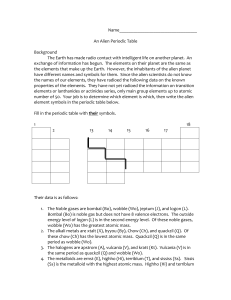
The Periodic Table
... • Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine.(Fl, Cl, Br) • Each element has 7 electrons in its outer shell. ...
... • Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine.(Fl, Cl, Br) • Each element has 7 electrons in its outer shell. ...
File
... 5. Identify which scientist did each of the following. a. Named small part of matter after Greek word atamos b. Discovered electrons c. Discovered dense, positively charged nucleus d. Proposed atoms were indestructible particles shaped like a solid sphere e. Proposed that electrons move in spherical ...
... 5. Identify which scientist did each of the following. a. Named small part of matter after Greek word atamos b. Discovered electrons c. Discovered dense, positively charged nucleus d. Proposed atoms were indestructible particles shaped like a solid sphere e. Proposed that electrons move in spherical ...
Reading the Periodic Table
... •"halogen" means "salt-former" and compounds containing halogens are called "salts" •exist in all three states of matter: •Solid- Iodine, Astatine •Liquid- Bromine •Gas- Fluorine, Chlorine ...
... •"halogen" means "salt-former" and compounds containing halogens are called "salts" •exist in all three states of matter: •Solid- Iodine, Astatine •Liquid- Bromine •Gas- Fluorine, Chlorine ...
Name
... (Nu). The solid left behind after the distillation consists of a crystal made up of byyou (By) and kratt (Kt). the element called doggone (D) has only 4 protons in its atom. Floxxit (Fx)is a black crystal and has 4 electrons in its outermost energy level. Both rhaatrap (Rh) and doadeer (Do) have ato ...
... (Nu). The solid left behind after the distillation consists of a crystal made up of byyou (By) and kratt (Kt). the element called doggone (D) has only 4 protons in its atom. Floxxit (Fx)is a black crystal and has 4 electrons in its outermost energy level. Both rhaatrap (Rh) and doadeer (Do) have ato ...
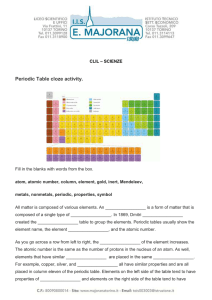
Periodic Table cloze activity.
... metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the _________________ table to group the elements. Periodic tables us ...
... metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the _________________ table to group the elements. Periodic tables us ...
Groups of the Periodic Table
... 16. What is the difference between an electrical conductor and a thermal conductor? ...
... 16. What is the difference between an electrical conductor and a thermal conductor? ...
Class 11 Class 12 The p- Block Element • Group13 (B to Tl
... • group members: boron (B), aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In) & thallium (Tl) . All, except boron, are metals. • Boron show diagonal relationship with Silicon; both are semiconductors metalloids & forms covalent compounds. • Boron compounds are electron deficient, they ...
... • group members: boron (B), aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In) & thallium (Tl) . All, except boron, are metals. • Boron show diagonal relationship with Silicon; both are semiconductors metalloids & forms covalent compounds. • Boron compounds are electron deficient, they ...
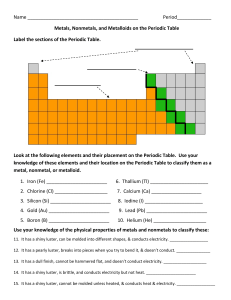
Name Period_____________ Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids on
... 13. It has a dull finish, cannot be hammered flat, and doesn’t conduct electricity. ___________________ 14. It has a shiny luster, is brittle, and conducts electricity but not heat. ______________________ 15. It has a shiny luster, cannot be molded unless heated, & conducts heat & electricity. _____ ...
... 13. It has a dull finish, cannot be hammered flat, and doesn’t conduct electricity. ___________________ 14. It has a shiny luster, is brittle, and conducts electricity but not heat. ______________________ 15. It has a shiny luster, cannot be molded unless heated, & conducts heat & electricity. _____ ...
CI_Chap_1_Test_A_Study_Guide
... The most common element in the universe is hydrogen. Atoms of an element always have a certain number of protons. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons. When an atom loses one or more electrons in becomes an ion with a + charge. The atomic mass number is the total number of protons ...
... The most common element in the universe is hydrogen. Atoms of an element always have a certain number of protons. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons. When an atom loses one or more electrons in becomes an ion with a + charge. The atomic mass number is the total number of protons ...
The Periodic Table
... Charge is usually 2 but can vary— usually 2 valence electrons These are the metals you are probably most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... Charge is usually 2 but can vary— usually 2 valence electrons These are the metals you are probably most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Atomic and Molecular Structure – Standard 1 Review
... 1d.4 Be able to predict the combination of elements in a compound using your knowledge of their valence electrons. ...
... 1d.4 Be able to predict the combination of elements in a compound using your knowledge of their valence electrons. ...
The Periodic Table Chemistry – Leaving Cert Quick Notes
... The Periodic Table An element is a substance that cannot be split into simpler substances by chemical means. Humphry Davy isolated potassium and sodium from their hydroxide compounds. Henry Moseley used the concept of atomic number to derive another definition for an element: a substance all of tho ...
... The Periodic Table An element is a substance that cannot be split into simpler substances by chemical means. Humphry Davy isolated potassium and sodium from their hydroxide compounds. Henry Moseley used the concept of atomic number to derive another definition for an element: a substance all of tho ...
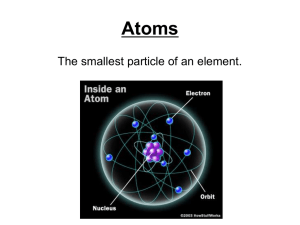
atomic number
... element has. For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is 1. The atomic number is unique to that element. No two elements have the same atomic number. ...
... element has. For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is 1. The atomic number is unique to that element. No two elements have the same atomic number. ...
for the quiz on 6 mar
... 19.98 In order to have a stronger acid, you want to make the O-H bond weaker. (There is a figure on p.646 in Ch. 15 which may help with this…) If you increase the number of oxygens in the molecule, you are drawing more electron density away from the Cl by bonding it to more (greater number of) elect ...
... 19.98 In order to have a stronger acid, you want to make the O-H bond weaker. (There is a figure on p.646 in Ch. 15 which may help with this…) If you increase the number of oxygens in the molecule, you are drawing more electron density away from the Cl by bonding it to more (greater number of) elect ...
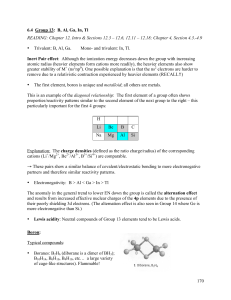
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
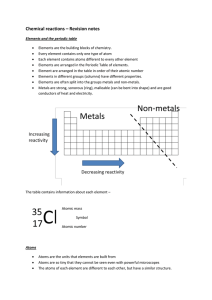
Chemical reactions revision
... The atoms of elements can be joined together to form compounds Once the atoms are joined in a compound, they are difficult to separate. Reactions are written as chemical equations – (element + element -> compound) ...
... The atoms of elements can be joined together to form compounds Once the atoms are joined in a compound, they are difficult to separate. Reactions are written as chemical equations – (element + element -> compound) ...
6.5 Main Group
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
The Periodic Table
... Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons. This identifies them as the element that they are. But all atoms of an element don’t have to have the same number of neutrons. For example, all boron atoms have 5 protons. However, four-fifths of them have 6 neutrons and one-fifth of ...
... Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons. This identifies them as the element that they are. But all atoms of an element don’t have to have the same number of neutrons. For example, all boron atoms have 5 protons. However, four-fifths of them have 6 neutrons and one-fifth of ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
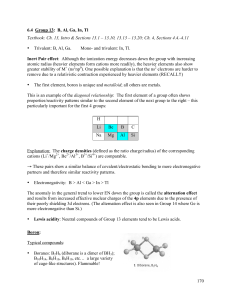
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... • Unlike the s-block elements, some of the elements of this group display lower valency state in addition to the group valency. The heavier elements in this group show an increased tendency to form univalent compounds, and univalent thallium compounds are the most stable. • This monovalency is due ...
... • Unlike the s-block elements, some of the elements of this group display lower valency state in addition to the group valency. The heavier elements in this group show an increased tendency to form univalent compounds, and univalent thallium compounds are the most stable. • This monovalency is due ...