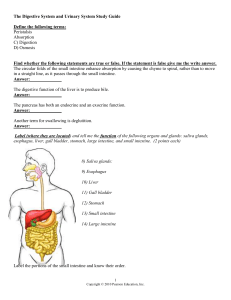
... The Digestive System and Urinary System Study Guide Define the following terms: Peristalsis Absorption C) Digestion D) Osmosis ...
... The Digestive System and Urinary System Study Guide Define the following terms: Peristalsis Absorption C) Digestion D) Osmosis ...
The digestive system can be divided into two main parts: the
... The digestive system can be divided into two main parts: the alimentary tract and accessory organs. The alimentary tract of the digestive system is composed of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum and anus. Associated with the alimentary tract are the following ...
... The digestive system can be divided into two main parts: the alimentary tract and accessory organs. The alimentary tract of the digestive system is composed of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum and anus. Associated with the alimentary tract are the following ...
lesson i - MisterSyracuse.com
... 7. Small intestine absorbs nutrients and moves food along. Duoudenum, jejunum, ileum. About 3 m in length. 8. Large intestine desiccates feces and stores it. About 1 m in length. 9. Rectum stores feces 10. Anus controls defication. 11. There are several organs through which food does not pass, but w ...
... 7. Small intestine absorbs nutrients and moves food along. Duoudenum, jejunum, ileum. About 3 m in length. 8. Large intestine desiccates feces and stores it. About 1 m in length. 9. Rectum stores feces 10. Anus controls defication. 11. There are several organs through which food does not pass, but w ...
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Different molecular forms of bile acids can be synthesized in the liver by different species. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine in the liver, forming bile salts.Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts in bile and are roughly equal in concentration. The conjugated salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids.Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids produces an increase in bile flow. The main function of bile acids is to facilitate the formation of micelles, which promotes digestion and absorption of dietary fat, but they are increasingly being shown to have hormonal actions throughout the body.