R09 SET-1 Code No: R09221902
... Explain how the deficiencies of weighted resister type DAC can be overcome through an R-2R ladder type network. Explain the conversion procedure in R-2R ladder type DAC. Define the terms ‘Resolution’, ‘Conversion time’ and ‘Linearity’ of an Analog to Digital converter. What is the resolution of a 11 ...
... Explain how the deficiencies of weighted resister type DAC can be overcome through an R-2R ladder type network. Explain the conversion procedure in R-2R ladder type DAC. Define the terms ‘Resolution’, ‘Conversion time’ and ‘Linearity’ of an Analog to Digital converter. What is the resolution of a 11 ...
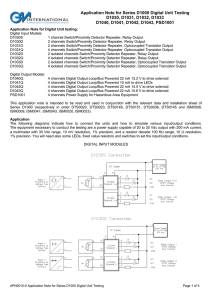
Analog Input / Output Modules
... variety of sensors and actuators can be connected using standard current (0 to 20 mA and 4 to 20 mA) and voltage range (±10 V to 100 mV) signal types. A 16-bit resolution also enables measurements from signals that do not make full use of the measuring range (e.g. 0 to 5 V) at sufficiently higher re ...
... variety of sensors and actuators can be connected using standard current (0 to 20 mA and 4 to 20 mA) and voltage range (±10 V to 100 mV) signal types. A 16-bit resolution also enables measurements from signals that do not make full use of the measuring range (e.g. 0 to 5 V) at sufficiently higher re ...
Series vs. Parallel Circuits
... • Working with your partner at your desk and your knowledge of circuits, make the lightbulb light up. ...
... • Working with your partner at your desk and your knowledge of circuits, make the lightbulb light up. ...
Download the Quiz
... What reading on the plate current meter of a vacuum tube RF power amplifier indicates correct adjustment of the plate tuning control? A. A pronounced peak B. A pronounced dip C. No change will be observed D. A slow, rhythmic oscillation G4A05 (C) p.231 What is a reason to use Automatic Level Control ...
... What reading on the plate current meter of a vacuum tube RF power amplifier indicates correct adjustment of the plate tuning control? A. A pronounced peak B. A pronounced dip C. No change will be observed D. A slow, rhythmic oscillation G4A05 (C) p.231 What is a reason to use Automatic Level Control ...
Chapter 4 Exercises and Answers
... What are the three terminals in a transistor and how do they operate? The source is an electric signal. The base value regulates a gate that determines whether the connection between the source and the ground (emitter) is made. An output line is usually connected to the source. If the base value is ...
... What are the three terminals in a transistor and how do they operate? The source is an electric signal. The base value regulates a gate that determines whether the connection between the source and the ground (emitter) is made. An output line is usually connected to the source. If the base value is ...
BITX40 with Raduino - tips and mods
... First off we have to move the BFO down in frequency by a khz or so, such that it is in the crystal filter passband. I assume the boards out now don't have C103 stuffed. So install a small variable cap at C103, likely needs well under 100pf, Set it for minimum capacitance, then tune in a CW station. ...
... First off we have to move the BFO down in frequency by a khz or so, such that it is in the crystal filter passband. I assume the boards out now don't have C103 stuffed. So install a small variable cap at C103, likely needs well under 100pf, Set it for minimum capacitance, then tune in a CW station. ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.