Somatic and Special Senses
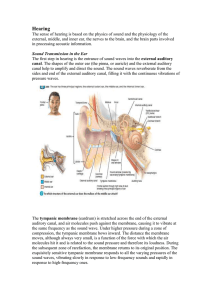
... – Connects each middle ear to the throat – Conducts air between the tympanic cavity and the outside of the body by way of the throat – Auditory tube helps maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum, which is necessary for normal hearing – Ex. Rapid changes in altitude may push eardrum ...
... – Connects each middle ear to the throat – Conducts air between the tympanic cavity and the outside of the body by way of the throat – Auditory tube helps maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum, which is necessary for normal hearing – Ex. Rapid changes in altitude may push eardrum ...
Nolte Chapter 22: Cerebral Cortex
... Broca’s area is in the opercular and triangular parts of the IFG. Wernicke’s is in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus. Together Broca’s and Wernicke’s are the perisylvian language zone. Inability to use language is known as aphasia. Broca’s aphasics can produce few words and tend to l ...
... Broca’s area is in the opercular and triangular parts of the IFG. Wernicke’s is in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus. Together Broca’s and Wernicke’s are the perisylvian language zone. Inability to use language is known as aphasia. Broca’s aphasics can produce few words and tend to l ...
Pitch - Auditory Neuroscience
... The observed orientation of their periodotopic map (mediodorsal to latero-ventral for high to low) appears to differ from that described by Schreiner & Langner (1988) in the cat (predimonantly caudal to ...
... The observed orientation of their periodotopic map (mediodorsal to latero-ventral for high to low) appears to differ from that described by Schreiner & Langner (1988) in the cat (predimonantly caudal to ...
The Somatic Senses - Appoquinimink High School
... Middle ear – includes tympanic cavity, eardrum, and auditory ossicles (three small bones) ...
... Middle ear – includes tympanic cavity, eardrum, and auditory ossicles (three small bones) ...
PDF
... dopaminergic neurons attach value to advance information signals just as they do to cues predicting reward9. That is, these neurons transiently increase their firing to the appearance of both types of cues. Here they found that this is also true for a subpopulation of neurons in the lateral habenula ...
... dopaminergic neurons attach value to advance information signals just as they do to cues predicting reward9. That is, these neurons transiently increase their firing to the appearance of both types of cues. Here they found that this is also true for a subpopulation of neurons in the lateral habenula ...
Assessment of the Ears
... • Inspection & palpation of external ear • Otoscopic exam including ear canal and tympanic membrane • Testing hearing acuity ...
... • Inspection & palpation of external ear • Otoscopic exam including ear canal and tympanic membrane • Testing hearing acuity ...
Final answers - Center for Neural Science
... The firing rates are more rapid when the signal is higher frequency (2 pts) and are phase locked to the signal (2 pts). 5) Michael Posner, a famous cognitive neuroscientist, was once asked what is the main difference between human brains and other primate (e.g., chimps) brains that has allowed human ...
... The firing rates are more rapid when the signal is higher frequency (2 pts) and are phase locked to the signal (2 pts). 5) Michael Posner, a famous cognitive neuroscientist, was once asked what is the main difference between human brains and other primate (e.g., chimps) brains that has allowed human ...
Discriminative Auditory Fear Learning Requires Both Tuned
... • Authors hypothesized that if the cortical pathway is engaged in auditory discrimination, it is probably via lemniscal projections from the MGv (indirect pathway), whereas MGm (direct nonlemniscal pathway) should not be required. • To test their hypothesis they assessed the effect of MGv or MGm bil ...
... • Authors hypothesized that if the cortical pathway is engaged in auditory discrimination, it is probably via lemniscal projections from the MGv (indirect pathway), whereas MGm (direct nonlemniscal pathway) should not be required. • To test their hypothesis they assessed the effect of MGv or MGm bil ...
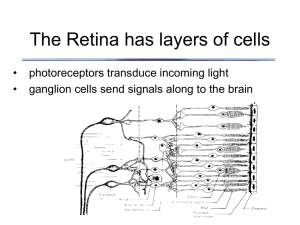
(一)Functional Anatomy of the Retina
... The membrane of the receptor region is, however, electrically inexcitable; it contains no voltage-gated ionic channels and does not generate spikes. If the receptor region generated action potentials, the graded nature of the generator potential would be destroyed because as soon as the generator p ...
... The membrane of the receptor region is, however, electrically inexcitable; it contains no voltage-gated ionic channels and does not generate spikes. If the receptor region generated action potentials, the graded nature of the generator potential would be destroyed because as soon as the generator p ...
Visual Processing - West Virginia University
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
Smell and Taste
... • Minor Senses - Really? • Chemical Senses • Smell and Taste very closely related to each other ...
... • Minor Senses - Really? • Chemical Senses • Smell and Taste very closely related to each other ...
How are axons guided to their targets?
... • Chemoaffinity Hypothesis – the specificity of wiring is based on recognition of chemical cues • Axons reach their targets in a series of discrete steps • Different cells respond to the same guidance cues in different ways • Chemical cues exist at many points along the axon guidance pathway e.g the ...
... • Chemoaffinity Hypothesis – the specificity of wiring is based on recognition of chemical cues • Axons reach their targets in a series of discrete steps • Different cells respond to the same guidance cues in different ways • Chemical cues exist at many points along the axon guidance pathway e.g the ...
1 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm
... 1.C.b. Next, the doctor checked whether the patient could feel pain at each part of the body. Does the patient have difficulty sensing pain? If so, state which part of the body has the defect and describe the relevant pathway. Yes, the right leg has the defect because of damage to the left anterolat ...
... 1.C.b. Next, the doctor checked whether the patient could feel pain at each part of the body. Does the patient have difficulty sensing pain? If so, state which part of the body has the defect and describe the relevant pathway. Yes, the right leg has the defect because of damage to the left anterolat ...
Unit 3 Summary
... The autonomic nervous system involves the network of neurons connecting the CNS with the internal muscles, organs and glands of the body (p79). Autonomous, independent and automatic, the ANS functions independently of the brain to keep vital organs in our bodies functioning (heart, stomach, kidneys, ...
... The autonomic nervous system involves the network of neurons connecting the CNS with the internal muscles, organs and glands of the body (p79). Autonomous, independent and automatic, the ANS functions independently of the brain to keep vital organs in our bodies functioning (heart, stomach, kidneys, ...
Auditory (Cochlear) System
... auditory radiation or gyri of Heschl cause bilateral hearing loses that are more prominent on the ear opposite the lesion ...
... auditory radiation or gyri of Heschl cause bilateral hearing loses that are more prominent on the ear opposite the lesion ...
hair cells
... The pressure applied to the cochlear fluid is about 22 times the pressure felt at the eardrum. This pressure amplification is enough to pass the sound information on to the inner ear, where it is translated into nerve impulses the brain can understand. ...
... The pressure applied to the cochlear fluid is about 22 times the pressure felt at the eardrum. This pressure amplification is enough to pass the sound information on to the inner ear, where it is translated into nerve impulses the brain can understand. ...
Lecture in Linköping 23/9 Music, the Brain and Multimodal
... Picture 4. Proportion of body representation in the brain. Picture 5. Listening to the same music leads to differing perceptions depending of the differences in sensory equipment and perception. Picture 6. The cerebellum contains body maps important for sequential movements. Other parts of the brai ...
... Picture 4. Proportion of body representation in the brain. Picture 5. Listening to the same music leads to differing perceptions depending of the differences in sensory equipment and perception. Picture 6. The cerebellum contains body maps important for sequential movements. Other parts of the brai ...
Sensation and Perception Unit IV
... • When you see the color red, it is not particles of the color red but pulses of electromagnetic energy that your visual system perceives as red • The whole spectrum of electromagnetic energy ranges from short gamma waves to long waves • Different animals are more sensitive to different parts of the ...
... • When you see the color red, it is not particles of the color red but pulses of electromagnetic energy that your visual system perceives as red • The whole spectrum of electromagnetic energy ranges from short gamma waves to long waves • Different animals are more sensitive to different parts of the ...
sensation - Warren County Schools
... ACCESSORY STRUCTURES modify/change environmental energy before “detected” by the sensory system itself (ex. the outer ear is an accessory structure that collects sound). ...
... ACCESSORY STRUCTURES modify/change environmental energy before “detected” by the sensory system itself (ex. the outer ear is an accessory structure that collects sound). ...
Psychology Lecture 02 - Biological Basis
... Cerebral Cortex divided into lobes, or regions of the brain ◦ Each lobe is (roughly) responsible for different higher-level functions, but remember that they do not work merely in isolation. ...
... Cerebral Cortex divided into lobes, or regions of the brain ◦ Each lobe is (roughly) responsible for different higher-level functions, but remember that they do not work merely in isolation. ...
Lect.14 - ALTERATIONS IN SENSORIMOTOR FUNCTION
... with a hearing aid, sufficient to enable successful processing of linguistic information through audition ...
... with a hearing aid, sufficient to enable successful processing of linguistic information through audition ...
October 25
... Taste buds (taste receptor neurons) line papillae found in different areas of the tongue. ...
... Taste buds (taste receptor neurons) line papillae found in different areas of the tongue. ...
Ear
... The specialized sense organs for taste are the 10,000 or so taste buds that are found primarily on the tongue. The receptor cells are arranged in the taste buds like the segments of an orange. A long narrow process on the upper surface of each receptor cell extends into a small pore at the surface o ...
... The specialized sense organs for taste are the 10,000 or so taste buds that are found primarily on the tongue. The receptor cells are arranged in the taste buds like the segments of an orange. A long narrow process on the upper surface of each receptor cell extends into a small pore at the surface o ...