RCP 112 Basic Concepts
... Exhalation is passive – muscles relax and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases and air is forced out. ...
... Exhalation is passive – muscles relax and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases and air is forced out. ...
On Rayleigh Optical Depth Calculations
... 4. Suggested method to calculate Rayleigh optical depth of air Here we suggest a method for calculation of Rayleigh optical depth that goes back to first principles as suggested by Penndorf (1957) rather than using curve-fitting techniques, although it is true that the refractive index of air is sti ...
... 4. Suggested method to calculate Rayleigh optical depth of air Here we suggest a method for calculation of Rayleigh optical depth that goes back to first principles as suggested by Penndorf (1957) rather than using curve-fitting techniques, although it is true that the refractive index of air is sti ...
Title Pressure effect on the eda
... pressure vessel which was made of stainless steel could be used up to 3000 kg; cm=. Pressure wns ap, plied through a piston cylinder type intensifier using silicone oil as a pressure transmitting medium. The high pressure vesseP had uvo 1-cm-thick quartz windows which were attached to the window plu ...
... pressure vessel which was made of stainless steel could be used up to 3000 kg; cm=. Pressure wns ap, plied through a piston cylinder type intensifier using silicone oil as a pressure transmitting medium. The high pressure vesseP had uvo 1-cm-thick quartz windows which were attached to the window plu ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign kj - Region 11 Math And Science Teacher
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign LQ
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
anatomy and physiology of nitrous oxide
... Due to rapid uptake, two phenomena are seen Concentration effect - higher concentrations cause more rapid uptake of N2O Second gas effect - a second anesthetic gas will also be taken up more rapidly than usual when added to N2O ...
... Due to rapid uptake, two phenomena are seen Concentration effect - higher concentrations cause more rapid uptake of N2O Second gas effect - a second anesthetic gas will also be taken up more rapidly than usual when added to N2O ...
CHAPTER 41
... stem, sensory nerve signals from the lungs also help control respiration. Most important, located in the muscular portions of the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles throughout the lungs are stretch receptors that transmit signals through the vagi into the dorsal respiratory group of neurons when t ...
... stem, sensory nerve signals from the lungs also help control respiration. Most important, located in the muscular portions of the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles throughout the lungs are stretch receptors that transmit signals through the vagi into the dorsal respiratory group of neurons when t ...
Properties of Pure Substance
... Ø Elements Substances which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means. Ø Compounds Can be decomposed into two or more elements. ...
... Ø Elements Substances which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means. Ø Compounds Can be decomposed into two or more elements. ...
O 2
... Determinants of Alveolar PO2 and PCO2 Factors affecting alveolar partial pressures PO2 and PCO2 of inspired air Minute alveolar ventilation Rates at which respiring tissue consume O2 and produce CO2 ...
... Determinants of Alveolar PO2 and PCO2 Factors affecting alveolar partial pressures PO2 and PCO2 of inspired air Minute alveolar ventilation Rates at which respiring tissue consume O2 and produce CO2 ...
Respiratory 4 Control of Respiration Control of Respiration
... return alveolar & arterial PCO2 to normal Return arterial and brain [H+] to normal ...
... return alveolar & arterial PCO2 to normal Return arterial and brain [H+] to normal ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... of matter: gases, liquids, solids, etc.; are there more states there? Yes – think of the chicken soup (suspension) you are warming up on the gas flame (plasma) while checking your watch display (liquid crystal), or think of the peanut butter (emulsion)–jam (gel) sandwich you had this morning. You may ...
... of matter: gases, liquids, solids, etc.; are there more states there? Yes – think of the chicken soup (suspension) you are warming up on the gas flame (plasma) while checking your watch display (liquid crystal), or think of the peanut butter (emulsion)–jam (gel) sandwich you had this morning. You may ...
1 Stoichiometry Problems Volume of CO2 (g) produced from the
... What is the density (g/L) of SF6 under standard conditions, 1.00 atm and 273K? Assume one liter of gas (so the mass can be determined for one liter). PV = nRT n = PV/RT = (1.00 atm)(1.00 L)/(0.0821 L•atm/mol•K)(273 K) = 0.0446 moles SF6 146.06 g ...
... What is the density (g/L) of SF6 under standard conditions, 1.00 atm and 273K? Assume one liter of gas (so the mass can be determined for one liter). PV = nRT n = PV/RT = (1.00 atm)(1.00 L)/(0.0821 L•atm/mol•K)(273 K) = 0.0446 moles SF6 146.06 g ...
Human Physiology Study Questions-3
... 11. Discuss breathing in terms of being controlled by a central pattern generator. Where in the nervous system is this CPG seemingly generated? What muscles are involved in inspiration and expiration during quiet breathing? 12. What factors modulate ventilation rate? Where are monitors to these fact ...
... 11. Discuss breathing in terms of being controlled by a central pattern generator. Where in the nervous system is this CPG seemingly generated? What muscles are involved in inspiration and expiration during quiet breathing? 12. What factors modulate ventilation rate? Where are monitors to these fact ...
Respiratory physiology - Assets - Cambridge
... body’s response to a raised PaCO2 , with the rest being due to the central chemoreceptors; however, it is the peripheral chemoreceptors that act fastest. Other receptors that feed information to the respiratory centre include lung stretch receptors in bronchial smooth muscle, which transmit signals ...
... body’s response to a raised PaCO2 , with the rest being due to the central chemoreceptors; however, it is the peripheral chemoreceptors that act fastest. Other receptors that feed information to the respiratory centre include lung stretch receptors in bronchial smooth muscle, which transmit signals ...
Respiratory physiology
... pressures, a compliance curve for the lung can be constructed. The slope of this plot is lung compliance. Normally, lung compliance is measured under static conditions, meaning no airflow is present at the time the relaxation (recoil) pressure is measured. Effect of thoracic cage Compliance of both ...
... pressures, a compliance curve for the lung can be constructed. The slope of this plot is lung compliance. Normally, lung compliance is measured under static conditions, meaning no airflow is present at the time the relaxation (recoil) pressure is measured. Effect of thoracic cage Compliance of both ...
Respiration - Weber State University
... located within the medulla – respond to changes in PCO2 & H+ in cerebral spinal fluid – ventilation increases with elevations of PCO2 or H+ ...
... located within the medulla – respond to changes in PCO2 & H+ in cerebral spinal fluid – ventilation increases with elevations of PCO2 or H+ ...
No Slide Title
... diminished brain blood flow. • Neurons in the vasomotor center respond directly and strongly. • Their stimulation results in systemic arterial pressure as high as the heart can pump. – Due to elevated level of CO2 stimulating sympathetic nervous system in medulla. – One of the most powerful activato ...
... diminished brain blood flow. • Neurons in the vasomotor center respond directly and strongly. • Their stimulation results in systemic arterial pressure as high as the heart can pump. – Due to elevated level of CO2 stimulating sympathetic nervous system in medulla. – One of the most powerful activato ...
Pulse
... Cyanosis - bluish tinge caused by decrease in O2 in RBC. Cyanosis is assessed by checking the mucous membranes of the conjunctiva (lower eyelids), under the tongue and inside the mouth..should be pink not pale or bluish ...
... Cyanosis - bluish tinge caused by decrease in O2 in RBC. Cyanosis is assessed by checking the mucous membranes of the conjunctiva (lower eyelids), under the tongue and inside the mouth..should be pink not pale or bluish ...
The endurance athlete`s lung:
... – VCO2 is carbon dioxide production, VA is alveolar ventilation and PACO2 is Alveolar CO2 So… in both cases, O2 and CO2, alveolar gases are related to the ratio of metabolic rate and alveolar ...
... – VCO2 is carbon dioxide production, VA is alveolar ventilation and PACO2 is Alveolar CO2 So… in both cases, O2 and CO2, alveolar gases are related to the ratio of metabolic rate and alveolar ...
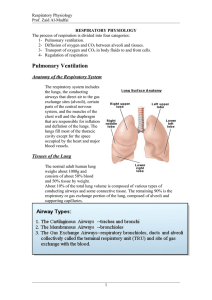
CHAPTER 1 Anatomy and physiology of the human respiratory system
... thoracic tissues are removed, since these are not a part of Rohrer’s estimates [10]. 2.3 Alveolar ventilation is not uniform even in the normal lung There are space-filling constraints within the lungs and thorax that prevent uniform distribution of ventilation even in the normal lung. As pointed ou ...
... thoracic tissues are removed, since these are not a part of Rohrer’s estimates [10]. 2.3 Alveolar ventilation is not uniform even in the normal lung There are space-filling constraints within the lungs and thorax that prevent uniform distribution of ventilation even in the normal lung. As pointed ou ...
File - Wk 1-2
... The partial pressure difference of a gas across the respiratory membrane is the difference between the partial pressure of the gas in the alveoli and the partial pressure of the gas in the blood of the pulmonary capillaries. Net diffusion occurs from higher to lower partial pressures. Normally PO2 i ...
... The partial pressure difference of a gas across the respiratory membrane is the difference between the partial pressure of the gas in the alveoli and the partial pressure of the gas in the blood of the pulmonary capillaries. Net diffusion occurs from higher to lower partial pressures. Normally PO2 i ...
Pressure - Peoria Public Schools
... Take notes on key information (not just the highlighted words) There are three questions I have to help guide your notes: What causes gases to exert pressure? What is the tool used to measure atmospheric pressure, and how does it work? What are the units in which pressure is commonly measured? ...
... Take notes on key information (not just the highlighted words) There are three questions I have to help guide your notes: What causes gases to exert pressure? What is the tool used to measure atmospheric pressure, and how does it work? What are the units in which pressure is commonly measured? ...