II. Sensory Receptors
... 2. Stereociliated hair cells located beneath the membrane generate nerve impulses when sound waves cause the membrane to vibrate. 3. Gravitational balance organs called statocysts are found in cnidarians, molluscs, and arthropods. B. The outer ear of birds and mammals has a recessed tympanic membran ...
... 2. Stereociliated hair cells located beneath the membrane generate nerve impulses when sound waves cause the membrane to vibrate. 3. Gravitational balance organs called statocysts are found in cnidarians, molluscs, and arthropods. B. The outer ear of birds and mammals has a recessed tympanic membran ...
Anatomy and Physiology- Assignment #1 1. The maintenance of
... The mitochondria are the power houses of the cells, and are composed of two membranous sacs that are situated one inside the other. The mitochondria are responsible for the process of aerobic or cellular respiration: tiny enzymes found within the walls of the mitochondria, help to break down glucose ...
... The mitochondria are the power houses of the cells, and are composed of two membranous sacs that are situated one inside the other. The mitochondria are responsible for the process of aerobic or cellular respiration: tiny enzymes found within the walls of the mitochondria, help to break down glucose ...
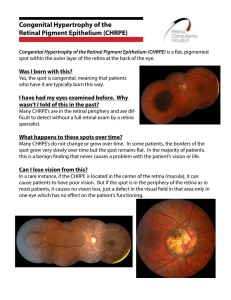
Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (CHRPE)
... cause patients to have poor vision. But if the spot is in the periphery of the retina as in most patients, it causes no vision loss, just a defect in the visual field in that area only in one eye which has no effect on the patient’s functioning. ...
... cause patients to have poor vision. But if the spot is in the periphery of the retina as in most patients, it causes no vision loss, just a defect in the visual field in that area only in one eye which has no effect on the patient’s functioning. ...
Chapter 39
... The Retina and Visual Processing • Rods (low light) and cones( bright and color) – Linked to neurons in the retina – Perform initial integration and processing of visual information ...
... The Retina and Visual Processing • Rods (low light) and cones( bright and color) – Linked to neurons in the retina – Perform initial integration and processing of visual information ...
Sensory Systems
... • Structures in the eye bend light rays • Light rays converge on the retina at a single focal point ...
... • Structures in the eye bend light rays • Light rays converge on the retina at a single focal point ...
BAD BLUE, GOOD BLUE, EYES and VISIOn
... by apoptosis. Molecular mechanisms were explored further by M. Rozanowksa [3] who showed a combined role played by rhodopsin and the 11-cis-retinal and 11-trans-retinal retinoids (“ATR” all-trans-retinal) the accumulation of which contributes to the phototoxicity mechanism on photoreceptors. The ac ...
... by apoptosis. Molecular mechanisms were explored further by M. Rozanowksa [3] who showed a combined role played by rhodopsin and the 11-cis-retinal and 11-trans-retinal retinoids (“ATR” all-trans-retinal) the accumulation of which contributes to the phototoxicity mechanism on photoreceptors. The ac ...
Chapter 2 The human visual system
... from human vision, amongst others because their visual system reacts differently (either weaker or stronger) to light of certain wavelengths. In biological visual systems, the main cause for this is the variety in cones that can be found. Some insects have been shown to have one or two types (mono- ...
... from human vision, amongst others because their visual system reacts differently (either weaker or stronger) to light of certain wavelengths. In biological visual systems, the main cause for this is the variety in cones that can be found. Some insects have been shown to have one or two types (mono- ...
Bio211 Lecture 22
... • receptor cells, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells - provide pathway for impulses triggered by photoreceptors to reach the optic nerve • horizontal cells and amacrine cells – modify impulses ...
... • receptor cells, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells - provide pathway for impulses triggered by photoreceptors to reach the optic nerve • horizontal cells and amacrine cells – modify impulses ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here
... b. Rods are highly sensitive and are best suited for night, noncolor (graytones) vision. Low acuity due to many rods converge into one ganglion; more numerous than cones (20:1); mostly in peripheral retina. c. Cones are less sensitive to light and are best adapted to bright light & color vision. Hig ...
... b. Rods are highly sensitive and are best suited for night, noncolor (graytones) vision. Low acuity due to many rods converge into one ganglion; more numerous than cones (20:1); mostly in peripheral retina. c. Cones are less sensitive to light and are best adapted to bright light & color vision. Hig ...
Genetics: the basics Genes: responsible for DNA: composed of
... Seems to be very important Lack of _____________________________has been shown to lead to _____________________________ Synaptic Pruning The nervous system overproduces the number of _____________________________ Within the first year of life, up to _____________________________may be eliminated Pro ...
... Seems to be very important Lack of _____________________________has been shown to lead to _____________________________ Synaptic Pruning The nervous system overproduces the number of _____________________________ Within the first year of life, up to _____________________________may be eliminated Pro ...
Lecture_8_fill_in
... Seems to be very important Lack of _____________________________has been shown to lead to _____________________________ Synaptic Pruning The nervous system overproduces the number of _____________________________ Within the first year of life, up to _____________________________may be eliminated Pro ...
... Seems to be very important Lack of _____________________________has been shown to lead to _____________________________ Synaptic Pruning The nervous system overproduces the number of _____________________________ Within the first year of life, up to _____________________________may be eliminated Pro ...
UROCHORDATES
... Nerve ganglion or brain(nerve cells,nerve fibres surrounded by large ganglion cells) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Three anterior and two posterior nerves ...
... Nerve ganglion or brain(nerve cells,nerve fibres surrounded by large ganglion cells) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Three anterior and two posterior nerves ...
Section II The Human Mind
... Floaters – small clumps of gel suspended in the vitreous humor Visible only when in the line of sight and usually harmless Cataracts – patterns of cloudiness inside the lens Lens may be removed and replaced with an artificial implant Glaucoma – disease of the optic nerve due to increase pr ...
... Floaters – small clumps of gel suspended in the vitreous humor Visible only when in the line of sight and usually harmless Cataracts – patterns of cloudiness inside the lens Lens may be removed and replaced with an artificial implant Glaucoma – disease of the optic nerve due to increase pr ...
Eye Notes
... a. The wall is composed of three tunics i. Fibrous tunic – Outer layer (Sclera) ii. Vascular tunic (uvea) – middle layer (Choroid) iii. Sensory tunic – inside layer (Retina) b. The Fibrous Tunic i. Sclera: White connective tissue layer 1. Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” ii. Cornea: Transpa ...
... a. The wall is composed of three tunics i. Fibrous tunic – Outer layer (Sclera) ii. Vascular tunic (uvea) – middle layer (Choroid) iii. Sensory tunic – inside layer (Retina) b. The Fibrous Tunic i. Sclera: White connective tissue layer 1. Seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” ii. Cornea: Transpa ...
Chapter 17: The Special Senses
... configurations: 11-cis form and 11-trans form. 2. Opsin activates transducin (a G protein), which in turn activates phosphodiesterase (PDE). 3. Cyclic-GMP (cGMP) levels decline, and gated sodium channels close. 4. the dark current is reduced and the rate of neurotransmitter release declines. ...
... configurations: 11-cis form and 11-trans form. 2. Opsin activates transducin (a G protein), which in turn activates phosphodiesterase (PDE). 3. Cyclic-GMP (cGMP) levels decline, and gated sodium channels close. 4. the dark current is reduced and the rate of neurotransmitter release declines. ...
Special Senses Summary
... 30. The nasolacrimal duct empties into the nasal cavity. (p. 549) 31. Rods are dim-light visual receptors, while cones are for bright-light and high-acuity color vision. (p. 553) 32. The fovea lies lateral to the optic disc. It contains only cones and provides detailed color vision for critical visi ...
... 30. The nasolacrimal duct empties into the nasal cavity. (p. 549) 31. Rods are dim-light visual receptors, while cones are for bright-light and high-acuity color vision. (p. 553) 32. The fovea lies lateral to the optic disc. It contains only cones and provides detailed color vision for critical visi ...
1 ARVO 2014: A Report from the Annual Meeting May 4
... model of inherited retinal disease. They had previously shown that ER stress is involved in retinal degeneration in this mouse. ER stress refers to a misfolding of protein within a cell organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Nanoceria and GRP78/Bip are both antioxidants but with different ...
... model of inherited retinal disease. They had previously shown that ER stress is involved in retinal degeneration in this mouse. ER stress refers to a misfolding of protein within a cell organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Nanoceria and GRP78/Bip are both antioxidants but with different ...
ARVO 2013 report to Retina International
... retinal prostheses. Eberhart Zrenner and his group, the makers of the Retina Implant AG, from Tubingen, Germany, have found that subretinal visual implants can cause retinal vascular changes. OMAG might be useful for addressing whether these changes signify recovery of retinal activity or an adverse ...
... retinal prostheses. Eberhart Zrenner and his group, the makers of the Retina Implant AG, from Tubingen, Germany, have found that subretinal visual implants can cause retinal vascular changes. OMAG might be useful for addressing whether these changes signify recovery of retinal activity or an adverse ...
Chapter 16- Sensory Organs
... sheet of nervous tissue made up of photoreceptors. – a. The photoreceptors consist of photoreceptor cells : rods= dark, grays and cones= bright, colors. There are blue, red and green light cones. They do not regenerate themselves. – b. Rods and cones contact a bipolar neuron that synapses with gangl ...
... sheet of nervous tissue made up of photoreceptors. – a. The photoreceptors consist of photoreceptor cells : rods= dark, grays and cones= bright, colors. There are blue, red and green light cones. They do not regenerate themselves. – b. Rods and cones contact a bipolar neuron that synapses with gangl ...
VISUAL PERCEPTION
... is accompanied by many technological challenges, the structure and function of the human image capturing device – the human eye – became even more astonishing. While comparing the resolution, sensitivity and dynamical range of the human eye to those of recent digital cameras, one can conclude that t ...
... is accompanied by many technological challenges, the structure and function of the human image capturing device – the human eye – became even more astonishing. While comparing the resolution, sensitivity and dynamical range of the human eye to those of recent digital cameras, one can conclude that t ...
E The Eye and Sense of Vision
... GRANULE CELL AXONS converge from the entire retina on an area medial to the visual axis of each eye, and at this point they gain their myelin sheath (which would not have been transparent on the surface of the retina!) and exit the retina and the eyeball as the optic "nerve." In humans there are abo ...
... GRANULE CELL AXONS converge from the entire retina on an area medial to the visual axis of each eye, and at this point they gain their myelin sheath (which would not have been transparent on the surface of the retina!) and exit the retina and the eyeball as the optic "nerve." In humans there are abo ...
The Special Senses
... • Amino acid sequence of opsin determines light sensitivity - four types – Light converts retinal from cis to trans form - isomerization • Retinal then separates from opsin - bleaching – In darkness (or absence of a certain color of light), retinal isomerase converts retinal back to cis form, which ...
... • Amino acid sequence of opsin determines light sensitivity - four types – Light converts retinal from cis to trans form - isomerization • Retinal then separates from opsin - bleaching – In darkness (or absence of a certain color of light), retinal isomerase converts retinal back to cis form, which ...
Photoreceptor cell

A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuron found in the retina that is capable of phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form a representation of the visual world, sight. The rods are narrower than the cones and distributed differently across the retina, but the chemical process in each that supports phototransduction is similar. A third class of photoreceptor cells was discovered during the 1990s: the photosensitive ganglion cells. These cells do not contribute to sight directly, but are thought to support circadian rhythms and pupillary reflex.There are major functional differences between the rods and cones. Rods are extremely sensitive, and can be triggered by a single photon. At very low light levels, visual experience is based solely on the rod signal. This explains why colors cannot be seen at low light levels: only one type of photoreceptor cell is active.Cones require significantly brighter light (i.e., a larger numbers of photons) in order to produce a signal. In humans, there are three different types of cone cell, distinguished by their pattern of response to different wavelengths of light. Color experience is calculated from these three distinct signals, perhaps via an opponent process. The three types of cone cell respond (roughly) to light of short, medium, and long wavelengths. Note that, due to the principle of univariance, the firing of the cell depends upon only the number of photons absorbed. The different responses of the three types of cone cells are determined by the likelihoods that their respective photoreceptor proteins will absorb photons of different wavelengths. So, for example, an L cone cell contains a photoreceptor protein that more readily absorbs long wavelengths of light (i.e., more ""red""). Light of a shorter wavelength can also produce the same response, but it must be much brighter to do so.The human retina contains about 120 million rod cells and 6 million cone cells. The number and ratio of rods to cones varies among species, dependent on whether an animal is primarily diurnal or nocturnal. Certain owls, such as the tawny owl, have a tremendous number of rods in their retinae. In addition, there are about 2.4 million to 3 million ganglion cells in the human visual system, the axons of these cells form the 2 optic nerves, 1 to 2% of them photosensitive.The pineal and parapineal glands are photoreceptive in non-mammalian vertebrates, but not in mammals. Birds have photoactive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons within the paraventricular organ that respond to light in the absence of input from the eyes or neurotransmitters. Invertebrate photoreceptors in organisms such as insects and molluscs are different in both their morphological organization and their underlying biochemical pathways. Described here are human photoreceptors.