擬平行搜尋法之雙向關連性記憶體
... Functional devices and circuits based on negative differential resistance (NDR) devices have generated substantial research interest owing to their unique NDR characteristic [1]-[2]. Taking advantage of the NDR feature, circuit complexity can be greatly reduced and novel circuit applications have al ...
... Functional devices and circuits based on negative differential resistance (NDR) devices have generated substantial research interest owing to their unique NDR characteristic [1]-[2]. Taking advantage of the NDR feature, circuit complexity can be greatly reduced and novel circuit applications have al ...
ECE1250F14_HW2_2p1soln
... Any network consisting of only resistors between two terminals may be replaced by a single equivalent resistor. ...
... Any network consisting of only resistors between two terminals may be replaced by a single equivalent resistor. ...
84` IIB
... The circuit in Figure 8 shows an NPN silicon transistor and two resistors connected to a 6 V d.c. power supply. The current gain of the transistor is 100. (i) ...
... The circuit in Figure 8 shows an NPN silicon transistor and two resistors connected to a 6 V d.c. power supply. The current gain of the transistor is 100. (i) ...
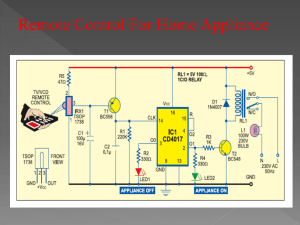
circuit description
... connects R646 to ground and brings the soft clip control voltages down to a much lower level than with SW202/R633. This level is set so that the amplifier's output cannot swing far enough positive or negative for the EDP circuits to turn on and connect the outputs to the high voltage supplies. Thus ...
... connects R646 to ground and brings the soft clip control voltages down to a much lower level than with SW202/R633. This level is set so that the amplifier's output cannot swing far enough positive or negative for the EDP circuits to turn on and connect the outputs to the high voltage supplies. Thus ...
BCR405U
... The advantages towards discrete solutions are: • lower assembly cost • smaller form factor • better quality due to less soldering points • higher output current accuracy due to pretested LED drivers Dimming is possible by using an external digital transistor at the ground pin. The BCR405U can be ope ...
... The advantages towards discrete solutions are: • lower assembly cost • smaller form factor • better quality due to less soldering points • higher output current accuracy due to pretested LED drivers Dimming is possible by using an external digital transistor at the ground pin. The BCR405U can be ope ...
Bds96 - Instituto de Ingeniería Eléctrica
... 2.a For the input differential pairs a higher value of gm/ID will give, on one hand, higher gm (and hence speed) for a given ID, higher gain, lower gate-source, saturation and offset voltages; on the other hand a higher gm/ID requires lower values of ID/(W/L) and therefore bigger transistors and par ...
... 2.a For the input differential pairs a higher value of gm/ID will give, on one hand, higher gm (and hence speed) for a given ID, higher gain, lower gate-source, saturation and offset voltages; on the other hand a higher gm/ID requires lower values of ID/(W/L) and therefore bigger transistors and par ...
Capacitor Self-Resonance
... operational amplifiers. In fact, that’s where the name “op-amp” came from: the ability of a highgain differential amplifier circuit to perform the mathematical operations of adding, subtracting, integrating and differentiating. With a bit of clever circuit design, multiplication and division can als ...
... operational amplifiers. In fact, that’s where the name “op-amp” came from: the ability of a highgain differential amplifier circuit to perform the mathematical operations of adding, subtracting, integrating and differentiating. With a bit of clever circuit design, multiplication and division can als ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.