Lesson 2.4: Communication with the Outside World Essential
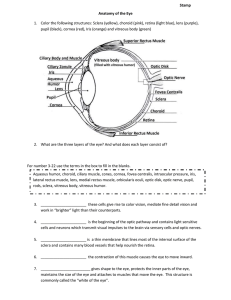
... The opaque muscular contractile diaphragm that is suspended in the aqueous humor in front of the lens of the eye, is perforated by the pupil and is continuous peripherally with the ciliary body, has a deeply pigmented posterior surface which excludes the entrance of light except through the pupil an ...
... The opaque muscular contractile diaphragm that is suspended in the aqueous humor in front of the lens of the eye, is perforated by the pupil and is continuous peripherally with the ciliary body, has a deeply pigmented posterior surface which excludes the entrance of light except through the pupil an ...
File
... pupil. 16. ______________________ allows the eyelids to open and close. 17. ______________________ this area is responsible for sharp central vision which is needed for reading, driving, etc. There is a high concentration of cone cells but rod cells are not present. 18. ____________________ is a hol ...
... pupil. 16. ______________________ allows the eyelids to open and close. 17. ______________________ this area is responsible for sharp central vision which is needed for reading, driving, etc. There is a high concentration of cone cells but rod cells are not present. 18. ____________________ is a hol ...
bionic eye
... are Progressive blinding disorders of the outer retina which involve degeneration of the neurons. ...
... are Progressive blinding disorders of the outer retina which involve degeneration of the neurons. ...
2.8 notes
... • Retina – Contains 3 layers: • Photoreceptors – Respond to various light waves – Rods » Sensitivity to low levels of light – Cones » Color vision, sharpness of vision ...
... • Retina – Contains 3 layers: • Photoreceptors – Respond to various light waves – Rods » Sensitivity to low levels of light – Cones » Color vision, sharpness of vision ...
Sensory Coding
... Cones: Are found mainly in the fovea, are highly sensitive and used for precise vision. There are three types (red, blue and green) which are maximally responsive to these colours. They do not work well in dim light. Rods and cones contain chemicals that release energy when struck by light (phot ...
... Cones: Are found mainly in the fovea, are highly sensitive and used for precise vision. There are three types (red, blue and green) which are maximally responsive to these colours. They do not work well in dim light. Rods and cones contain chemicals that release energy when struck by light (phot ...
Low-level Vision
... Blind spot: nasal to fovea, where optic nerve fibers leave retina: no photoreceptor Cones: detect color. 3 varieties: RGB, not very sensitive, day vision Rods: low light gray-scale receptors. 10 times as many as cones, (108) Cones: less sensitive, faster response, directionally sensitive, connected ...
... Blind spot: nasal to fovea, where optic nerve fibers leave retina: no photoreceptor Cones: detect color. 3 varieties: RGB, not very sensitive, day vision Rods: low light gray-scale receptors. 10 times as many as cones, (108) Cones: less sensitive, faster response, directionally sensitive, connected ...
Chapter 5 PowerPoint Notes
... _______________________ faraway objects seen more clearly lens focuses near objects behind retina ________________ near center of retina (fovea) fine detail and color vision daylight or well-lit conditions ________________ peripheral retina detect black, white and gray twilight or lo ...
... _______________________ faraway objects seen more clearly lens focuses near objects behind retina ________________ near center of retina (fovea) fine detail and color vision daylight or well-lit conditions ________________ peripheral retina detect black, white and gray twilight or lo ...
Economics
... Accommodation – the process by which the eye’s lens changes shape to help focus near or far objects on the retina’ Acuity – sharpness of vision Retina – the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing receptor rods and cones in addition to layers of other neurons (bipolar, ganglion cell ...
... Accommodation – the process by which the eye’s lens changes shape to help focus near or far objects on the retina’ Acuity – sharpness of vision Retina – the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing receptor rods and cones in addition to layers of other neurons (bipolar, ganglion cell ...
Cow Eye Dissection Data Sheet
... ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ _____________ ...
... ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ _____________ ...
Bio_246_files/Sensory Physiology
... The Eye • The eyes have binocular vision (we see with both eyes) • Sclera is the white of the ...
... The Eye • The eyes have binocular vision (we see with both eyes) • Sclera is the white of the ...
Powerpoint
... Lens- transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape through accommodation to focus images on the retina ...
... Lens- transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape through accommodation to focus images on the retina ...
retina - eSSUIR
... motor centers in the FRONTAL LOBES. Impulses from one side of the cerebral cortex turn both eyes to the other side of the field of vision. REFLEX EYE MOVEMENTS. SACCADES – rapid jerky movements from one fixation point to another – allow sweeping search of visual field and move visual images over rec ...
... motor centers in the FRONTAL LOBES. Impulses from one side of the cerebral cortex turn both eyes to the other side of the field of vision. REFLEX EYE MOVEMENTS. SACCADES – rapid jerky movements from one fixation point to another – allow sweeping search of visual field and move visual images over rec ...
Unit 2D Audio Visual - Iowa State University
... 3. Far sighted = 4. Abnormal shape of eye = 5. Vision difficulty due to aging = ...
... 3. Far sighted = 4. Abnormal shape of eye = 5. Vision difficulty due to aging = ...
unit 4 — sensation - Mayfield City Schools
... Pupil- adjustable opening in the center of the eye Iris- a ring of muscle that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening Lens- transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape through accommodation to focus images on the retina Retina- the ...
... Pupil- adjustable opening in the center of the eye Iris- a ring of muscle that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening Lens- transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape through accommodation to focus images on the retina Retina- the ...
Sensation
... Pupil- adjustable opening in the center of the eye Iris- a ring of muscle that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening Lens- transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape through accommodation to focus images on the retina Retina- the ...
... Pupil- adjustable opening in the center of the eye Iris- a ring of muscle that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening Lens- transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape through accommodation to focus images on the retina Retina- the ...
Cell division takes place next to the RPE. Neuroblastic cells have
... reduced or absent irrespective of the genetic cause. Their diversity implies that there is a fundamental disruption in early retinal development in the absences of pigment. A key feature of albino retinal development is that cells stay in the cell cycle too long. They miss their exit points. ...
... reduced or absent irrespective of the genetic cause. Their diversity implies that there is a fundamental disruption in early retinal development in the absences of pigment. A key feature of albino retinal development is that cells stay in the cell cycle too long. They miss their exit points. ...
Word version of this scenario
... Elicit a relevant history of visual loss and its associated features Elicit a relevant past medical history, medication history, and systems review to identify risk factors for central retinal artery occlusion Differential diagnosis of visual loss Relevance of giant cell arteritis (temporal arteriti ...
... Elicit a relevant history of visual loss and its associated features Elicit a relevant past medical history, medication history, and systems review to identify risk factors for central retinal artery occlusion Differential diagnosis of visual loss Relevance of giant cell arteritis (temporal arteriti ...
Eye Presentation - Downey Unified School District
... Interpreting Sight Cont. ● Dark vs. Light vision ○ Pupil expands and contracts depending on the amount of light, and could physically block out light form the eye ○ Cone cells can perceive color in bright light. ○ Rod cells perceive black and white images and work best in low light. ■ contains Rhod ...
... Interpreting Sight Cont. ● Dark vs. Light vision ○ Pupil expands and contracts depending on the amount of light, and could physically block out light form the eye ○ Cone cells can perceive color in bright light. ○ Rod cells perceive black and white images and work best in low light. ■ contains Rhod ...
S & P Day 1a
... Biology of Vision: Know the Steps 4. Image coming through activates photoreceptors in the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. As rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which transducts light energy into neural impul ...
... Biology of Vision: Know the Steps 4. Image coming through activates photoreceptors in the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. As rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which transducts light energy into neural impul ...
slides - Smith Lab
... connected to the inner segment by the cilium Constant shedding of discs as exposed to light High concentration of mitochondria in the inner segment to provide the energy requirements ...
... connected to the inner segment by the cilium Constant shedding of discs as exposed to light High concentration of mitochondria in the inner segment to provide the energy requirements ...
slides - Smith Lab
... connected to the inner segment by the cilium Constant shedding of discs as exposed to light High concentration of mitochondria in the inner segment to provide the energy requirements ...
... connected to the inner segment by the cilium Constant shedding of discs as exposed to light High concentration of mitochondria in the inner segment to provide the energy requirements ...
Sensory Physiology
... Voluntary fixation (premotor area) Involuntary fixation (visual area) ...
... Voluntary fixation (premotor area) Involuntary fixation (visual area) ...
Retina

The retina (/ˈrɛtɪnə/ RET-i-nə, pl. retinae, /ˈrɛtiniː/; from Latin rēte, meaning ""net"") is the third and inner coat of the eye which is a light-sensitive layer of tissue. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina (through the cornea and lens), which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical events that ultimately trigger nerve impulses. These are sent to various visual centres of the brain through the fibres of the optic nerve.In vertebrate embryonic development, the retina and the optic nerve originate as outgrowths of the developing brain, so the retina is considered part of the central nervous system (CNS) and is actually brain tissue. It is the only part of the CNS that can be visualized non-invasively.The retina is a layered structure with several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses. The only neurons that are directly sensitive to light are the photoreceptor cells. These are mainly of two types: the rods and cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide black-and-white vision, while cones support daytime vision and the perception of colour. A third, much rarer type of photoreceptor, the intrinsically photosensitive ganglion cell, is important for reflexive responses to bright daylight.Neural signals from the rods and cones undergo processing by other neurons of the retina. The output takes the form of action potentials in retinal ganglion cells whose axons form the optic nerve. Several important features of visual perception can be traced to the retinal encoding and processing of light.