2. Physiology_Respiratory_System
... ♦ The equation can also be used to measure the anatomic dead space if one replaces PaCO 2 with alveolar PCO 2 (PACO2), Which is the PCO2 of the last 10ml of expired gas. 409. (c) Chronic bronchitis Ref: Ganong - 652 The fraction of the vital capacity expired during the first second of a forced expir ...
... ♦ The equation can also be used to measure the anatomic dead space if one replaces PaCO 2 with alveolar PCO 2 (PACO2), Which is the PCO2 of the last 10ml of expired gas. 409. (c) Chronic bronchitis Ref: Ganong - 652 The fraction of the vital capacity expired during the first second of a forced expir ...
Air Pressure - Mrs. Meadows Science
... Cold Front: Weather map symbol • A cold front symbol—The direction that the teeth point indicate the direction the front is moving. ...
... Cold Front: Weather map symbol • A cold front symbol—The direction that the teeth point indicate the direction the front is moving. ...
Respiratory Physiology
... the autonomic nervous system (sympathetic nerve, relaxation, resistance↓; parasympathetic nerve, contraction, resistance↑). Irritants such as cigarette smoke cause an increase in resistance. An increase in lung volume reduces resistance because the bronchi are pulled open. Patients with elevated air ...
... the autonomic nervous system (sympathetic nerve, relaxation, resistance↓; parasympathetic nerve, contraction, resistance↑). Irritants such as cigarette smoke cause an increase in resistance. An increase in lung volume reduces resistance because the bronchi are pulled open. Patients with elevated air ...
12879_2017_2228_MOESM1_ESM
... Ultrahypertension—— blood pressure >2 SD, or >(99th percentile + 5mmHg).16 Hypertension—— blood pressure >1 SD, or 95th - (99th percentile + 5mmHg).16 Arrhythmia—— any arrhythmia except tachycardia and bradycardia. Bradycardia—— heart rate slower than normal. ...
... Ultrahypertension—— blood pressure >2 SD, or >(99th percentile + 5mmHg).16 Hypertension—— blood pressure >1 SD, or 95th - (99th percentile + 5mmHg).16 Arrhythmia—— any arrhythmia except tachycardia and bradycardia. Bradycardia—— heart rate slower than normal. ...
Exam 3 study guide Lecture 1 Animal Structure and Function Most
... Found in snails, a few fishes, spiders, vertebrates Structure of the mammalian lung - main structure need to know is alveoli and that alveoli are surrounded by capillaries Tidal ventilation of mammalian lung Negative pressure breathing Tidal volume - volume inhaled and exhaled (around 500 ml in huma ...
... Found in snails, a few fishes, spiders, vertebrates Structure of the mammalian lung - main structure need to know is alveoli and that alveoli are surrounded by capillaries Tidal ventilation of mammalian lung Negative pressure breathing Tidal volume - volume inhaled and exhaled (around 500 ml in huma ...
Slide 1 - OCCC.edu
... Since O2 is carried in such high reserves and saturation, it has little effect on the rate of ventilation CO2 concentration and pH do significantly change and have an immediate effect on ventilation ...
... Since O2 is carried in such high reserves and saturation, it has little effect on the rate of ventilation CO2 concentration and pH do significantly change and have an immediate effect on ventilation ...
Physiology Objectives 43
... Oxygen capacity: oxygen can combine with 1.34 ml of hemoglobin when hemoglobin is fully saturated. Thus, the oxygen capacity for a solution with a given concentration of hemoglobin at a specific volume is equal to the total amount of hemoglobin/ml multiplied by full oxygen saturation (1.34). Oxygen ...
... Oxygen capacity: oxygen can combine with 1.34 ml of hemoglobin when hemoglobin is fully saturated. Thus, the oxygen capacity for a solution with a given concentration of hemoglobin at a specific volume is equal to the total amount of hemoglobin/ml multiplied by full oxygen saturation (1.34). Oxygen ...
Regulation of Respiration
... The effect of low arterial PO2 on alveolar ventilation is far greater under some conditions including the following: *pulmonary disease: no adequate gas exchange, too little O2 is absorbed into the arterial bl. &at same time the arterial PCO2& H+ conc. remain near normal or are ↑↑because of poor tr ...
... The effect of low arterial PO2 on alveolar ventilation is far greater under some conditions including the following: *pulmonary disease: no adequate gas exchange, too little O2 is absorbed into the arterial bl. &at same time the arterial PCO2& H+ conc. remain near normal or are ↑↑because of poor tr ...
Lab # 28: Calculating the Value of the Ideal Gas Constant “R”
... Disposable plastic lighters are filled with lighter fluid, mostly butane (C4H10), which liquefies under pressure. In this lab, you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the value of the ideal gas constant “R”. We will collect a sample of gas from a lighter by water displacement. See Figure 1 for t ...
... Disposable plastic lighters are filled with lighter fluid, mostly butane (C4H10), which liquefies under pressure. In this lab, you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the value of the ideal gas constant “R”. We will collect a sample of gas from a lighter by water displacement. See Figure 1 for t ...
volumetric changes
... more room than before. Each water molecule takes up just as much “room” as each air molecule. Part of the problem lies in the use of the term “saturation” in discussions of humidity. It implies that there is no more space available. Actually, of course, the air and vapor molecules take up only a sma ...
... more room than before. Each water molecule takes up just as much “room” as each air molecule. Part of the problem lies in the use of the term “saturation” in discussions of humidity. It implies that there is no more space available. Actually, of course, the air and vapor molecules take up only a sma ...
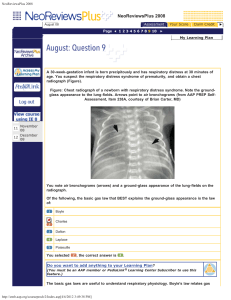
NeoReviewsPlus 2008 - American Academy of Pediatrics
... gas, R is the ideal gas constant (8.315 J/mol/K), and T is the temperature in Kelvins. The ideal gas law allows calculations of gas exchange and ventilation, including the basic observation that delivering more gas to a lung (increasing n) will cause an increase in P or V or both. Dalton's law state ...
... gas, R is the ideal gas constant (8.315 J/mol/K), and T is the temperature in Kelvins. The ideal gas law allows calculations of gas exchange and ventilation, including the basic observation that delivering more gas to a lung (increasing n) will cause an increase in P or V or both. Dalton's law state ...
CHAPTER 2 - PULMONARY FUNCTION, TRANSPORT OF BLOOD
... b) During the hockey match, the player must increase the volume of gas exchanged in the lungs and muscles. Explain the ...
... b) During the hockey match, the player must increase the volume of gas exchanged in the lungs and muscles. Explain the ...
AHF 2203 AVIATION HUMAN FACTORS
... • The oxygen levels are usually sufficient for human body requirements. ...
... • The oxygen levels are usually sufficient for human body requirements. ...
No Slide Title
... • The activity of the upper airway muscles (nose, pharynx and larynx) also decreases during sleep. • The negative pressure during inspiration is normally counterbalanced by activity of the upper airway muscles that function to keep the upper airway open. • Inspiration tends to collapse the upper air ...
... • The activity of the upper airway muscles (nose, pharynx and larynx) also decreases during sleep. • The negative pressure during inspiration is normally counterbalanced by activity of the upper airway muscles that function to keep the upper airway open. • Inspiration tends to collapse the upper air ...
B. True or False/Edit
... ___ 46. Which factor does not contribute to the rapid exchange of gases that takes place between the alveoli and the blood capillaries? a. a very large surface area present in the alveoli b. a very steep temperature gradient between the outside atmosphere and the alveoli c. a very short distance re ...
... ___ 46. Which factor does not contribute to the rapid exchange of gases that takes place between the alveoli and the blood capillaries? a. a very large surface area present in the alveoli b. a very steep temperature gradient between the outside atmosphere and the alveoli c. a very short distance re ...
Respiratory Physiology
... In this section of the course your main source of information will be Chapter 13 in your textbook: Human Physiology, 11th Ed., by Widmaier, Raff & Strang. This entire chapter is assigned reading; it should be your major source of information about respiratory physiology. Please read, or at least ski ...
... In this section of the course your main source of information will be Chapter 13 in your textbook: Human Physiology, 11th Ed., by Widmaier, Raff & Strang. This entire chapter is assigned reading; it should be your major source of information about respiratory physiology. Please read, or at least ski ...
Determination of the Molar Volume of a Gas KClO3 breaks down
... Open the pinch clamp on the rubber tubing and blow into the short tube until water drains into the beaker. Then, close the clamp. Transfer about 3.5 grams of the potassium chlorate - manganese dioxide mixture to the test tube. Determine the mass of the test tube and contents. Attach the test tube to ...
... Open the pinch clamp on the rubber tubing and blow into the short tube until water drains into the beaker. Then, close the clamp. Transfer about 3.5 grams of the potassium chlorate - manganese dioxide mixture to the test tube. Determine the mass of the test tube and contents. Attach the test tube to ...
Animal Kingdom: Evolution and Diversity
... Parts arrayed around a central point Bilateral symmetry Two halves that mirror each other Cephalization Concentration of nerve and sensory cells at anterior end ...
... Parts arrayed around a central point Bilateral symmetry Two halves that mirror each other Cephalization Concentration of nerve and sensory cells at anterior end ...
Physiology (L09) Slides#58 + #59 :
... -The amount of oxygen in pulmonary vein and in radial artery is the same, what differs is the amount of oxygen in the artery and the vein of one structure because between we have a capillary where exchange of materials occur. -Pre-capillary center is within the arteriol that comes from the heart. -T ...
... -The amount of oxygen in pulmonary vein and in radial artery is the same, what differs is the amount of oxygen in the artery and the vein of one structure because between we have a capillary where exchange of materials occur. -Pre-capillary center is within the arteriol that comes from the heart. -T ...
Lecture Outline (WORD)
... Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere (continued) 6. Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere (Temperature) Troposphere (Review first few points that we covered Monday, then continue) o Lowest layer, extending from the ground surface up to about 11 km above the surface. 11 km is an average … the top of ...
... Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere (continued) 6. Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere (Temperature) Troposphere (Review first few points that we covered Monday, then continue) o Lowest layer, extending from the ground surface up to about 11 km above the surface. 11 km is an average … the top of ...
Chapter 12 Gases
... The force of gas particle collisions on the walls of the container creates pressure; however, gas particles do not exert force on each other. At a given temperature, all gas particles have the same amount of kinetic energy (temperature). The distance between gas particles is very large. ...
... The force of gas particle collisions on the walls of the container creates pressure; however, gas particles do not exert force on each other. At a given temperature, all gas particles have the same amount of kinetic energy (temperature). The distance between gas particles is very large. ...
Respiratory Physio Detailed File
... • Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs • External respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood • Transport: O2 and CO2 in the blood • Internal respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between systemic blood vessels and tissues ...
... • Pulmonary ventilation (breathing): movement of air into and out of the lungs • External respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood • Transport: O2 and CO2 in the blood • Internal respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange between systemic blood vessels and tissues ...
Mechanical Ventilation
... At sea level we live under a layer of air that is several miles deep – the atmosphere. The pressure on our bodies is about the same as 10 metres of sea water pressing down on us all the time. At sea level, because air is compressible, the weight of the air around us compresses making it denser. As y ...
... At sea level we live under a layer of air that is several miles deep – the atmosphere. The pressure on our bodies is about the same as 10 metres of sea water pressing down on us all the time. At sea level, because air is compressible, the weight of the air around us compresses making it denser. As y ...