Music 100 Placement Exam
... 32. The home base of a scale is called the _____________________________________. 33. The nineteenth-century orchestra has how many principal instrumental groups? _____ 34. Moving from one key to another is called __________________________________. 35. The Classical-era symphony usually contains ho ...
... 32. The home base of a scale is called the _____________________________________. 33. The nineteenth-century orchestra has how many principal instrumental groups? _____ 34. Moving from one key to another is called __________________________________. 35. The Classical-era symphony usually contains ho ...
lecture 18
... A few general observations may be made about the technical differences between Romantic and Classic music. In Romantic music, long sections -even an entire movement- may continue as one unbroken rhythmic pattern, with the monotony and the cumulative effect of an incantation. A movement of a sonata i ...
... A few general observations may be made about the technical differences between Romantic and Classic music. In Romantic music, long sections -even an entire movement- may continue as one unbroken rhythmic pattern, with the monotony and the cumulative effect of an incantation. A movement of a sonata i ...
Music of WWI
... studied at the St. Petersburg conservatory with famed Russian composer Nicolai Rimsky-Korsakov. Early in his career, he was commissioned to compose three ballets for the Ballet Russe. Other that “Rite of Spring” the other well known ballet composed by Stravinsky was “Partushka” which was considered ...
... studied at the St. Petersburg conservatory with famed Russian composer Nicolai Rimsky-Korsakov. Early in his career, he was commissioned to compose three ballets for the Ballet Russe. Other that “Rite of Spring” the other well known ballet composed by Stravinsky was “Partushka” which was considered ...
Music Periods, Styles, Composers
... The first attempts at music printing came shortly after the appearance of Gutenberg's Bible (c. 1455). The first book of music ever printed is a Gradual; the date (probably c. 1473) and the name of the printer are unknown. Petrucci adapted Gutenberg's process of printing, and published music quickl ...
... The first attempts at music printing came shortly after the appearance of Gutenberg's Bible (c. 1455). The first book of music ever printed is a Gradual; the date (probably c. 1473) and the name of the printer are unknown. Petrucci adapted Gutenberg's process of printing, and published music quickl ...
Modern Art Music Terms - Western Michigan University
... at the top, go around the circle to "B" at the bottom, then continue around the circle back to "A Theme & Variations Form: A form that presents a musical "theme" and then a series of variations on that theme: - Theme 1 - Variation 1 - Variation 2 - Variation 3 - Variation 4 (etc.) Through-composed D ...
... at the top, go around the circle to "B" at the bottom, then continue around the circle back to "A Theme & Variations Form: A form that presents a musical "theme" and then a series of variations on that theme: - Theme 1 - Variation 1 - Variation 2 - Variation 3 - Variation 4 (etc.) Through-composed D ...
National 5 Musical Periods and Styles
... • Classical composers such as Haydn and Mozart used this technique extensively in their piano music. The chord is played in the order: low - high - middle - high. Mozart Sonata in C Mozart Piano Concerto no.26 Beethoven Pathetique Sonata ...
... • Classical composers such as Haydn and Mozart used this technique extensively in their piano music. The chord is played in the order: low - high - middle - high. Mozart Sonata in C Mozart Piano Concerto no.26 Beethoven Pathetique Sonata ...
Preface
... as he himself called it “poetic” tone. The “Romantic character piece” is basically his invention, even if precursors may be found in Beethoven (Bagatellen) and Schubert (Impromptus and Moments musicaux). Without wishing to throw the traditional forms of the sonata and of the variations to the four w ...
... as he himself called it “poetic” tone. The “Romantic character piece” is basically his invention, even if precursors may be found in Beethoven (Bagatellen) and Schubert (Impromptus and Moments musicaux). Without wishing to throw the traditional forms of the sonata and of the variations to the four w ...
The Late Baroque Era (1700-1750) Johann Sebastian Bach 1685
... Instrumental flourished in the Baroque era – solo music, chamber music and orchestral music The period saw many developments and improvements to instruments, and composers wrote increasingly for them The chamber suite was one such genre Suite: an international genre of music comprised of a sequence ...
... Instrumental flourished in the Baroque era – solo music, chamber music and orchestral music The period saw many developments and improvements to instruments, and composers wrote increasingly for them The chamber suite was one such genre Suite: an international genre of music comprised of a sequence ...
Music - Z pen driva - lena1magda
... The music of the Classical period, which spans from 1750 to 1820, is characterized by simpler melodies and forms such as the sonatas. The piano was the primary instrument used by composers during the Classical period. Classical Musical Instruments: The Piano Romantic Historiographers define the Roma ...
... The music of the Classical period, which spans from 1750 to 1820, is characterized by simpler melodies and forms such as the sonatas. The piano was the primary instrument used by composers during the Classical period. Classical Musical Instruments: The Piano Romantic Historiographers define the Roma ...
WORLD OF THE STRING QUARTET Glossary
... been applied generically to any movement that takes the place of a minuet in a sonata cycle, and it has also been used to indicate a comic or ironically comic composition, usually fast-moving and often one movement within a larger work.^ Franz Schubert (1797-1828) – Austrian composer who made semina ...
... been applied generically to any movement that takes the place of a minuet in a sonata cycle, and it has also been used to indicate a comic or ironically comic composition, usually fast-moving and often one movement within a larger work.^ Franz Schubert (1797-1828) – Austrian composer who made semina ...
joseph haydn (1732-1809) julius conus (1869-1942)
... with scenery, with characters who move about on stage, and as part of the cinema classic Fantasia, Beethoven took care to advise that the symphony is “more an expression of feeling than painting”. Each listener should let his imagination work its own spell. After all, wrote Beethoven, “composing is ...
... with scenery, with characters who move about on stage, and as part of the cinema classic Fantasia, Beethoven took care to advise that the symphony is “more an expression of feeling than painting”. Each listener should let his imagination work its own spell. After all, wrote Beethoven, “composing is ...
MusicHistory2
... Piano Music – Sonatas, many descriptive songs (programme music) Art Songs – Single songs or set of songs (song cycles) intended to be solo showpieces or poetry set to music Operas – Much “heavier” theatrical sounding music, the “Ring” opera (fat ladies/horns) Instruments Piano Full orchestra Technic ...
... Piano Music – Sonatas, many descriptive songs (programme music) Art Songs – Single songs or set of songs (song cycles) intended to be solo showpieces or poetry set to music Operas – Much “heavier” theatrical sounding music, the “Ring” opera (fat ladies/horns) Instruments Piano Full orchestra Technic ...
Glossary and Resource List
... Suite: an ordered series of instrumental movements of any character. Symphonic Poem: see Tone Poem. Symphony: A long and complex work in sonata form for symphony orchestra. ...
... Suite: an ordered series of instrumental movements of any character. Symphonic Poem: see Tone Poem. Symphony: A long and complex work in sonata form for symphony orchestra. ...
Notes for Class 3 - Midcoast Senior College
... The above traits could be said to characterize Beethoven (!), or Beethoven’s 19th century followers Schubert, Schumann, Brahms, Wagner, Liszt, etc. The Post-Wagnerians, in fact, extend this tradition --- perhaps in unexpected directions. Schoenberg, Berg and Webern (a trio often referred to as the S ...
... The above traits could be said to characterize Beethoven (!), or Beethoven’s 19th century followers Schubert, Schumann, Brahms, Wagner, Liszt, etc. The Post-Wagnerians, in fact, extend this tradition --- perhaps in unexpected directions. Schoenberg, Berg and Webern (a trio often referred to as the S ...
MUSIC APPRECIATION CHAPTER ONE
... The kinds of music you like reveal something about who you are As humans, we can like more than one type of music Music style refers to ...
... The kinds of music you like reveal something about who you are As humans, we can like more than one type of music Music style refers to ...
International Baccalaureate Music and Advanced Placement Music
... railroads. This was all made possible by the Industrial Revolution, which allowed a series of invention, including the cast iron frame for the piano, an instrument now found in most homes (upper and middle classes). The culture of the 18th century was under the patronage of an aristocracy for whom t ...
... railroads. This was all made possible by the Industrial Revolution, which allowed a series of invention, including the cast iron frame for the piano, an instrument now found in most homes (upper and middle classes). The culture of the 18th century was under the patronage of an aristocracy for whom t ...
document
... the piccolo all joined the standard orchestra, and only occasionally saxophones were used. The string section had to be greatly increased to keep up with the expanded brass and woodwinds. The percussion section was also expanded from the 2 or 3 timpani of the Classical period. The Romantic orchestra ...
... the piccolo all joined the standard orchestra, and only occasionally saxophones were used. The string section had to be greatly increased to keep up with the expanded brass and woodwinds. The percussion section was also expanded from the 2 or 3 timpani of the Classical period. The Romantic orchestra ...
Year 12
... • To know the different periods in the progression of western classical music and to understand some of the musical characteristics of these periods. • To look at one musical period in more detail Initial Questions: 1. When did music begin? 2. Why do we talk about ‘western’ and ‘non-western’ musics? ...
... • To know the different periods in the progression of western classical music and to understand some of the musical characteristics of these periods. • To look at one musical period in more detail Initial Questions: 1. When did music begin? 2. Why do we talk about ‘western’ and ‘non-western’ musics? ...
Program Design - NYU Computer Science Department
... An algorithm is the series of steps that can be followed again and again for the same results. Cooking receipe Celtic knot designs, craft patterns, repeated calculations The steps in running a science experiement Playing the notes of a musical scale or reading a musical score to perform an entire pi ...
... An algorithm is the series of steps that can be followed again and again for the same results. Cooking receipe Celtic knot designs, craft patterns, repeated calculations The steps in running a science experiement Playing the notes of a musical scale or reading a musical score to perform an entire pi ...
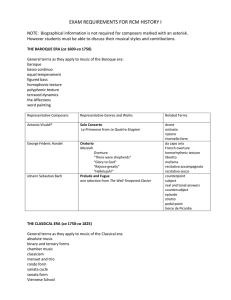
Sample History Placement Exam 2013
... 2. Arrange the following names in ascending chronological order according to birthdate. It is not necessary to provide the actual birthdates for each composer. • Ludwig van Beethoven • Guillaume de Machaut • Johann Sebastian Bach • Heinrich Schütz • Josquin des Prez • Hector Berlioz • Arnold Schoenb ...
... 2. Arrange the following names in ascending chronological order according to birthdate. It is not necessary to provide the actual birthdates for each composer. • Ludwig van Beethoven • Guillaume de Machaut • Johann Sebastian Bach • Heinrich Schütz • Josquin des Prez • Hector Berlioz • Arnold Schoenb ...
1b_LINE_MUSICs
... Beethoven, Symphony No. 7 in A Major, Op 92, second movement (1813) - single line repeated with different lines added each time an implied line (Composite line as a gesture) Richard Strauss, Ein Heldenleben (A Hero's Life, 1898) Analogous to Jackson Pollock? Witold Lutoslawski, Symphony No. 3 (1983) ...
... Beethoven, Symphony No. 7 in A Major, Op 92, second movement (1813) - single line repeated with different lines added each time an implied line (Composite line as a gesture) Richard Strauss, Ein Heldenleben (A Hero's Life, 1898) Analogous to Jackson Pollock? Witold Lutoslawski, Symphony No. 3 (1983) ...