Construction of a Variable Frequency High Voltage Power Supply
... Here, we describe the design of a high voltage, variable frequency power supply for driving plasmas and testing the frequency responses of Dielectric Barrier Discharges (DBDs). DBDs are frequently used for surface treating, ozone production, and as UV sources. A DBD is an electrical discharge where ...
... Here, we describe the design of a high voltage, variable frequency power supply for driving plasmas and testing the frequency responses of Dielectric Barrier Discharges (DBDs). DBDs are frequently used for surface treating, ozone production, and as UV sources. A DBD is an electrical discharge where ...
CR circuit - schoolphysics
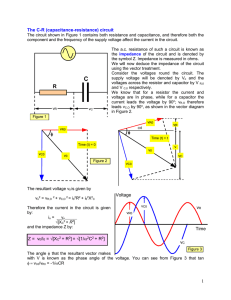
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
ETA1035 1 - ETA Solutions
... as low as 0.85V, it also incorporates circuits that disconnect the input from output, during shutdown, short-circuit, output current overloading, or other events when output is higher than the input. This eliminates the need for an external MOSFET and its control circuitry to disconnect the input fr ...
... as low as 0.85V, it also incorporates circuits that disconnect the input from output, during shutdown, short-circuit, output current overloading, or other events when output is higher than the input. This eliminates the need for an external MOSFET and its control circuitry to disconnect the input fr ...
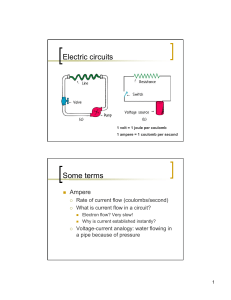
Circuit Basics
... • Remember, Ohm’s Law is an equation that expresses the relationship between these three variables. • Conceptually Ohm’s Law makes more sense if we write it like this: I=V/R Because voltage is only affected by the battery and resistance is only affected by the light bulbs. • CURRENT is being affecte ...
... • Remember, Ohm’s Law is an equation that expresses the relationship between these three variables. • Conceptually Ohm’s Law makes more sense if we write it like this: I=V/R Because voltage is only affected by the battery and resistance is only affected by the light bulbs. • CURRENT is being affecte ...
Electronics
... operating in the common emitter mode. IC is the collector current, IB is the base current and VCE is ...
... operating in the common emitter mode. IC is the collector current, IB is the base current and VCE is ...
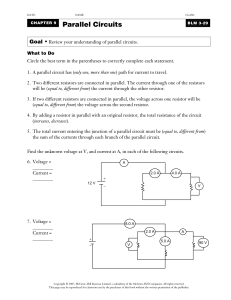
Series and Parallel Circuits
... More than one resistor in multiple paths Electrons may go through any path More electrons will go through path with less resistance Overall resistance goes down because more than one electron can get through at once ...
... More than one resistor in multiple paths Electrons may go through any path More electrons will go through path with less resistance Overall resistance goes down because more than one electron can get through at once ...
Electrical principles: math for electronics, electronic principles
... Power is the rate at which electrical energy is generated or consumed. The formula used to calculate electrical power in a DC circuit is power (P) equals voltage (E) multiplied by current (I) (T5C08) P= E × I 138 watts is the power being used in a circuit when the applied voltage is 13.8 volts DC an ...
... Power is the rate at which electrical energy is generated or consumed. The formula used to calculate electrical power in a DC circuit is power (P) equals voltage (E) multiplied by current (I) (T5C08) P= E × I 138 watts is the power being used in a circuit when the applied voltage is 13.8 volts DC an ...
Electronics Lab Intro (Lab#0) Introduction Procedure Part I. Ohm`s
... Electronics Lab Intro (Lab#0) Introduction The main purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with some of the equipment used for the electronics labs, while investigating Ohm’s Law and Resistive-Capacitive (RC) circuits. Recall that Ohm’s Law states that the electrical current through a circuit com ...
... Electronics Lab Intro (Lab#0) Introduction The main purpose of this lab is to familiarize you with some of the equipment used for the electronics labs, while investigating Ohm’s Law and Resistive-Capacitive (RC) circuits. Recall that Ohm’s Law states that the electrical current through a circuit com ...
2006-02-20
... • Common-Drain amplifier: gain is independent of gm and if there is no body effect, change in bias voltages doesn’t affect the gain. • Common-Gate amplifier: the current gain is independent of g m . So, changes in bias don’t affect the gain. • Common-Source amplifier: gain depends on gm and it is no ...
... • Common-Drain amplifier: gain is independent of gm and if there is no body effect, change in bias voltages doesn’t affect the gain. • Common-Gate amplifier: the current gain is independent of g m . So, changes in bias don’t affect the gain. • Common-Source amplifier: gain depends on gm and it is no ...
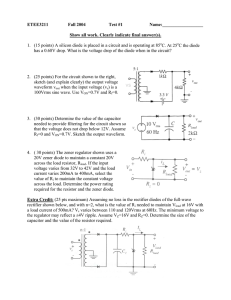
ETEE3211 Fall 2004
... voltage varies from 32V to 42V and the load current varies 200mA to 400mA, select the value of Ri to maintain the constant voltage across the load. Determine the power rating required for the resistor and the zener diode. Extra Credit: (25 pts maximum) Assuming no loss in the rectifier diodes of the ...
... voltage varies from 32V to 42V and the load current varies 200mA to 400mA, select the value of Ri to maintain the constant voltage across the load. Determine the power rating required for the resistor and the zener diode. Extra Credit: (25 pts maximum) Assuming no loss in the rectifier diodes of the ...
U00d9#U2026#U00d8#U00b4#U00d8#U00b1#U00d9
... which also defines the Emitter terminal this time pointing inwards in the transistor symbol. Also, all the polarities are reversed which means that PNP Transistors "sink" current as opposed to the NPN transistor which "sources" current. Then, PNP Transistors use a small output base current and a neg ...
... which also defines the Emitter terminal this time pointing inwards in the transistor symbol. Also, all the polarities are reversed which means that PNP Transistors "sink" current as opposed to the NPN transistor which "sources" current. Then, PNP Transistors use a small output base current and a neg ...
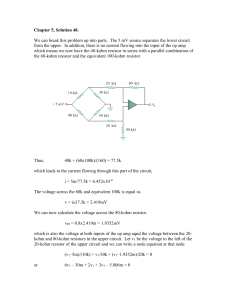
Soln0548 051017
... which leads to the current flowing through this part of the circuit, i = 5m/77.5k = 6.452x10–8 The voltage across the 60k and equivalent 100k is equal to, v = ix37.5k = 2.419mV We can now calculate the voltage across the 80-kohm resistor. v80 = 0.8x2.419m = 1.9352mV which is also the voltage at both ...
... which leads to the current flowing through this part of the circuit, i = 5m/77.5k = 6.452x10–8 The voltage across the 60k and equivalent 100k is equal to, v = ix37.5k = 2.419mV We can now calculate the voltage across the 80-kohm resistor. v80 = 0.8x2.419m = 1.9352mV which is also the voltage at both ...
MIL-STD-883H METHOD 3021 HIGH IMPEDANCE (OFF
... 1. PURPOSE. This method establishes the means for assuring circuit performance to the limits specified in the applicable acquisition document in regard to output leakage current when an output is in the high-impedance state with a high-level voltage applied. This current should normally be specified ...
... 1. PURPOSE. This method establishes the means for assuring circuit performance to the limits specified in the applicable acquisition document in regard to output leakage current when an output is in the high-impedance state with a high-level voltage applied. This current should normally be specified ...
r -5 sin (37"/r+ 40")
... Class : First Year - Energl, Engineering Branch Subject: Basic Electrical Engineering Examiner : Fatin N. Abdullah Name: ...
... Class : First Year - Energl, Engineering Branch Subject: Basic Electrical Engineering Examiner : Fatin N. Abdullah Name: ...