Neural Coding and Auditory Perception
... present in the VAS stimuli, low-CF cells maintain better directional sensitivity in reverberation than high-CF cells. Using recordings from primary auditory neurons, we show that this result can be attributed to the fact that reverberation degrades the directional information in envelope ITDs more s ...
... present in the VAS stimuli, low-CF cells maintain better directional sensitivity in reverberation than high-CF cells. Using recordings from primary auditory neurons, we show that this result can be attributed to the fact that reverberation degrades the directional information in envelope ITDs more s ...
03/14 PPT
... in olfactory bulb. The glomeruli serve as modules, and are selectively sensitive to particular odors ...
... in olfactory bulb. The glomeruli serve as modules, and are selectively sensitive to particular odors ...
Ch 15 Chemical Senses
... Figure 15.6 Recognition profiles for some odorants. Large dots indicate that the odorant causes a high firing rate for the receptor listed along the top; small dots indicate lower firing rates for the receptor. The structures of the compounds are shown on the right. (Adapted from Malnic et al., 199 ...
... Figure 15.6 Recognition profiles for some odorants. Large dots indicate that the odorant causes a high firing rate for the receptor listed along the top; small dots indicate lower firing rates for the receptor. The structures of the compounds are shown on the right. (Adapted from Malnic et al., 199 ...
Circuits, Circuits
... a) it fired/depolarized, and b) significant event (STOP) signalled. After learning, S will only fire when B & D are active (i.e. after a time interval of duration = t1). Details are unclear as to whether A & C develop inhibitory links to S. In future (e.g. when repeating the dance), the instructor s ...
... a) it fired/depolarized, and b) significant event (STOP) signalled. After learning, S will only fire when B & D are active (i.e. after a time interval of duration = t1). Details are unclear as to whether A & C develop inhibitory links to S. In future (e.g. when repeating the dance), the instructor s ...
chapt10answers
... _visceral____ pain receptors are the only receptors in the organs that produce sensations. __referred____ pain occurs because of the common nerve pathways leading from skin and internal organs. An example would be a heart attack being felt as pain in the arm or as heartburn. What is the difference b ...
... _visceral____ pain receptors are the only receptors in the organs that produce sensations. __referred____ pain occurs because of the common nerve pathways leading from skin and internal organs. An example would be a heart attack being felt as pain in the arm or as heartburn. What is the difference b ...
ecture 23- special senses
... Odorants are small organic molecules. The strongest smells are associated with molecules of high solubility both in water and lipids. ...
... Odorants are small organic molecules. The strongest smells are associated with molecules of high solubility both in water and lipids. ...
Visual pathways pathology
... develop in infancy; ref. them kittens who were kept in the dark from birth and went blind despite having healthy eyes. ...
... develop in infancy; ref. them kittens who were kept in the dark from birth and went blind despite having healthy eyes. ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... motion and are linked to the vestibular nerve. Liquid-filled structure that links the semi-circular canals to the cochlea. Plays a role in balancing the body when not in motion and is also linked to the vestibular nerve. Liquid-filled structure whose walls are covered with auditory neurons and are l ...
... motion and are linked to the vestibular nerve. Liquid-filled structure that links the semi-circular canals to the cochlea. Plays a role in balancing the body when not in motion and is also linked to the vestibular nerve. Liquid-filled structure whose walls are covered with auditory neurons and are l ...
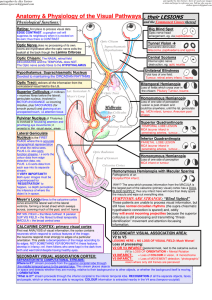
Visual Field and the Human Visual System
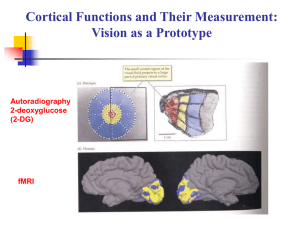
... Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
... Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
The Special Senses
... Achieved by both eyes viewing the same image from slightly different angles Three-dimensional vision results from cortical fusion of the slightly different images If only one eye is used, depth perception is lost and the observer must rely on learned clues to determine depth ...
... Achieved by both eyes viewing the same image from slightly different angles Three-dimensional vision results from cortical fusion of the slightly different images If only one eye is used, depth perception is lost and the observer must rely on learned clues to determine depth ...
Perception - U
... medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus; and from there, fibers ascend to the primary cortex in the lateral fissure • The projections from each ear are bilateral ...
... medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus; and from there, fibers ascend to the primary cortex in the lateral fissure • The projections from each ear are bilateral ...
Mirror neurons: A sensorimotor representation system
... lead to different results. Interestingly, it is the saccade mode which leads to the illusion, while the fixation mode results in the correct perception. Scanning through the known geometrical illusions, quite a number of them were found to disappear with stationary fixation (Fischer et al. 2001b). I ...
... lead to different results. Interestingly, it is the saccade mode which leads to the illusion, while the fixation mode results in the correct perception. Scanning through the known geometrical illusions, quite a number of them were found to disappear with stationary fixation (Fischer et al. 2001b). I ...
Neurophysiological Aspects of Song Pattern Recognition and Sound
... responses. However, for pattern recognition as well as for coding of directional information, it seems necessary for the animal to evaluate a whole set of parallel receptor fibres to achieve the precision observed in behavior. The information of receptors converges onto thoracic neurons which drive ...
... responses. However, for pattern recognition as well as for coding of directional information, it seems necessary for the animal to evaluate a whole set of parallel receptor fibres to achieve the precision observed in behavior. The information of receptors converges onto thoracic neurons which drive ...
commissural axons
... interconnect the two sides of the central nervous system and ensure coordination and integration of motor and sensory commands. A crucial step in their navigation is the crossing of the midline dividing the nervous system, which is controlled by multiple axon guidance cues. In the spinal cord, the c ...
... interconnect the two sides of the central nervous system and ensure coordination and integration of motor and sensory commands. A crucial step in their navigation is the crossing of the midline dividing the nervous system, which is controlled by multiple axon guidance cues. In the spinal cord, the c ...
Olfactory Physiology - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... changed by 30% before difference can be detected; vs. ≈ 1% in visual discrimination). determination of DIRECTION from which smell comes: 1) slight difference in time of molecule arrival in two nostrils. 2) head turning single olfactory receptors (vs. olfactory mucous membrane as whole) have rela ...
... changed by 30% before difference can be detected; vs. ≈ 1% in visual discrimination). determination of DIRECTION from which smell comes: 1) slight difference in time of molecule arrival in two nostrils. 2) head turning single olfactory receptors (vs. olfactory mucous membrane as whole) have rela ...
The Special Senses Throughout Life
... • Located in the solitary nucleus • Impulses are transmitted to the thalamus and ultimately to the gustatory area of the cerebral cortex in the insula ...
... • Located in the solitary nucleus • Impulses are transmitted to the thalamus and ultimately to the gustatory area of the cerebral cortex in the insula ...
Lecture 18: Sensation
... 1. External ear A. Sound waves are “caught” by the pinna, travel through the ear canal, and run into the tympanic membrane and VIBRATE the membrane. 2. Middle ear: A. Middle ear bones (malleus, incus, stapes) are attached at one end to the tympanic membrane and at the other end to the oval windo ...
... 1. External ear A. Sound waves are “caught” by the pinna, travel through the ear canal, and run into the tympanic membrane and VIBRATE the membrane. 2. Middle ear: A. Middle ear bones (malleus, incus, stapes) are attached at one end to the tympanic membrane and at the other end to the oval windo ...
Slide
... those glomeruli had similar locations in six different bulbs. distinct odor perceptions ...
... those glomeruli had similar locations in six different bulbs. distinct odor perceptions ...
The neural mechanisms of top- down attentional control
... analysis13,14 allowed us to combine the spatial resolution necessary for localization of neural activity, which this technique provides, with neuroimaging methods that selectively extract components of hemodynamic activity15 correlated with distinct aspects of complex-task performance. Here we used ...
... analysis13,14 allowed us to combine the spatial resolution necessary for localization of neural activity, which this technique provides, with neuroimaging methods that selectively extract components of hemodynamic activity15 correlated with distinct aspects of complex-task performance. Here we used ...
Assignment 8
... 39. Gustatory nerve impulses travel to the medulla oblongata and then to the hypothalamus and amygdala to activate what autonomic reflexes? What part of the brain relays gustatory nerve impulses to the cerebral cortex? 40. Describe the sensory receptor for smell. ...
... 39. Gustatory nerve impulses travel to the medulla oblongata and then to the hypothalamus and amygdala to activate what autonomic reflexes? What part of the brain relays gustatory nerve impulses to the cerebral cortex? 40. Describe the sensory receptor for smell. ...
Chapter 9 Senses - msubillings.edu
... radiations) in the lateral geniculate nucleus – some separate out, extending off the optic tracts, to terminate in the superior colliculi (center for visual reflexes of the extrinsic eye muscles) and pretectal nuclei (involved in photopupillary and accommodation reflexes) located in the midbrain e. ...
... radiations) in the lateral geniculate nucleus – some separate out, extending off the optic tracts, to terminate in the superior colliculi (center for visual reflexes of the extrinsic eye muscles) and pretectal nuclei (involved in photopupillary and accommodation reflexes) located in the midbrain e. ...
chemical senses - (canvas.brown.edu).
... I. TRUE or FALSE. Circle the appropriate letter. T F 1. Gustatory receptors are neurons. T F 2. The vagus nerve conveys gustatory signals originating from the oropharynx and upper esophogus. T F 3. The thalamic terminations of the ascending taste pathways lie in the ventral nuclear group, near the t ...
... I. TRUE or FALSE. Circle the appropriate letter. T F 1. Gustatory receptors are neurons. T F 2. The vagus nerve conveys gustatory signals originating from the oropharynx and upper esophogus. T F 3. The thalamic terminations of the ascending taste pathways lie in the ventral nuclear group, near the t ...
Auditory Hallucinations as a Separate Entitity
... auditory space processing pathways can be differentiated based on the nature of the task. More specifically, it is proposed that the forebrain pathway primarily participates in voluntary shifts of gaze, such as those that require access to memory stores and that the midbrain pathway participates in ...
... auditory space processing pathways can be differentiated based on the nature of the task. More specifically, it is proposed that the forebrain pathway primarily participates in voluntary shifts of gaze, such as those that require access to memory stores and that the midbrain pathway participates in ...