Q. Give a feature of the kidney which indicates that it is an
... Q. Explain the term glomerular filtrate. A. Plasma that has entered Bowman’s capsule Q. Carbon dioxide is an excretory product. Name a substance from which it is derived. A. Carbohydrate or Fat or Fatty acids Q. What is the source of the heat that keeps the body at a fairly constant temperature? A. ...
... Q. Explain the term glomerular filtrate. A. Plasma that has entered Bowman’s capsule Q. Carbon dioxide is an excretory product. Name a substance from which it is derived. A. Carbohydrate or Fat or Fatty acids Q. What is the source of the heat that keeps the body at a fairly constant temperature? A. ...
Chapter_25_Metabolism
... citric acid cycle or can be converted to ketone bodies. • Other lipids are used as structural molecules or to synthesize essential molecules. Examples include ...
... citric acid cycle or can be converted to ketone bodies. • Other lipids are used as structural molecules or to synthesize essential molecules. Examples include ...
Excretory System
... 1. Sweat helps body temperature stay the same 2. Sweat is excreted through sweat glands 3. Sweat glands contain salt and water (the salt helps evaporate the water to keep the body cool) 4. Sweat glands located all over body ...
... 1. Sweat helps body temperature stay the same 2. Sweat is excreted through sweat glands 3. Sweat glands contain salt and water (the salt helps evaporate the water to keep the body cool) 4. Sweat glands located all over body ...
Use food products in two ways
... Occurs in liver & muscle cells Process of joining glucose molecules together > glycogen (animal starch) ...
... Occurs in liver & muscle cells Process of joining glucose molecules together > glycogen (animal starch) ...
Words to Pronounce ACIDS: Sulfuric Acid Sulfurous Acid
... 5a. The main force in chemical reactions is electrical attraction and repulsion between the protons and electrons in atoms. Attraction brings atoms together. Repulsion keeps atoms apart. This balancing act creates molecules, and we get the world around us. This same force causes oxygen to cling to r ...
... 5a. The main force in chemical reactions is electrical attraction and repulsion between the protons and electrons in atoms. Attraction brings atoms together. Repulsion keeps atoms apart. This balancing act creates molecules, and we get the world around us. This same force causes oxygen to cling to r ...
Workshop: Biology 3 Final Ray Chen Lilit Haroyan
... • Inorganic chemistry - chemistry of the nonliving world • Organic chemistry - chemistry of the living world – Carbon-based molecules are called organic compounds – By sharing electrons (what type of bond?), carbon can bond to four other atoms – By doing so, it can branch in up to four directions • ...
... • Inorganic chemistry - chemistry of the nonliving world • Organic chemistry - chemistry of the living world – Carbon-based molecules are called organic compounds – By sharing electrons (what type of bond?), carbon can bond to four other atoms – By doing so, it can branch in up to four directions • ...
Biochemistry
... Biochemistry Covalent bond - Chemical bond formed by the sharing of one or more electron pairs between two atoms Ionic bond - Chemical bonding resulting from the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom or a group of atoms to another. ...
... Biochemistry Covalent bond - Chemical bond formed by the sharing of one or more electron pairs between two atoms Ionic bond - Chemical bonding resulting from the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom or a group of atoms to another. ...
Part I - Nutrition. I. How to obtain food: This is descriptive
... problem. [Fig. 21.15,p. 442]. This illustrates the need for balance. Insufficient energy causes weight loss, then protein breakdown, muscle breakdown etc. Result => undernourishment and in extreme cases, death. iv) raw materials: Briefly, animals need organic carbon to manufacture needed organic mol ...
... problem. [Fig. 21.15,p. 442]. This illustrates the need for balance. Insufficient energy causes weight loss, then protein breakdown, muscle breakdown etc. Result => undernourishment and in extreme cases, death. iv) raw materials: Briefly, animals need organic carbon to manufacture needed organic mol ...
Nutrition: How to obtain food: This is descriptive
... Briefly, animals need organic carbon to manufacture needed organic molecules. Another example is nitrogenous compounds. Animals (or plants, for that matter) can’t fix nitrogen, so animals need to get this from diet. Nitrogen is important for amino acids (see below), and other organic molecules. v) e ...
... Briefly, animals need organic carbon to manufacture needed organic molecules. Another example is nitrogenous compounds. Animals (or plants, for that matter) can’t fix nitrogen, so animals need to get this from diet. Nitrogen is important for amino acids (see below), and other organic molecules. v) e ...
File - G. Scott`s Bio Page
... – Made up of fatty acids (monomer) – Chain of fatty acids (polymer) ex fats – Provides long term energy storage, makes up the cell membrane ...
... – Made up of fatty acids (monomer) – Chain of fatty acids (polymer) ex fats – Provides long term energy storage, makes up the cell membrane ...
lecture 13 ppt
... • Animals can synthesize most fatty acids they need • The essential fatty acids are certain unsaturated fatty acids that must be obtained from the diet • Deficiencies in fatty acids are rare ...
... • Animals can synthesize most fatty acids they need • The essential fatty acids are certain unsaturated fatty acids that must be obtained from the diet • Deficiencies in fatty acids are rare ...
A. The study of chemistry is essential for the study of physiology
... d. Two types of simple sugars are monosaccharides and disaccharides. e. Monosaccharides have 3-7 carbons. f. Disaccharides have 12 carbons. g. Three examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. h. Two examples of disaccharides are sucrose and lactose. i. Complex carbohydrates ar ...
... d. Two types of simple sugars are monosaccharides and disaccharides. e. Monosaccharides have 3-7 carbons. f. Disaccharides have 12 carbons. g. Three examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. h. Two examples of disaccharides are sucrose and lactose. i. Complex carbohydrates ar ...
4. Bases are substances that combine with hydrogen ions.
... d. Two types of simple sugars are monosaccharides and disaccharides. e. Monosaccharides have 3-7 carbons. f. Disaccharides have 12 carbons. g. Three examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. h. Two examples of disaccharides are sucrose and lactose. i. Complex carbohydrates ar ...
... d. Two types of simple sugars are monosaccharides and disaccharides. e. Monosaccharides have 3-7 carbons. f. Disaccharides have 12 carbons. g. Three examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. h. Two examples of disaccharides are sucrose and lactose. i. Complex carbohydrates ar ...
File
... 9. Which organelle is responsible for producing lipids? 10. Which organelle breaks down long fatty acids? What is this process called? ...
... 9. Which organelle is responsible for producing lipids? 10. Which organelle breaks down long fatty acids? What is this process called? ...
1. Hydrogen ion concentration is typically measured in grams of ions
... because of a carbon atom’s ability to form four covalent bonds. 4. Inorganic chemicals usually dissociate in water. 5. Organic chemicals usually dissolve in organic liquids. 6. Nonelectrolytes are compounds that do not release ions when dissolved in water. B. Inorganic Substances 1. Introduction a. ...
... because of a carbon atom’s ability to form four covalent bonds. 4. Inorganic chemicals usually dissociate in water. 5. Organic chemicals usually dissolve in organic liquids. 6. Nonelectrolytes are compounds that do not release ions when dissolved in water. B. Inorganic Substances 1. Introduction a. ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Basis of Life
... d. Two types of simple sugars are monosaccharides and disaccharides. e. Monosaccharides have 3-7 carbons. f. Disaccharides have 12 carbons. g. Three examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. h. Two examples of disaccharides are sucrose and lactose. i. Complex carbohydrates ar ...
... d. Two types of simple sugars are monosaccharides and disaccharides. e. Monosaccharides have 3-7 carbons. f. Disaccharides have 12 carbons. g. Three examples of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and galactose. h. Two examples of disaccharides are sucrose and lactose. i. Complex carbohydrates ar ...
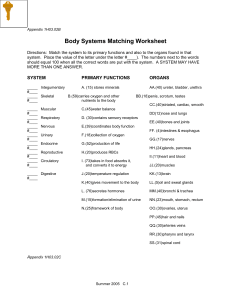
Body Systems Matching Worksheet
... Directions: Match the system to its primary functions and also to the organs found in that system. Place the value of the letter under the letter #____). The numbers next to the words should equal 100 when all the correct words are put with the system. A SYSTEM MAY HAVE MORE THAN ONE ANSWER. ...
... Directions: Match the system to its primary functions and also to the organs found in that system. Place the value of the letter under the letter #____). The numbers next to the words should equal 100 when all the correct words are put with the system. A SYSTEM MAY HAVE MORE THAN ONE ANSWER. ...
Honors Biology - Honors Class Help
... from small intestine to bloodstream 3. Elimination - disposal of undigested materials left over from food we eat 4. Digestion - breakdown of food to small nutrient molecules Ex: glucose, amino acids, fatty acids & glycerol a. Mechanical - physical processes such as chewing, exposes food to chemicals ...
... from small intestine to bloodstream 3. Elimination - disposal of undigested materials left over from food we eat 4. Digestion - breakdown of food to small nutrient molecules Ex: glucose, amino acids, fatty acids & glycerol a. Mechanical - physical processes such as chewing, exposes food to chemicals ...
Slide 1
... • Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA of cells. • The damage is caused by a photon, electron, proton, neutron, or ion beam directly or indirectly ionizing the atoms which make up the DNA chain. • Cells have mechanisms for repairing DNA damage, breaking the DNA on both strands proves to be th ...
... • Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA of cells. • The damage is caused by a photon, electron, proton, neutron, or ion beam directly or indirectly ionizing the atoms which make up the DNA chain. • Cells have mechanisms for repairing DNA damage, breaking the DNA on both strands proves to be th ...
Chemistry Enzymes, Vitamins, and Hormones
... diseases now known as scurvy and beriberi. Vitamins are organic substances that are essential for normal nutrition, but they are not carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, or fats. The British sailors lacked ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, in their onboard diets. A daily ration of lemon or lime juice provide ...
... diseases now known as scurvy and beriberi. Vitamins are organic substances that are essential for normal nutrition, but they are not carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, or fats. The British sailors lacked ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, in their onboard diets. A daily ration of lemon or lime juice provide ...
water - Manhasset Schools
... • A unit used to measure the energy content of food (nutrients). • More specifically, a calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree ...
... • A unit used to measure the energy content of food (nutrients). • More specifically, a calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree ...
Animal nutrition

Animal nutrition focuses on the dietary needs of domesticated animals, primarily those in agriculture and food production.