lecture 3 Introduction to Laser
... Do not require a signal external to the laser (such as the driving signal of a modulator) to produce pulses. ...
... Do not require a signal external to the laser (such as the driving signal of a modulator) to produce pulses. ...
Enhanced localization of Dyakonov-like surface waves in left
... reversion of the Goos-Hänchen shifts.15 The negative refraction has already been experimentally confirmed by several groups, in both photonic crystals and LH materials.13,16,17 In order to meet the requirements for applications a great effort has been made in the past few years to find and engineer ...
... reversion of the Goos-Hänchen shifts.15 The negative refraction has already been experimentally confirmed by several groups, in both photonic crystals and LH materials.13,16,17 In order to meet the requirements for applications a great effort has been made in the past few years to find and engineer ...
Photo Detector Principle of Operation
... thick I-layer between the PN junction. This widens the depletion layer when a reverse bias is applied, and allows the diode to be used at a high reverse bias voltage. The high electrical field conductivity in the wide depletion layer prompts the carriers to move, and has the effect of increasing res ...
... thick I-layer between the PN junction. This widens the depletion layer when a reverse bias is applied, and allows the diode to be used at a high reverse bias voltage. The high electrical field conductivity in the wide depletion layer prompts the carriers to move, and has the effect of increasing res ...
unit 29: reflection and mirrors
... activity to their Activity Guide when it is handed in.) For the following activities you will need: ...
... activity to their Activity Guide when it is handed in.) For the following activities you will need: ...
Introduction to Acousto Optics
... materials, glucose and glycole. The key to interpreting NIR spectra is on-line data processing and chemometrics, which has become possible with the advent of spectroscopic systems with intelligence in the form of dedicated, or in some cases, built-in microprocessors or PC's. Typically, the analysis ...
... materials, glucose and glycole. The key to interpreting NIR spectra is on-line data processing and chemometrics, which has become possible with the advent of spectroscopic systems with intelligence in the form of dedicated, or in some cases, built-in microprocessors or PC's. Typically, the analysis ...
Di raction and Interference PRECAUTION
... In this experiment you will examine what happens when a plane coherent monochromatic beam of light from a laser is incident on single slits of various widths, and double slits of various widths and separations. The former is called single slit diffraction, and the latter is called two slit interfere ...
... In this experiment you will examine what happens when a plane coherent monochromatic beam of light from a laser is incident on single slits of various widths, and double slits of various widths and separations. The former is called single slit diffraction, and the latter is called two slit interfere ...
LASERS How do they work?
... Pumped amplifying media could be used to increase the intensity of light at particular wavelengths and such arrangements are often incorporated into laser systems. However, except in a few exceptional cases, light amplifiers would not be regarded as lasers. A laser consists of a pumped amplifying m ...
... Pumped amplifying media could be used to increase the intensity of light at particular wavelengths and such arrangements are often incorporated into laser systems. However, except in a few exceptional cases, light amplifiers would not be regarded as lasers. A laser consists of a pumped amplifying m ...
Three Lasers Converging at a Focal Point : A Demonstration
... 1. Clear a space on a table. Set up three lasers next to each other so they will produce parallel beams of light. The lasers need to be close together so they all pass through the lens. There are two ways to accomplish this. One is to not use the supports and use a rubber band to hold the lasers tog ...
... 1. Clear a space on a table. Set up three lasers next to each other so they will produce parallel beams of light. The lasers need to be close together so they all pass through the lens. There are two ways to accomplish this. One is to not use the supports and use a rubber band to hold the lasers tog ...
LED Turning Lights on the Traction Avant
... original Scintex flashers which are still in working condition. Keeping the Scintex Flasher Replacing the light bulbs with the LED units –which is deadly simple- would not allow me to use the old Scintex flashers anymore, so I ran a test with both the LED and the 18 watt light bulb mounted onto the ...
... original Scintex flashers which are still in working condition. Keeping the Scintex Flasher Replacing the light bulbs with the LED units –which is deadly simple- would not allow me to use the old Scintex flashers anymore, so I ran a test with both the LED and the 18 watt light bulb mounted onto the ...
A History of Imaging
... ers have applied optics’ quantum nature to new imaging modalities—for example, quantum coincidence imaging. Coincidence imaging is an indirect form of imaging that does not use optical elements to map object points to image points. Rather, it relies on a pair of quantum entangled photons that travel ...
... ers have applied optics’ quantum nature to new imaging modalities—for example, quantum coincidence imaging. Coincidence imaging is an indirect form of imaging that does not use optical elements to map object points to image points. Rather, it relies on a pair of quantum entangled photons that travel ...
Calculation of the Induced Charge Distribution on the Surface of a
... method of image charges which is an analytical method.However,this method is not applicable in dynamic problems when the dielectric constant of the metallic nanosphere has an imaginary part. The situation is worse when the nanoparticle has an irregular and asymmetric geometry, when the use of numeri ...
... method of image charges which is an analytical method.However,this method is not applicable in dynamic problems when the dielectric constant of the metallic nanosphere has an imaginary part. The situation is worse when the nanoparticle has an irregular and asymmetric geometry, when the use of numeri ...
Optical Lenses part 2
... A lens is a curved transparent material that is smooth and regularly shaped so that when light strikes it, the light refracts in a predictable and useful way. Made of transparent glass or very hard plastic ...
... A lens is a curved transparent material that is smooth and regularly shaped so that when light strikes it, the light refracts in a predictable and useful way. Made of transparent glass or very hard plastic ...
Rapid fabrication of 3D terahertz split ring resonator arrays by novel
... performed in a 20 µm square cell with scattering boundary conditions. 9.5 µm of air above 5 µm of resist placed on 5.5 µm of glass are used as the sample. Laser illumination is simulated using the analytical Gaussian equation with polarization of the electric field perpendicular to the cell. 3D reso ...
... performed in a 20 µm square cell with scattering boundary conditions. 9.5 µm of air above 5 µm of resist placed on 5.5 µm of glass are used as the sample. Laser illumination is simulated using the analytical Gaussian equation with polarization of the electric field perpendicular to the cell. 3D reso ...
Verification on Malus`s Law
... Polarization is the property of electromagnetic waves that describes the orientation of their field oscillation. Students face hard problem to visualize the important of the polarization in daily life. In common practice, students are taught with the help of sketch diagram. In this project, we descr ...
... Polarization is the property of electromagnetic waves that describes the orientation of their field oscillation. Students face hard problem to visualize the important of the polarization in daily life. In common practice, students are taught with the help of sketch diagram. In this project, we descr ...
spectroscopic ellipsometry as a versatile tool to study thin films
... topography. For example, in VLSI circuit structures, contact holes with micron or submicron dimensions should be uniformly coated with metal films not only inside the small contact cavities, but also on their vertical walls [4]. This is referred to as step coverage or conformality. Among the thin fi ...
... topography. For example, in VLSI circuit structures, contact holes with micron or submicron dimensions should be uniformly coated with metal films not only inside the small contact cavities, but also on their vertical walls [4]. This is referred to as step coverage or conformality. Among the thin fi ...
Microscope
... which has the same optical properties as glass, i.e. immersion oil. By collecting extra oblique light, the oil provides better resolution and a brighter image. ...
... which has the same optical properties as glass, i.e. immersion oil. By collecting extra oblique light, the oil provides better resolution and a brighter image. ...
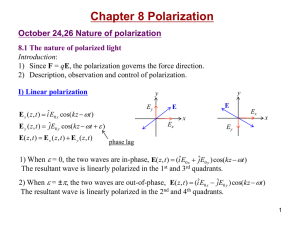
Chapter 8
... a = kz-t, the resultant wave is right-circularly polarized (rotate clockwise). 2) When E0x=E0y=E0, = p /2 , E( z, t ) E0 [iˆ cos(kz t ) ˆj sin( kz t )] a = -kz +t, the resultant wave is left-circularly polarized (rotate counterclockwise). Circular light: i)The amplitude E0 does not cha ...
... a = kz-t, the resultant wave is right-circularly polarized (rotate clockwise). 2) When E0x=E0y=E0, = p /2 , E( z, t ) E0 [iˆ cos(kz t ) ˆj sin( kz t )] a = -kz +t, the resultant wave is left-circularly polarized (rotate counterclockwise). Circular light: i)The amplitude E0 does not cha ...
Slide 1
... plastic. The basic optical fiber material must have the following properties: (i) Efficient guide for the light waves (ii) Low scattering losses (iii) The absorption, attenuation and dispersion of optical energy must be low. Based on the material used for fabrication, they are classified into two ty ...
... plastic. The basic optical fiber material must have the following properties: (i) Efficient guide for the light waves (ii) Low scattering losses (iii) The absorption, attenuation and dispersion of optical energy must be low. Based on the material used for fabrication, they are classified into two ty ...
X-rays as a branch of optics A C Nobel Lecture, December 12, 1927
... oscillators in the refractive medium has foiled all such attempts. For the extreme frequencies of X-rays, however, the problem has become greatly simplified. In the case of substances such as glass, the X-ray frequencies are much higher than the natural frequencies of the oscillators in the medium, ...
... oscillators in the refractive medium has foiled all such attempts. For the extreme frequencies of X-rays, however, the problem has become greatly simplified. In the case of substances such as glass, the X-ray frequencies are much higher than the natural frequencies of the oscillators in the medium, ...
Document
... group of children. A small round hole with luminous red contour was formed in the glass. Then the diameter of the hole enlarged reaching 3–4 cm, and the BL disappeared with a burst of light and loud sound. At the moment when the BL disappeared the teacher who was holding an epidiascope plugged into ...
... group of children. A small round hole with luminous red contour was formed in the glass. Then the diameter of the hole enlarged reaching 3–4 cm, and the BL disappeared with a burst of light and loud sound. At the moment when the BL disappeared the teacher who was holding an epidiascope plugged into ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.