DS1249Y/AB 2048k Nonvolatile SRAM FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT
... 6. If the CE low transition occurs simultaneously with or latter than the WE low transition in Write Cycle 1, the output buffers remain in a high-impedance state during this period. 7. If the CE high transition occurs prior to or simultaneously with the WE high transition, the output buffers remain ...
... 6. If the CE low transition occurs simultaneously with or latter than the WE low transition in Write Cycle 1, the output buffers remain in a high-impedance state during this period. 7. If the CE high transition occurs prior to or simultaneously with the WE high transition, the output buffers remain ...
TPS77101-Q1 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... the PMOS pass element is a voltage-driven device, the quiescent current is low and independent of output loading (typically 92 µA over the full range of output current, 0 mA to 150 mA). These two key specifications yield a significant improvement in operating life for battery-powered systems. The de ...
... the PMOS pass element is a voltage-driven device, the quiescent current is low and independent of output loading (typically 92 µA over the full range of output current, 0 mA to 150 mA). These two key specifications yield a significant improvement in operating life for battery-powered systems. The de ...
TPA032D03 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... coupling capacitors on the output. Included is a Class-AB headphone amplifier with interface logic to select between the two modes of operation. Only one amplifier is active at any given time, and the other is in power-saving sleep mode. Also, a chip-level shutdown control is provided to limit total ...
... coupling capacitors on the output. Included is a Class-AB headphone amplifier with interface logic to select between the two modes of operation. Only one amplifier is active at any given time, and the other is in power-saving sleep mode. Also, a chip-level shutdown control is provided to limit total ...
Optocoupler Common Mode Transient Immunity (CMTI)
... immunity (CMTI) properties of optocouplers. It covers phototransistor output and optically coupled logic gates. Common mode transient immunity, (CMTI), common mode transient rejection (CMTR), or common mode rejection (CMR), are a measure of ability of an optocoupler’s output amplifier to reject fast ...
... immunity (CMTI) properties of optocouplers. It covers phototransistor output and optically coupled logic gates. Common mode transient immunity, (CMTI), common mode transient rejection (CMTR), or common mode rejection (CMR), are a measure of ability of an optocoupler’s output amplifier to reject fast ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... Figure 1 shows the DC-coupled, gain of +2, dual powersupply circuit configuration used as the basis of the ±5V Electrical Characteristic tables and Typical Characteristic curves. For test purposes, the input impedance is set to 50Ω with a resistor to ground and the output impedance is set to 50Ω wit ...
... Figure 1 shows the DC-coupled, gain of +2, dual powersupply circuit configuration used as the basis of the ±5V Electrical Characteristic tables and Typical Characteristic curves. For test purposes, the input impedance is set to 50Ω with a resistor to ground and the output impedance is set to 50Ω wit ...
KSA115 6 PNP Silicon Transistor Absolute Maximum Ratings
... result in significant injury to the user. ...
... result in significant injury to the user. ...
EE2003 Circuit Theory
... Under balance condition where no current flow between BD, VAD VAB or I1 R1 I 2 R2 and VDC VBC or I 3 R3 I 4 R4 Current in each resistance arm, ...
... Under balance condition where no current flow between BD, VAD VAB or I1 R1 I 2 R2 and VDC VBC or I 3 R3 I 4 R4 Current in each resistance arm, ...
ADP1611 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... To prevent input inrush current at startup, connect a capacitor from SS to GND to set the soft-start period. When the device is in shutdown (SD is at GND) or the input voltage is below the 2.4 V undervoltage lockout voltage, SS is internally shorted to GND to discharge the soft start capacitor. Once ...
... To prevent input inrush current at startup, connect a capacitor from SS to GND to set the soft-start period. When the device is in shutdown (SD is at GND) or the input voltage is below the 2.4 V undervoltage lockout voltage, SS is internally shorted to GND to discharge the soft start capacitor. Once ...
Instructions - Meldrum Academy
... be supplied in the short period of time that the shutter is open. In this time a large amount of light energy must be emitted. This is stored as electrical energy in a capacitor until it is needed. Apparatus: 1.5 µF capacitor, neon lamp, 100 kΩ resistor, 120 d.c. supply, 1 SPST switch 1 push switch ...
... be supplied in the short period of time that the shutter is open. In this time a large amount of light energy must be emitted. This is stored as electrical energy in a capacitor until it is needed. Apparatus: 1.5 µF capacitor, neon lamp, 100 kΩ resistor, 120 d.c. supply, 1 SPST switch 1 push switch ...
Single phase PWM controller
... L6726A is a single-phase PWM controller with embedded high-current drivers that provides complete control logic and protections to realize in an easy and simple way a general DCDC step-down converter. Designed to drive N-channel MOSFETs in a synchronous buck topology, with its high level of integrat ...
... L6726A is a single-phase PWM controller with embedded high-current drivers that provides complete control logic and protections to realize in an easy and simple way a general DCDC step-down converter. Designed to drive N-channel MOSFETs in a synchronous buck topology, with its high level of integrat ...
AD8553 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... low noise, rail-to-rail output and a power-saving shutdown mode. The AD8553 also features low offset voltage and drift coupled with high common-mode rejection. In shutdown mode, the total supply current is reduced to less than 4 μA. The AD8553 is capable of operating from 1.8 V to 5.5 V. With a low ...
... low noise, rail-to-rail output and a power-saving shutdown mode. The AD8553 also features low offset voltage and drift coupled with high common-mode rejection. In shutdown mode, the total supply current is reduced to less than 4 μA. The AD8553 is capable of operating from 1.8 V to 5.5 V. With a low ...
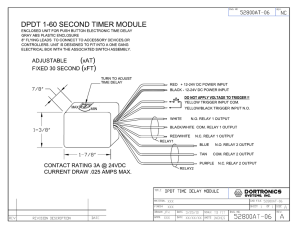
CK series Mid-Priced CMOS IC Time Delay Relay
... Delay on operate – Delay period begins when input voltage is applied. At the end of the delay period, the relay will operate and will not release until input voltage is removed. Reset occurs when input voltage is reapplied. ...
... Delay on operate – Delay period begins when input voltage is applied. At the end of the delay period, the relay will operate and will not release until input voltage is removed. Reset occurs when input voltage is reapplied. ...
CIM800 Contact Input Module Datasheet
... switches, non indicating detectors, etc. The LED illuminates when any input goes into alarm, and can also be programmed to blink when polled by the Tyco MX Control and Indicating Equipment (CIE.). The CIM800 can be configured to supervise: · Two circuits of multiple normally-open contacts; with sho ...
... switches, non indicating detectors, etc. The LED illuminates when any input goes into alarm, and can also be programmed to blink when polled by the Tyco MX Control and Indicating Equipment (CIE.). The CIM800 can be configured to supervise: · Two circuits of multiple normally-open contacts; with sho ...
MAX1121 1.8V, 8-Bit, 250Msps Analog-to-Digital Converter with LVDS Outputs for Wideband Applications
... dynamic performance at high IF frequencies up to 500MHz. The product operates with conversion rates of up to 250Msps while consuming only 477mW. At 250Msps and an input frequency of 100MHz, the MAX1121 achieves a spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of 68dBc. Its excellent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) ...
... dynamic performance at high IF frequencies up to 500MHz. The product operates with conversion rates of up to 250Msps while consuming only 477mW. At 250Msps and an input frequency of 100MHz, the MAX1121 achieves a spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) of 68dBc. Its excellent signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.