Chapter 19-special senses-vision
... outside fovea centralis – cones process color, are most sensitive in highintensity light, most numerous within fovea centralis ...
... outside fovea centralis – cones process color, are most sensitive in highintensity light, most numerous within fovea centralis ...
E The Eye and Sense of Vision
... GRANULE CELL AXONS converge from the entire retina on an area medial to the visual axis of each eye, and at this point they gain their myelin sheath (which would not have been transparent on the surface of the retina!) and exit the retina and the eyeball as the optic "nerve." In humans there are abo ...
... GRANULE CELL AXONS converge from the entire retina on an area medial to the visual axis of each eye, and at this point they gain their myelin sheath (which would not have been transparent on the surface of the retina!) and exit the retina and the eyeball as the optic "nerve." In humans there are abo ...
Exam1_2017_with_key
... A) They are typically homonymous B) They have a slowly moving leading edge that scintillates (a flickering “fortification” pattern) C) They produce a scotoma that recovers after a few minutes D) They are a retinal phenomenon E) They may precede or occur in conjunction with severe headache. 13) The p ...
... A) They are typically homonymous B) They have a slowly moving leading edge that scintillates (a flickering “fortification” pattern) C) They produce a scotoma that recovers after a few minutes D) They are a retinal phenomenon E) They may precede or occur in conjunction with severe headache. 13) The p ...
Senses Notes
... smoking, sun damage. Lens: transparent, flexible Vitamin C decreases risk. structure, focuses images Ciliary body: ring of smooth muscle, controls the shape of the lens. ...
... smoking, sun damage. Lens: transparent, flexible Vitamin C decreases risk. structure, focuses images Ciliary body: ring of smooth muscle, controls the shape of the lens. ...
SPECIAL SENSES
... - optic disc - blind spot where optic nerve enters the eye - two major portions to the retina - Pigmented Layer - nonoptical retina - black color prevents light from bouncing around inside the eye - Optical portion - responsible for vision - multi-layered (10 layers including the pigmented layer) - ...
... - optic disc - blind spot where optic nerve enters the eye - two major portions to the retina - Pigmented Layer - nonoptical retina - black color prevents light from bouncing around inside the eye - Optical portion - responsible for vision - multi-layered (10 layers including the pigmented layer) - ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” ...
... Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” ...
The Visual Process & Implications of Visual Disabilities
... eyelids- closes light off of eye, protects, distributes tears ...
... eyelids- closes light off of eye, protects, distributes tears ...
Eye and Ear - smithlhhsb121
... focus on near objects ◦ When the relax, lens lengthens, focus on distance objects ...
... focus on near objects ◦ When the relax, lens lengthens, focus on distance objects ...
Sensation & Perception - Texas Christian University
... Nearsightedness-- eyeball is shorter than normal, causing focus to later than normal and therefore objects up close appear blurred. Focusing the image in front of the retina. ...
... Nearsightedness-- eyeball is shorter than normal, causing focus to later than normal and therefore objects up close appear blurred. Focusing the image in front of the retina. ...
hino Hills Eyecare - Dr. Suneet Gupta, OD
... vision evaluation today. Eye drops are used to enlarge the pupils of the eye. The larger viewing area allows a three-dimensional inspection of the retina, optic nerve and blood vessels. This leads to easier diagnosis of eye diseases such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and ca ...
... vision evaluation today. Eye drops are used to enlarge the pupils of the eye. The larger viewing area allows a three-dimensional inspection of the retina, optic nerve and blood vessels. This leads to easier diagnosis of eye diseases such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and ca ...
Special Sensory Systems
... ¤ photoreceptors-light-detecting cells (neurons) of the retina that contain the visual pigments and convert the incoming light into a neural signal (change in membrane potential) rod photoreceptors-work in dim light; use rhodopsin; cone photoreceptors- work in bright light; coneopsin visual pigments ...
... ¤ photoreceptors-light-detecting cells (neurons) of the retina that contain the visual pigments and convert the incoming light into a neural signal (change in membrane potential) rod photoreceptors-work in dim light; use rhodopsin; cone photoreceptors- work in bright light; coneopsin visual pigments ...
LISC 322 Neuroscience Normal Vision Retinal Image Formation
... A lens opacity (cataract) scatters light and precludes a clear retinal image. ...
... A lens opacity (cataract) scatters light and precludes a clear retinal image. ...
the eye - Mrothery.co.uk
... (courtesy of Scott Mittman and David R. Copenhagen) shows rods and cones in the retina of the tiger salamander. Each type of receptor has its own special pigment for absorbing light. Each consists of: a transmembrane protein called opsin coupled to the prosthetic group retinal. Retinal is a deri ...
... (courtesy of Scott Mittman and David R. Copenhagen) shows rods and cones in the retina of the tiger salamander. Each type of receptor has its own special pigment for absorbing light. Each consists of: a transmembrane protein called opsin coupled to the prosthetic group retinal. Retinal is a deri ...
Cones
... spectrum. The Sensory organ is the Eye The eye is regarded as an optical instrument for focusing of images on retina by refraction of light rays. Refractive power Cornea: 40 dioptres its fixed Lens: 20 dioptres its adjustable Photoreceptors on retina are rods and cones ...
... spectrum. The Sensory organ is the Eye The eye is regarded as an optical instrument for focusing of images on retina by refraction of light rays. Refractive power Cornea: 40 dioptres its fixed Lens: 20 dioptres its adjustable Photoreceptors on retina are rods and cones ...
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)
... compression or notching of a vein within the retina. It will only affect one eye. Vision may be blurred or a ‘blackout’ area of vision may be experienced. How does BRVO occur? The retina is part of the brain and forms a thin nerve tissue lining within the eye. The retina functions like the film in a ...
... compression or notching of a vein within the retina. It will only affect one eye. Vision may be blurred or a ‘blackout’ area of vision may be experienced. How does BRVO occur? The retina is part of the brain and forms a thin nerve tissue lining within the eye. The retina functions like the film in a ...
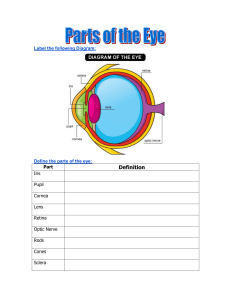
Parts of the Eye - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... can see the movie clearly. In the eye's case, however, the film screen is your retina. The image is then sent to the brain through the optic nerve . Your retina is in the very back of the eye. It holds millions of cells that are sensitive to light. The retina takes the light the eye receives and cha ...
... can see the movie clearly. In the eye's case, however, the film screen is your retina. The image is then sent to the brain through the optic nerve . Your retina is in the very back of the eye. It holds millions of cells that are sensitive to light. The retina takes the light the eye receives and cha ...
Technology will be crafted to study glaucoma, other
... foundation selected Dr. Dubra to bring his adaptive optics expertise to a four-‐member, nationwide team dedicated to identifying biomarkers for glaucoma. “Identifying new biomarkers will allow us to identify th ...
... foundation selected Dr. Dubra to bring his adaptive optics expertise to a four-‐member, nationwide team dedicated to identifying biomarkers for glaucoma. “Identifying new biomarkers will allow us to identify th ...
Incontinentia Pigmenti
... normal copy of the gene, allows the cell to produce enough normal protein to prevent death, but not disease. Because of these genetic considerations, 97% of living patients with Incontinentia Pigmenti are females, and the rare males who survive often have an additional genetic abnormality such as th ...
... normal copy of the gene, allows the cell to produce enough normal protein to prevent death, but not disease. Because of these genetic considerations, 97% of living patients with Incontinentia Pigmenti are females, and the rare males who survive often have an additional genetic abnormality such as th ...
vocab review unit 4 sensation and perception
... • information processing guided by higherlevel mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations. ...
... • information processing guided by higherlevel mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations. ...
Human Eye A human eyeball is like a simple camera!
... Hyperopia. The shape of your eye does not bend light correctly, resulting in a blurred image. A convex lens is usually used to ...
... Hyperopia. The shape of your eye does not bend light correctly, resulting in a blurred image. A convex lens is usually used to ...
2014-2015 Gross Anatomy of the eyeball: The eyeball lies in a
... 2- The middle coat (uvea or uveal tract): consists of the posterior part which is called the Choroid, a triangular shape muscular thickening called ciliary body and anteriorly, diaphragm like structure called the iris. The iris perforated centrally by regular and round opening called the pupil. Fun ...
... 2- The middle coat (uvea or uveal tract): consists of the posterior part which is called the Choroid, a triangular shape muscular thickening called ciliary body and anteriorly, diaphragm like structure called the iris. The iris perforated centrally by regular and round opening called the pupil. Fun ...
29 - Alamo Colleges
... Absorb all wavelengths of visible light Perceived input is in gray tones only Sum of visual input from many rods feeds into a single ganglion cell Results in fuzzy and indistinct images ...
... Absorb all wavelengths of visible light Perceived input is in gray tones only Sum of visual input from many rods feeds into a single ganglion cell Results in fuzzy and indistinct images ...
sards
... at the back of the eye) converts the light into an electrical signal that is sent to the brain through the optic nerve, where it is interpreted as vision. We can measure the electrical activity of the retina by electroretinography. An electroretinogram is a diagnostic test where several small, non-p ...
... at the back of the eye) converts the light into an electrical signal that is sent to the brain through the optic nerve, where it is interpreted as vision. We can measure the electrical activity of the retina by electroretinography. An electroretinogram is a diagnostic test where several small, non-p ...
Retina

The retina (/ˈrɛtɪnə/ RET-i-nə, pl. retinae, /ˈrɛtiniː/; from Latin rēte, meaning ""net"") is the third and inner coat of the eye which is a light-sensitive layer of tissue. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina (through the cornea and lens), which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical events that ultimately trigger nerve impulses. These are sent to various visual centres of the brain through the fibres of the optic nerve.In vertebrate embryonic development, the retina and the optic nerve originate as outgrowths of the developing brain, so the retina is considered part of the central nervous system (CNS) and is actually brain tissue. It is the only part of the CNS that can be visualized non-invasively.The retina is a layered structure with several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses. The only neurons that are directly sensitive to light are the photoreceptor cells. These are mainly of two types: the rods and cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide black-and-white vision, while cones support daytime vision and the perception of colour. A third, much rarer type of photoreceptor, the intrinsically photosensitive ganglion cell, is important for reflexive responses to bright daylight.Neural signals from the rods and cones undergo processing by other neurons of the retina. The output takes the form of action potentials in retinal ganglion cells whose axons form the optic nerve. Several important features of visual perception can be traced to the retinal encoding and processing of light.