Series and Parallel Resistive Circuits
... A loop is a closed path through a circuit which does not meet the same node more than once. Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) describes the principle for voltage in a loop. The algebraic sum of the voltages around any loop in a circuit is identically zero at any time. ...
... A loop is a closed path through a circuit which does not meet the same node more than once. Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) describes the principle for voltage in a loop. The algebraic sum of the voltages around any loop in a circuit is identically zero at any time. ...
Introduction - facstaff.bucknell.edu
... As we have seen, it can be difficult to solve circuit problems using the diode equation because of its nonlinear form. The piecewise linear (PWL) model of the diode has therefore been developed to approximate the i-v characteristic. Its circuit representation consists of linear circuit elements, spe ...
... As we have seen, it can be difficult to solve circuit problems using the diode equation because of its nonlinear form. The piecewise linear (PWL) model of the diode has therefore been developed to approximate the i-v characteristic. Its circuit representation consists of linear circuit elements, spe ...
High Performance AUDIO OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS FEATURES DESCRIPTION
... provide superior sound quality and speed for exceptional audio performance. This in combination with high output drive capability and excellent dc performance allows use in a wide variety of demanding applications. In addition, the OPA134’s wide output swing, to within 1V of the rails, allows increa ...
... provide superior sound quality and speed for exceptional audio performance. This in combination with high output drive capability and excellent dc performance allows use in a wide variety of demanding applications. In addition, the OPA134’s wide output swing, to within 1V of the rails, allows increa ...
ET 304b
... The superposition theorem is a technique for solving electric circuits that have more than one source. Nodal and mesh analysis also can find solutions for complex networks that include multiple sources, but require the solution of an entire set of voltages or currents. Another limitation of these me ...
... The superposition theorem is a technique for solving electric circuits that have more than one source. Nodal and mesh analysis also can find solutions for complex networks that include multiple sources, but require the solution of an entire set of voltages or currents. Another limitation of these me ...
Application Note No. 066
... For some LED applications, including fixed or “architectural” displays, voltages greater than the 18 V maximum rating (pin 3) of the BCR402R may be encountered. For example +24 V is frequently used in so-called architectural display. This section describes the advantages of using BCR402R in such sys ...
... For some LED applications, including fixed or “architectural” displays, voltages greater than the 18 V maximum rating (pin 3) of the BCR402R may be encountered. For example +24 V is frequently used in so-called architectural display. This section describes the advantages of using BCR402R in such sys ...
SN74LVTH32374-EP 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The SN74LVTH32374 is a 32-bit edge-triggered D-type flip-flop designed for low-voltage (3.3-V) VCC operation, but with the capability to provide a TTL interface to a 5-V system environment. This device is particularly suitable for implementing buffer registers, I/O ports, bidirectional bus drivers, ...
... The SN74LVTH32374 is a 32-bit edge-triggered D-type flip-flop designed for low-voltage (3.3-V) VCC operation, but with the capability to provide a TTL interface to a 5-V system environment. This device is particularly suitable for implementing buffer registers, I/O ports, bidirectional bus drivers, ...
HMC728LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
... routes one of the two single-ended inputs to the differential output upon assertion of the proper select port. All differential inputs to the HMC728LC3C are CML and terminated on-chip with 50 Ohms to the positive supply, GND, and may be DC or AC coupled. The differential CMl outputs are source termi ...
... routes one of the two single-ended inputs to the differential output upon assertion of the proper select port. All differential inputs to the HMC728LC3C are CML and terminated on-chip with 50 Ohms to the positive supply, GND, and may be DC or AC coupled. The differential CMl outputs are source termi ...
78Q8392L/A03 Low Power Ethernet Coaxial Transceiver
... off, the capacitance of the transmit driver is isolated from the transmission media by an external diode with a low capacitance node. The shield of the transmission media serves as the ground return for the transmitter function. A transmit squelch circuit, which consists of a pulse threshold detecto ...
... off, the capacitance of the transmit driver is isolated from the transmission media by an external diode with a low capacitance node. The shield of the transmission media serves as the ground return for the transmitter function. A transmit squelch circuit, which consists of a pulse threshold detecto ...
MAX14840E/MAX14841E 40Mbps, +3.3V, RS
... Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a four-layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maximintegrated.com/thermal-tutorial. Note 2: Operation is specified with junction temper ...
... Note 1: Package thermal resistances were obtained using the method described in JEDEC specification JESD51-7, using a four-layer board. For detailed information on package thermal considerations, refer to www.maximintegrated.com/thermal-tutorial. Note 2: Operation is specified with junction temper ...
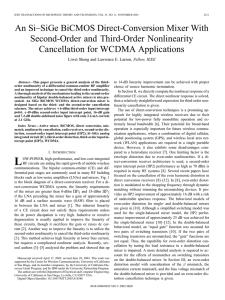
An Si–SiGe BiCMOS Direct-Conversion Mixer With Second-Order and Third-Order Nonlinearity
... is the impedance from ground to the connecting point of the two emitters. To simplify the analysis, the following assumptions were made, similar to that in [3]. The collector current is only a function of the base–emitter voltage. The Early effect is ignored because the transistor output resistance ...
... is the impedance from ground to the connecting point of the two emitters. To simplify the analysis, the following assumptions were made, similar to that in [3]. The collector current is only a function of the base–emitter voltage. The Early effect is ignored because the transistor output resistance ...
PIN and APD Photodiode characteristics
... Quantum efficiency is defined for photodiodes as the fraction of incident photons having sufficient energy to liberate electrons. The symbol used is R and by definition it is dependent both on wave-length and photodiode material. Responsivity of a photodiode is a practical measure of output current ...
... Quantum efficiency is defined for photodiodes as the fraction of incident photons having sufficient energy to liberate electrons. The symbol used is R and by definition it is dependent both on wave-length and photodiode material. Responsivity of a photodiode is a practical measure of output current ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.