LTC3541-1
... The LTC3541-1 contains a high efficiency synchronous buck converter, a very low dropout regulator (VLDO) and a linear regulator. It can be used to provide up to two output voltages from a single input voltage making the LTC3541-1 ideal for applications with limited board space. The combination and c ...
... The LTC3541-1 contains a high efficiency synchronous buck converter, a very low dropout regulator (VLDO) and a linear regulator. It can be used to provide up to two output voltages from a single input voltage making the LTC3541-1 ideal for applications with limited board space. The combination and c ...
Note to EE 312 Students
... sheets for the 1N4004 silicon diode were consulted. The 1N4004 data sheets gave values for the forward recovery time in the 150 to 250 ns range. These times are sufficiently short so that the 1N4004 silicon diode can be switched on and off at a rate up to 100 kHz. To achieve 150 to 250 ns recovery t ...
... sheets for the 1N4004 silicon diode were consulted. The 1N4004 data sheets gave values for the forward recovery time in the 150 to 250 ns range. These times are sufficiently short so that the 1N4004 silicon diode can be switched on and off at a rate up to 100 kHz. To achieve 150 to 250 ns recovery t ...
MAX12559 Dual, 96Msps, 14-Bit, IF/Baseband ADC General Description Features
... The MAX12559 supports either a single-ended or differential input clock. User-selectable divide-by-two (DIV2) and divide-by-four (DIV4) modes allow for design flexibility and help to reduce the negative effects of clock jitter. Wide variations in the clock duty cycle are compensated with the ADC’s i ...
... The MAX12559 supports either a single-ended or differential input clock. User-selectable divide-by-two (DIV2) and divide-by-four (DIV4) modes allow for design flexibility and help to reduce the negative effects of clock jitter. Wide variations in the clock duty cycle are compensated with the ADC’s i ...
HEF4046B 1. General description Phase-locked loop
... amplifier and a common comparator input. A 7 V regulator (Zener) diode is provided for supply voltage regulation if necessary. For a functional description see Section 6. It operates over a recommended VDD power supply range of 3 V to 15 V referenced to VSS (usually ground). Unused inputs must be co ...
... amplifier and a common comparator input. A 7 V regulator (Zener) diode is provided for supply voltage regulation if necessary. For a functional description see Section 6. It operates over a recommended VDD power supply range of 3 V to 15 V referenced to VSS (usually ground). Unused inputs must be co ...
ADP1740 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... regulators that operate from 1.6 V to 3.6 V and provide up to 2 A of output current. These low VIN/VOUT LDOs are ideal for regulation of nanometer FPGA geometries operating from 2.5 V down to 1.8 V I/O rails, and for powering core voltages down to 0.75 V. Using an advanced, proprietary architecture, ...
... regulators that operate from 1.6 V to 3.6 V and provide up to 2 A of output current. These low VIN/VOUT LDOs are ideal for regulation of nanometer FPGA geometries operating from 2.5 V down to 1.8 V I/O rails, and for powering core voltages down to 0.75 V. Using an advanced, proprietary architecture, ...
Sample Assessment Materials
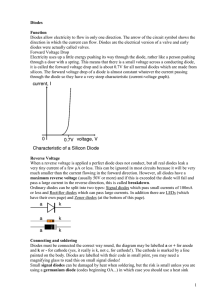
... A basic circuit diagram or a description of a suitable circuit is provided for obtaining the results required– possibly missing a method of varying the voltage / current. There is a plan to collect I – V measurements with an attempt to describe which graph to plot to show the characteristic curve. T ...
... A basic circuit diagram or a description of a suitable circuit is provided for obtaining the results required– possibly missing a method of varying the voltage / current. There is a plan to collect I – V measurements with an attempt to describe which graph to plot to show the characteristic curve. T ...
A functional model of silicon carbide JFET and its
... nanoseconds. Therefore, the time constant of Vg in Figure 1(c) is actually less than that of Vs, which makes the gate switch on/off current not significantly increased when R decreases. However, when R < 1 Ω, a small variation of the gate signal can cause large impact on gate current. This means tha ...
... nanoseconds. Therefore, the time constant of Vg in Figure 1(c) is actually less than that of Vs, which makes the gate switch on/off current not significantly increased when R decreases. However, when R < 1 Ω, a small variation of the gate signal can cause large impact on gate current. This means tha ...
11.3 Gbps, Active Back-Termination, Differential Laser Diode Driver ADN2531
... The DATAP and DATAN pins are terminated internally with a 100 Ω differential termination resistor. This minimizes signal reflections at the input that could otherwise lead to degradation in the output eye diagram. It is not recommended to drive the ADN2531 with single-ended data signal sources. The ...
... The DATAP and DATAN pins are terminated internally with a 100 Ω differential termination resistor. This minimizes signal reflections at the input that could otherwise lead to degradation in the output eye diagram. It is not recommended to drive the ADN2531 with single-ended data signal sources. The ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.