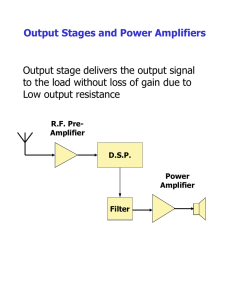
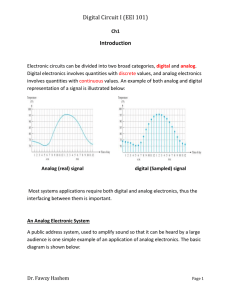
DN142 - Ultralow Quiescent Current DC/DC Converters for Light Load Applications
... The micropower linear regulator shown in Figure 5 delivers a regulated 3.3V output using less than 5µA quiescent current. With such low operating current, a standard 9V alkaline battery can power this regulator for 10 years. Circuit operation is very straightforward. The LTC1440’s internal reference ...
... The micropower linear regulator shown in Figure 5 delivers a regulated 3.3V output using less than 5µA quiescent current. With such low operating current, a standard 9V alkaline battery can power this regulator for 10 years. Circuit operation is very straightforward. The LTC1440’s internal reference ...
STK4142II AF Power Amplifier (Split Power Supply) (25W + 25W min
... Assuming VCC = ±26V, RL = 8Ω, VCC = ±22V, RL = 4Ω, RL = 8Ω : Pd1 = 23.6W at 1/10 Po max. RL = 4Ω : Pd2 = 28.2W at 1/10 Po max. The thermal resistance of a heat sink is obtained from Figure 3. RL = 8Ω : θc-a1 = 3.18°C/W RL = 4Ω : θc-a2 = 2.66°C/W Tj when a heat sink is used is obtained from ...
... Assuming VCC = ±26V, RL = 8Ω, VCC = ±22V, RL = 4Ω, RL = 8Ω : Pd1 = 23.6W at 1/10 Po max. RL = 4Ω : Pd2 = 28.2W at 1/10 Po max. The thermal resistance of a heat sink is obtained from Figure 3. RL = 8Ω : θc-a1 = 3.18°C/W RL = 4Ω : θc-a2 = 2.66°C/W Tj when a heat sink is used is obtained from ...
AD53500 英文数据手册DataSheet 下载
... sequencing and may ultimately cause them to fail, rendering the part nonfunctional. Finally, the AD53500 may appear to function normally for small output steps (less than 3 V or so) if one or both of these caps is absent, but it may exhibit excessive rise or fall times for steps of larger amplitude. ...
... sequencing and may ultimately cause them to fail, rendering the part nonfunctional. Finally, the AD53500 may appear to function normally for small output steps (less than 3 V or so) if one or both of these caps is absent, but it may exhibit excessive rise or fall times for steps of larger amplitude. ...
FST6800 10-Bit Bus Switch with Precharged Outputs FST6 800 1
... The device is organized as a 10-bit switch with a bus enable (OE) signal. When OE is LOW, the switch is ON and Port A is connected to Port B. When OE is HIGH, the switch is OPEN and the B Port is precharged to BiasV through an equivalent 10-kΩ resistor. ...
... The device is organized as a 10-bit switch with a bus enable (OE) signal. When OE is LOW, the switch is ON and Port A is connected to Port B. When OE is HIGH, the switch is OPEN and the B Port is precharged to BiasV through an equivalent 10-kΩ resistor. ...
IC 15030870 rishabh_C12
... measure phase angle difference between two synchronised single phase balanced network having sine wave form. The output signal is proportional load independent DC voltage or current. The transducer is available in AC or DC auxiliary supply and also in self power version. ...
... measure phase angle difference between two synchronised single phase balanced network having sine wave form. The output signal is proportional load independent DC voltage or current. The transducer is available in AC or DC auxiliary supply and also in self power version. ...
EUP3406 1.5MHz, 600mA Synchronous Step-Down Converter
... The EUP3406 is a constant frequency, current mode, PWM step-down converter. The device integrates a main switch and a synchronous rectifier for high efficiency. The 2.5V to 5.5V input voltage range makes the EUP3406 ideal for powering portable equipment that runs from a single cell Lithium-Ion (Li+) ...
... The EUP3406 is a constant frequency, current mode, PWM step-down converter. The device integrates a main switch and a synchronous rectifier for high efficiency. The 2.5V to 5.5V input voltage range makes the EUP3406 ideal for powering portable equipment that runs from a single cell Lithium-Ion (Li+) ...
assignment 03- boolean algebra
... a) Write the Boolean equation for each of the logic circuits shown in Figure 3.1 b) Create the truth table for each circuit ...
... a) Write the Boolean equation for each of the logic circuits shown in Figure 3.1 b) Create the truth table for each circuit ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.