4Pi Microscopy
... properties of the dye to break the diffraction barrier. Using two lenses for STED, the axial resolution was improved down to 30 to 50 nm (Dyba and Hell, 2002; Dyba et al., 2003). However, as STED is still in its infancy and, unlike I5M and 4Pi microscopy, relies on the specific properties of the dye ...
... properties of the dye to break the diffraction barrier. Using two lenses for STED, the axial resolution was improved down to 30 to 50 nm (Dyba and Hell, 2002; Dyba et al., 2003). However, as STED is still in its infancy and, unlike I5M and 4Pi microscopy, relies on the specific properties of the dye ...
Effect of barrier height on linear and nonlinear
... R=16Å and at incident intensity I=20 MW/cm2. It is noticed that the maximum value of linear refractive index change decreases with the increase in the barrier height. This is due to decrease in the value of the transition matrix at larger value of barrier height. The resonance position which is the ...
... R=16Å and at incident intensity I=20 MW/cm2. It is noticed that the maximum value of linear refractive index change decreases with the increase in the barrier height. This is due to decrease in the value of the transition matrix at larger value of barrier height. The resonance position which is the ...
Assessing the Contributions of Surface Waves and Complex Rays to
... The infinite series of transverse-electric (TE) and transverse-magnetic (TM) spherical multipole partial waves, known as the Mie scattering formalism, is an exact solution to the scattering of a linearly polarized plane electromagnetic wave by a dielectric sphere.' 3 Being an exact solution, the Mie ...
... The infinite series of transverse-electric (TE) and transverse-magnetic (TM) spherical multipole partial waves, known as the Mie scattering formalism, is an exact solution to the scattering of a linearly polarized plane electromagnetic wave by a dielectric sphere.' 3 Being an exact solution, the Mie ...
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics
... after extrapolation). Then you should know that your drawing is inaccurate, and you should improve it. In an accurate drawing, these three rays will necessarily go through one point, either in front of the mirror, or in the back of the mirror after backward extrapolation of the three reflected rays. ...
... after extrapolation). Then you should know that your drawing is inaccurate, and you should improve it. In an accurate drawing, these three rays will necessarily go through one point, either in front of the mirror, or in the back of the mirror after backward extrapolation of the three reflected rays. ...
Compact Magnetic Antennas for Directional Excitation of Surface Plasmons Yongmin Liu, Stefano Palomba,
... of D = 300 nm and electric field polarization along the x-axis (Figure 4d), we observe that the SPP phase front propagates away from the nanostructures along the −x direction, which is consistent with the numerical simulation (Figure 3a). The experimental result shown in Figure 4d is after proper nor ...
... of D = 300 nm and electric field polarization along the x-axis (Figure 4d), we observe that the SPP phase front propagates away from the nanostructures along the −x direction, which is consistent with the numerical simulation (Figure 3a). The experimental result shown in Figure 4d is after proper nor ...
Compact Magnetic Antennas for Directional Excitation of Surface Plasmons Yongmin Liu, Stefano Palomba,
... of D = 300 nm and electric field polarization along the x-axis (Figure 4d), we observe that the SPP phase front propagates away from the nanostructures along the −x direction, which is consistent with the numerical simulation (Figure 3a). The experimental result shown in Figure 4d is after proper nor ...
... of D = 300 nm and electric field polarization along the x-axis (Figure 4d), we observe that the SPP phase front propagates away from the nanostructures along the −x direction, which is consistent with the numerical simulation (Figure 3a). The experimental result shown in Figure 4d is after proper nor ...
Generation of a dark hollow beam by a four
... one can obtain that formula (5) and (6) are overlying of Laguerre-Gaussian functions LG0l . It is easy to see that intensity is zero on z axis and the maximum of the intensity around z axis generates DHBOP. When illuminated by the light beam showed in Fig.1(c), two DHBOPs will cross vertically and a ...
... one can obtain that formula (5) and (6) are overlying of Laguerre-Gaussian functions LG0l . It is easy to see that intensity is zero on z axis and the maximum of the intensity around z axis generates DHBOP. When illuminated by the light beam showed in Fig.1(c), two DHBOPs will cross vertically and a ...
Strong enhancement of light extraction efficiency in GaInAsP 2D
... the ohmic contact. The effect of the textured surface also depends on the mirror reflectivity [15]. This method achieved 30% efficiency in an LED with a nonannealed metal mirror separated from electrodes. This paper discusses the extraction efficiency in 2-Darranged semiconductor microcolumns, desig ...
... the ohmic contact. The effect of the textured surface also depends on the mirror reflectivity [15]. This method achieved 30% efficiency in an LED with a nonannealed metal mirror separated from electrodes. This paper discusses the extraction efficiency in 2-Darranged semiconductor microcolumns, desig ...
Preview of “ZEISS Microscopy Online ...opy Basics | Objectives”
... Such objectives are corrected for axial chromatic aberration in blue and red wavelengths, which are about 486 and 656 nanometers, respectively. Both are brought into a single common focal point. Achromatic objectives are also corrected for spherical aberration in ...
... Such objectives are corrected for axial chromatic aberration in blue and red wavelengths, which are about 486 and 656 nanometers, respectively. Both are brought into a single common focal point. Achromatic objectives are also corrected for spherical aberration in ...
Effective Wavelength Scaling for Optical Antennas
... In the radio frequency and microwave regimes antennas are widely employed to convert electromagnetic radiation into localized energy and vice versa. However, at optical frequencies, lenses and mirrors are used to redirect the wave fronts of propagating radiation and the antenna concept is widely une ...
... In the radio frequency and microwave regimes antennas are widely employed to convert electromagnetic radiation into localized energy and vice versa. However, at optical frequencies, lenses and mirrors are used to redirect the wave fronts of propagating radiation and the antenna concept is widely une ...
Initial demonstration of a local, evanescent, array coupled biosensor concept
... is about ∆P/P=81%. Noise in the measured intensity originates from the scattered light due to the surface roughness. The average noise level is approximately Pn=26 counts and therefore the estimated optical SNR is 55:1. This important result supports the potential application of this waveguide senso ...
... is about ∆P/P=81%. Noise in the measured intensity originates from the scattered light due to the surface roughness. The average noise level is approximately Pn=26 counts and therefore the estimated optical SNR is 55:1. This important result supports the potential application of this waveguide senso ...
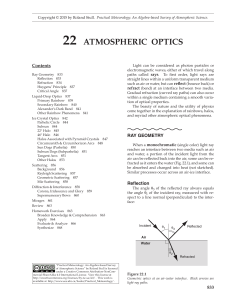
Atmospheric Optics
... the circle, and are the brightest and most easily seen (Fig. 22.7). The viewing angle (θview = angle between two lines: the line from your eye to the rainbow and the line from your eye and the antisolar point) is about 42°. Secondary rainbows have red on the inside at viewing angle of about 50°. Sup ...
... the circle, and are the brightest and most easily seen (Fig. 22.7). The viewing angle (θview = angle between two lines: the line from your eye to the rainbow and the line from your eye and the antisolar point) is about 42°. Secondary rainbows have red on the inside at viewing angle of about 50°. Sup ...
WAVE PLATES
... mirrors. There is no change in the polarization state of the reflection if the beam is incident normally on the mirrors, or if the plane of polarization lies in or normal to the plane of incidence. However, if the polarization direction makes some angle with the plane of incidence, then the reflecti ...
... mirrors. There is no change in the polarization state of the reflection if the beam is incident normally on the mirrors, or if the plane of polarization lies in or normal to the plane of incidence. However, if the polarization direction makes some angle with the plane of incidence, then the reflecti ...
System for measuring the angular response of radiometers
... properly aligned. The first case can be dismissed by making measurements at other azimuth angles. Figure 4(A, B, C) shows the angular response of three quantum radiometers : two radiometers for global radiation measurements from 400 to 1100 nm (K&Z and LI-COR) and one PAR sensor for measuring photos ...
... properly aligned. The first case can be dismissed by making measurements at other azimuth angles. Figure 4(A, B, C) shows the angular response of three quantum radiometers : two radiometers for global radiation measurements from 400 to 1100 nm (K&Z and LI-COR) and one PAR sensor for measuring photos ...
Computer-generated holograms for three
... strength11 are calculated by methods based on wave optics. The major advantage of wave-oriented methods is that they can use a fast Fourier transform (FFT) for numerical calculations. Therefore the computation time is shorter than for point source methods, especially in full parallax holograms. Howe ...
... strength11 are calculated by methods based on wave optics. The major advantage of wave-oriented methods is that they can use a fast Fourier transform (FFT) for numerical calculations. Therefore the computation time is shorter than for point source methods, especially in full parallax holograms. Howe ...
تحليل التوليد الفائق المســـــــتمر في الياف البلورة
... certain side, but that could change shape of the curve shows more than values of 0 . All other subfigure in Fig.(3) represent 's as functions of . The 2 may be equal to zero depending on d value, this means that 0 of the fiber used will vary from case to case, where the case D 0 happen at ...
... certain side, but that could change shape of the curve shows more than values of 0 . All other subfigure in Fig.(3) represent 's as functions of . The 2 may be equal to zero depending on d value, this means that 0 of the fiber used will vary from case to case, where the case D 0 happen at ...
PDF
... In order to demonstrate the quantitative capability of this instrument, we first image 1 micron diameter polystyrene beads immersed in water. Throughout our measurements, we used a 40X (0.75 NA) microscope objective. The images in Fig. 2 were obtained using a gray scale CCD (Zeiss Axiocam MRm). The ...
... In order to demonstrate the quantitative capability of this instrument, we first image 1 micron diameter polystyrene beads immersed in water. Throughout our measurements, we used a 40X (0.75 NA) microscope objective. The images in Fig. 2 were obtained using a gray scale CCD (Zeiss Axiocam MRm). The ...
PDF
... telescope optical tolerances as the bright light from the star never enters the telescope. In order to image an extrasolar planet, the occulter must be designed to account for diffraction so that the overall imaging system achieves a contrast (the ratio between the intensity of the bright object to t ...
... telescope optical tolerances as the bright light from the star never enters the telescope. In order to image an extrasolar planet, the occulter must be designed to account for diffraction so that the overall imaging system achieves a contrast (the ratio between the intensity of the bright object to t ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.