smith_wangaDAC2
... by 400mV over -40C to 85C (3.2 mV/˚C) • 1.1V reference varies by 150mV over -40C to 85C (1.2 mV/˚C) ...
... by 400mV over -40C to 85C (3.2 mV/˚C) • 1.1V reference varies by 150mV over -40C to 85C (1.2 mV/˚C) ...
Equations and Key Concepts (Excellence Project)
... Key Terms and Concepts Voltage is the potential or difference. It is the energy or pressure in a circuit. In S.I. units it is 1 joule/coulomb. (See p. 4). Current is the flow of electrons in a circuit. It is measured in amperes. 1 ampere = 6.24 x 1018/sec. Resistance is the tendency of a material to ...
... Key Terms and Concepts Voltage is the potential or difference. It is the energy or pressure in a circuit. In S.I. units it is 1 joule/coulomb. (See p. 4). Current is the flow of electrons in a circuit. It is measured in amperes. 1 ampere = 6.24 x 1018/sec. Resistance is the tendency of a material to ...
FET Current Mirrors
... • Ideal independent current sources are difficult to make and are almost impossible to fabricate on an integrated circuit. • Instead, current mirrors are fabricated. ▫ These are circuits that contain two or more FETs, where the drain of one of the FETs is connected to the rest of the circuit. ▫ This ...
... • Ideal independent current sources are difficult to make and are almost impossible to fabricate on an integrated circuit. • Instead, current mirrors are fabricated. ▫ These are circuits that contain two or more FETs, where the drain of one of the FETs is connected to the rest of the circuit. ▫ This ...
0496755001195066370
... Vdc output voltage. The converter is capable of delivering 280 Watts continuously at 14 Vdc (20 amperes output). The 14 Vdc output is buck converted from the input voltage and therefore the output voltage is not isolated from the input. A state of the art "Synchronous Current Mode Switching" topolog ...
... Vdc output voltage. The converter is capable of delivering 280 Watts continuously at 14 Vdc (20 amperes output). The 14 Vdc output is buck converted from the input voltage and therefore the output voltage is not isolated from the input. A state of the art "Synchronous Current Mode Switching" topolog ...
Hall Effect Devices as Current Sensors
... Monitoring current in a test fixture is typically accomplished by monitoring the voltage dropped across a resistor in series with the load. In Figure 1 we see a typical circuit. When the voltage across R5 reaches about 600 mV the transistor Q2 starts to conduct. As Q2 conducts the voltage across R7 ...
... Monitoring current in a test fixture is typically accomplished by monitoring the voltage dropped across a resistor in series with the load. In Figure 1 we see a typical circuit. When the voltage across R5 reaches about 600 mV the transistor Q2 starts to conduct. As Q2 conducts the voltage across R7 ...
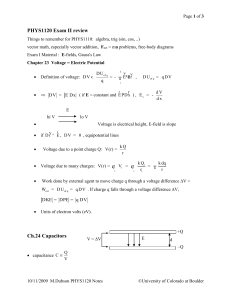
PHYS1120ExamIIReview.. - University of Colorado Boulder
... Ohm's Law: V I R (where R = constant) lo V hi V ...
... Ohm's Law: V I R (where R = constant) lo V hi V ...
transistors
... Draw the symbol for an LED What happens to the resistance of a thermistor as it is heated up? What happens to the resistance of an LDR if ...
... Draw the symbol for an LED What happens to the resistance of a thermistor as it is heated up? What happens to the resistance of an LDR if ...
Use the proportionality property of linear circuits to find the voltage Vx
... Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when given any input. So set Vx = 1 V and let the input be unknown. There is no current flowing through either the 22 Ω resistor or the 81 Ω resistor. This means that the voltage across each element is 0V. So we can replace the ...
... Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when given any input. So set Vx = 1 V and let the input be unknown. There is no current flowing through either the 22 Ω resistor or the 81 Ω resistor. This means that the voltage across each element is 0V. So we can replace the ...
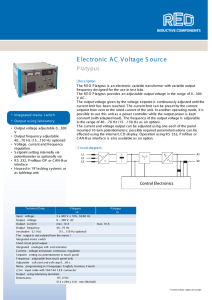
Electronic AC Voltage Source
... T he R E O P latypus is an electronic variable trans former with variable output frequency des igned for the us e in tes t labs . T he R E O P latypus provides an adjus table output voltage in the range of 0...300 V AC . T he output voltage given by the voltage s etpoint is continuous ly adjus ted u ...
... T he R E O P latypus is an electronic variable trans former with variable output frequency des igned for the us e in tes t labs . T he R E O P latypus provides an adjus table output voltage in the range of 0...300 V AC . T he output voltage given by the voltage s etpoint is continuous ly adjus ted u ...
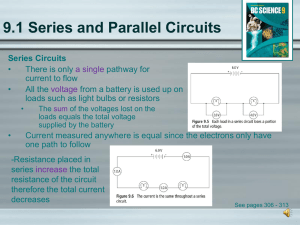
PP-Series and Parrellel circuts
... Current measured anywhere is equal since the electrons only have one path to follow -Resistance placed in series increase the total resistance of the circuit therefore the total current decreases ...
... Current measured anywhere is equal since the electrons only have one path to follow -Resistance placed in series increase the total resistance of the circuit therefore the total current decreases ...
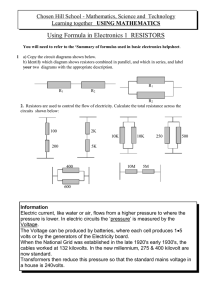
Written - Rose
... resistance circuit. The two resistors can be combine into a since they are in series. For the parallel circuit, the current through one of the resistor is proportional to the total current. The proportionality is the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors divided by its resistance. The equi ...
... resistance circuit. The two resistors can be combine into a since they are in series. For the parallel circuit, the current through one of the resistor is proportional to the total current. The proportionality is the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors divided by its resistance. The equi ...
**** 1
... • DC-DC converters are invented to accomplish voltage conversion to higher/lower levels without unnecessary power consumption. They utilize switches to change the voltage levels. • In this design project, a DC-DC converter topology called the boost converter is considered which changes the voltage t ...
... • DC-DC converters are invented to accomplish voltage conversion to higher/lower levels without unnecessary power consumption. They utilize switches to change the voltage levels. • In this design project, a DC-DC converter topology called the boost converter is considered which changes the voltage t ...
Feedback_what did I learn
... Good. I can add 1. For balanced differential signals, the DA can be modeled as a half circuit (a CE or CS amplifier) 2. The output resistance RI of the bias current source influences the CMRR of the DA. Higher in the CMRR, better is the DA. (Week of Sep.17’12) ...
... Good. I can add 1. For balanced differential signals, the DA can be modeled as a half circuit (a CE or CS amplifier) 2. The output resistance RI of the bias current source influences the CMRR of the DA. Higher in the CMRR, better is the DA. (Week of Sep.17’12) ...
4. Replace the BJT with one of its small
... 1) Write the steps through which small signal equivalent circuit model can be used in the analysis of transistor amplifier. Soln. 1. Determine the dc operating point of the BJT and in particular the dc collector current I C. 2. Calculate the values of the small-signal model parameters: ...
... 1) Write the steps through which small signal equivalent circuit model can be used in the analysis of transistor amplifier. Soln. 1. Determine the dc operating point of the BJT and in particular the dc collector current I C. 2. Calculate the values of the small-signal model parameters: ...