L13_FatDigst
... • In both structures, polar heads are facing the aqueous environment while the hydrophobic tails are buried in the core • Micelles can also be formed using bile salts ...
... • In both structures, polar heads are facing the aqueous environment while the hydrophobic tails are buried in the core • Micelles can also be formed using bile salts ...
Digestive System (Human): Introduction
... canal churns, disinfects, and starts digesting food, producing chyme, a semifluid mixture. Sphincters These are rings of smooth muscle that contract to close an orifice. They include the pyloric sphincter (between the stomach and duodenum) and two anal sphincters. Digestive juices Saliva and juices ...
... canal churns, disinfects, and starts digesting food, producing chyme, a semifluid mixture. Sphincters These are rings of smooth muscle that contract to close an orifice. They include the pyloric sphincter (between the stomach and duodenum) and two anal sphincters. Digestive juices Saliva and juices ...
Digestive System
... glucose = blood sugar fructose = fruit sugar galactose = milk sugar cellulose not broken down by humans (no enzyme for it) 2. Proteins polypeptides, peptides into amino acids (20) ...
... glucose = blood sugar fructose = fruit sugar galactose = milk sugar cellulose not broken down by humans (no enzyme for it) 2. Proteins polypeptides, peptides into amino acids (20) ...
Chapter 24
... • Most nutrients are absorbed by active transport. – Glucose, amino acids, & nucleic acids are absorbed by secondary active transport with sodium. – Iron and calcium require transport proteins (ferritin) or cofactors (vitamin D). – Anions follow Na+. ...
... • Most nutrients are absorbed by active transport. – Glucose, amino acids, & nucleic acids are absorbed by secondary active transport with sodium. – Iron and calcium require transport proteins (ferritin) or cofactors (vitamin D). – Anions follow Na+. ...
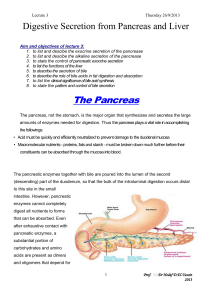
The Pancreas
... Once trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen are released into the lumen of the small intestine, they must be converted into their active forms in order to digest proteins, Trypsinogen is activated by the enzyme enterokinase, which is embedded in the intestinal mucosa. Once trypsin is formed, it activates ...
... Once trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen are released into the lumen of the small intestine, they must be converted into their active forms in order to digest proteins, Trypsinogen is activated by the enzyme enterokinase, which is embedded in the intestinal mucosa. Once trypsin is formed, it activates ...
Digestive System
... converted to pepsin by HCl environment of stomach Brush border enzymes and pancreatic enzymes (Trypsin/Chymotrypsin) digest proteins all the way to amino acids ...
... converted to pepsin by HCl environment of stomach Brush border enzymes and pancreatic enzymes (Trypsin/Chymotrypsin) digest proteins all the way to amino acids ...
Digestion and Substances Involved in Digestion
... Storage of food and the initial digestion of proteins ...
... Storage of food and the initial digestion of proteins ...
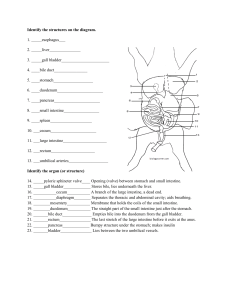
Fetal Pig Review Cont`d KEY - OG
... 14. _____pyloric sphincter valve____ Opening (valve) between stomach and small intestine. 15. _____gall bladder_____________ Stores bile, lies underneath the liver. 16. ___________cecum___________ A branch of the large intestine, a dead end. 17. ___________diaphragm________ Separates the thoracic an ...
... 14. _____pyloric sphincter valve____ Opening (valve) between stomach and small intestine. 15. _____gall bladder_____________ Stores bile, lies underneath the liver. 16. ___________cecum___________ A branch of the large intestine, a dead end. 17. ___________diaphragm________ Separates the thoracic an ...
session 40
... and fibrous. Hepatitis is most often due to viral infection resulting from drinking contaminated water or transmitted in blood via transfusion or contaminated needles. Cirrhosis is almost guaranteed when one drinks alcoholic beverages in excess for many years, and it is a common consequence of sever ...
... and fibrous. Hepatitis is most often due to viral infection resulting from drinking contaminated water or transmitted in blood via transfusion or contaminated needles. Cirrhosis is almost guaranteed when one drinks alcoholic beverages in excess for many years, and it is a common consequence of sever ...
The Digestive System
... Pharynx-passageway for food Esophagus-tube going from pharynx to stomach Stomach-where acids and enzymes continue to break down food Small intestine-uses enzymes and bile to break down food and absorb nutrients Large intestine-moves waste to rectum Liver- makes chemicals for the body and processes t ...
... Pharynx-passageway for food Esophagus-tube going from pharynx to stomach Stomach-where acids and enzymes continue to break down food Small intestine-uses enzymes and bile to break down food and absorb nutrients Large intestine-moves waste to rectum Liver- makes chemicals for the body and processes t ...
Test 4 - spring 2005
... 25. Enzymes that break down _____________ need to be made and secreted in their inactive form so they don’t breakdown the cells that made them. a. Carbohydrates b. Lipids c. Proteins d. Nucleic acids ...
... 25. Enzymes that break down _____________ need to be made and secreted in their inactive form so they don’t breakdown the cells that made them. a. Carbohydrates b. Lipids c. Proteins d. Nucleic acids ...
The Living World
... This stimulates neurons to send impulses to the swallowing center in the brain Muscles contract and raise the larynx The glottis is pushed against the epiglottis which keeps food out of the respiratory tract, and into the esophagus ...
... This stimulates neurons to send impulses to the swallowing center in the brain Muscles contract and raise the larynx The glottis is pushed against the epiglottis which keeps food out of the respiratory tract, and into the esophagus ...
Digestive System: What you need to know!!!!! Structures: a. mouth
... Diarrhea causes water and electrolytes to be lost from the body, this effects hydration, blood pH, nerve and muscle function. Water alone can not treat dehydration. ORS contain salts, glucose and sucrose. Obesity is a form of malnutrition, due to overconsumption of food, often processed and high fat ...
... Diarrhea causes water and electrolytes to be lost from the body, this effects hydration, blood pH, nerve and muscle function. Water alone can not treat dehydration. ORS contain salts, glucose and sucrose. Obesity is a form of malnutrition, due to overconsumption of food, often processed and high fat ...
GI I and II
... 32. Describe the cellular mechanisms of absorption of amino acids and di- and tripeptides in the intestine. a. Di and tripeptides are absorbed across the luminal membrane by cotransport with H+ b. Amino acids are absorbed by cotransport with Na+ 33. Define amphipathic and give examples of amphipathi ...
... 32. Describe the cellular mechanisms of absorption of amino acids and di- and tripeptides in the intestine. a. Di and tripeptides are absorbed across the luminal membrane by cotransport with H+ b. Amino acids are absorbed by cotransport with Na+ 33. Define amphipathic and give examples of amphipathi ...
The Lower Alimentary Organs
... • Secretes pancreatic juices into duodenum • digestive enzymes • Bicarbonate (alkaline)- increase pH level after chyme has left acidic stomach • Secretes hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate glucose levels in the ...
... • Secretes pancreatic juices into duodenum • digestive enzymes • Bicarbonate (alkaline)- increase pH level after chyme has left acidic stomach • Secretes hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate glucose levels in the ...
Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption
... • HCl: converts pepsinogen to pepsin; low pH kills microorganisms • Intrinsic factor: binds to vitamin B12 to promote absorption in SI • Gastrin: hormone that regulates stomach secretions; influenced by “hunger” • Mucus: lubricates and protects cells from chyme (acidic) & pepsin (protein digesting e ...
... • HCl: converts pepsinogen to pepsin; low pH kills microorganisms • Intrinsic factor: binds to vitamin B12 to promote absorption in SI • Gastrin: hormone that regulates stomach secretions; influenced by “hunger” • Mucus: lubricates and protects cells from chyme (acidic) & pepsin (protein digesting e ...
dark blue parotid – light green Large intestine
... 2. produces enzymes to break down all categories of digestible foods 3. enzymes are secreted i/t duodenum 4. enzymes neutralize acidic chyme from stomach 5. pancreatic juice contains enzymes: a. amylase – starch dig. b. trypsin – protein dig. c. lipase – lipid dig. d. nuclease – nucleic acid dig. D. ...
... 2. produces enzymes to break down all categories of digestible foods 3. enzymes are secreted i/t duodenum 4. enzymes neutralize acidic chyme from stomach 5. pancreatic juice contains enzymes: a. amylase – starch dig. b. trypsin – protein dig. c. lipase – lipid dig. d. nuclease – nucleic acid dig. D. ...
Digestive System: True-False Review
... The salivary gland directly below the ear is called the sublingual gland. The pancreas is superior to the stomach. Herbivores use their molars/premolars to grind and crush food. Long canines are present in both carnivores and herbivores. Taste buds are also called papillae. Each taste bud is actuall ...
... The salivary gland directly below the ear is called the sublingual gland. The pancreas is superior to the stomach. Herbivores use their molars/premolars to grind and crush food. Long canines are present in both carnivores and herbivores. Taste buds are also called papillae. Each taste bud is actuall ...
Chapter 27 Digestive System
... from anus is called defecation. 14. Eating disorders: Anorexia is self starvation to keep already underweight body more thinly. Bulemia is the behavior pattern of alternate binge eating and purging the body by induced vomiting etc. Malnutrition is deficiency of one or more nutrients mostly essential ...
... from anus is called defecation. 14. Eating disorders: Anorexia is self starvation to keep already underweight body more thinly. Bulemia is the behavior pattern of alternate binge eating and purging the body by induced vomiting etc. Malnutrition is deficiency of one or more nutrients mostly essential ...
Animation: Lipid Absorption Lipids are digested and absorbed
... Lipids are digested and absorbed differently from carbohydrates and proteins because they are not soluble in water and so cannot enter our bloodstream easily. Digestion of triglycerides in our foods begins in the mouth. The lingual glands in the tongue produce an enzyme known as lipase that chemical ...
... Lipids are digested and absorbed differently from carbohydrates and proteins because they are not soluble in water and so cannot enter our bloodstream easily. Digestion of triglycerides in our foods begins in the mouth. The lingual glands in the tongue produce an enzyme known as lipase that chemical ...
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Different molecular forms of bile acids can be synthesized in the liver by different species. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine in the liver, forming bile salts.Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts in bile and are roughly equal in concentration. The conjugated salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids.Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids produces an increase in bile flow. The main function of bile acids is to facilitate the formation of micelles, which promotes digestion and absorption of dietary fat, but they are increasingly being shown to have hormonal actions throughout the body.