Document
... that perceive discriminatory touch. They are located mostly in nonhairy skin and regions of the body more sensitive to touch. Meissner’s corpuscles are specialized for tactile discrimination. They are located in the dermal papillae of the glabrous portion of the fingers and palms of the hands. Pacin ...
... that perceive discriminatory touch. They are located mostly in nonhairy skin and regions of the body more sensitive to touch. Meissner’s corpuscles are specialized for tactile discrimination. They are located in the dermal papillae of the glabrous portion of the fingers and palms of the hands. Pacin ...
22-Visual
... • Retinal photoreceptors are of two types, rods and cones. • Rods are about 20 times more than the cones. • These cells share many structural similarities. • Rods are exquisitely sensitive to light. • They are particularly important for vision in dim light. • Cones are responsible for color vision, ...
... • Retinal photoreceptors are of two types, rods and cones. • Rods are about 20 times more than the cones. • These cells share many structural similarities. • Rods are exquisitely sensitive to light. • They are particularly important for vision in dim light. • Cones are responsible for color vision, ...
lec_1
... Colour vision testing is sometimes useful in the clinical evaluation of hereditary fundus dystrophies, where impairment may be present prior to the development of visual acuity and visual field changes. Colour vision is a function of three populations of retinal cones each with its specific sensitiv ...
... Colour vision testing is sometimes useful in the clinical evaluation of hereditary fundus dystrophies, where impairment may be present prior to the development of visual acuity and visual field changes. Colour vision is a function of three populations of retinal cones each with its specific sensitiv ...
INTRODUCTION - Downloadmela
... visual information to the visual cortex and its various areas in the back of the brain. The area of the retina that receives and processes the detailed images—and then sends them via the optic nerve to the brain—is referred to as the macula. The macula is of significant importance in that this area ...
... visual information to the visual cortex and its various areas in the back of the brain. The area of the retina that receives and processes the detailed images—and then sends them via the optic nerve to the brain—is referred to as the macula. The macula is of significant importance in that this area ...
6) ch 8 special senses - Cal State LA
... • Suspended in its perilymph are two sacs: the saccule and utricle • The saccule extends into the cochlea • The utricle extends into the semicircular ...
... • Suspended in its perilymph are two sacs: the saccule and utricle • The saccule extends into the cochlea • The utricle extends into the semicircular ...
Technology will be crafted to study glaucoma, other
... If detected in time, that is often effective enough to slow down the disease’s progression so that no major consequences occur,” Dr. Dubra said. “With today’s treatments alone, many more people could be ...
... If detected in time, that is often effective enough to slow down the disease’s progression so that no major consequences occur,” Dr. Dubra said. “With today’s treatments alone, many more people could be ...
The Skull Protects the Eye
... Two other common vision problems, near-sighted ness (m yopia) and far-sightedness (hyperopia), occur when the focal point falls either in front of the retina or behind th e retina, respecti vely (Fig. 10-35 e ). These conditions are caused by ab ...
... Two other common vision problems, near-sighted ness (m yopia) and far-sightedness (hyperopia), occur when the focal point falls either in front of the retina or behind th e retina, respecti vely (Fig. 10-35 e ). These conditions are caused by ab ...
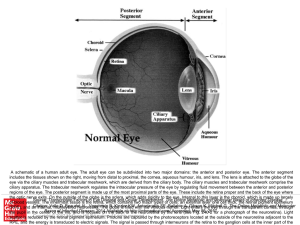
The Eyes and Ears MT 11
... Adnexa-means appendages or accessory structures of an organ. Lacrimal Apparatus:produce, store, and remove tears ...
... Adnexa-means appendages or accessory structures of an organ. Lacrimal Apparatus:produce, store, and remove tears ...
Reading guide - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 4. Differentiate between rods and cones. What type are you likely to use more frequently at night? 5. Why is the fovea centralis important for seeing well? ...
... 4. Differentiate between rods and cones. What type are you likely to use more frequently at night? 5. Why is the fovea centralis important for seeing well? ...
Sheep Brain 3 - Crossword Labs
... 8. Part of the basal ganglia. Regulates movements and influences some learning. 9. Sensory relay station of the brain 10. Relay center for visual information 11. Visual reflex center. Orients the head ...
... 8. Part of the basal ganglia. Regulates movements and influences some learning. 9. Sensory relay station of the brain 10. Relay center for visual information 11. Visual reflex center. Orients the head ...
ipsilateral
... Color opponency in the LGN • Most parvocellular cells display color opponency. • Some centers are excited by one color, but inhibited by others. • For example, red/green and blue/yellow. ...
... Color opponency in the LGN • Most parvocellular cells display color opponency. • Some centers are excited by one color, but inhibited by others. • For example, red/green and blue/yellow. ...
Deakin Research Online
... infection in the eye was monitored with a Heidelberg retinal angiograph (HRA). Eyes were also processed for histology and immunfluorescence microscopy to determine the nature of infected cells in various ocular compartments. At indicated times after infection, FACS analysis was performed to investig ...
... infection in the eye was monitored with a Heidelberg retinal angiograph (HRA). Eyes were also processed for histology and immunfluorescence microscopy to determine the nature of infected cells in various ocular compartments. At indicated times after infection, FACS analysis was performed to investig ...
Early Ultrastructural Changes After Low-Dose X-Irradiation
... observed in irradiated retina was the appear ance of small (80-130 nm) membranous whorls within the rod cell outer segment (ROS) membrane stacks. Whorls were not seen in the control retinas but were present in 200 Rad rats at one hour post irradiation (Fig. 1). 500 Rad rats showed a much larger num ...
... observed in irradiated retina was the appear ance of small (80-130 nm) membranous whorls within the rod cell outer segment (ROS) membrane stacks. Whorls were not seen in the control retinas but were present in 200 Rad rats at one hour post irradiation (Fig. 1). 500 Rad rats showed a much larger num ...
Vision research special issue: Sight restoration: Prosthetics
... This special issue is inspired by the wide variety of innovative approaches that are currently being developed to prolong or partially restore vision. Our primary goal was to provide an integrated discussion of these various approaches in a single volume. Current sight restoration research involves ...
... This special issue is inspired by the wide variety of innovative approaches that are currently being developed to prolong or partially restore vision. Our primary goal was to provide an integrated discussion of these various approaches in a single volume. Current sight restoration research involves ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
... of blood vessels. The innermost tissue is the retina, which contains two major types of cells: an external layer one cell thick, the retinal pigment epithelium Citation: Valle D, Beaudet AL, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW,with Antonarakis SE,humor. BallabioLight A, Gibson G. Thethe Online Metabolic and Mo ...
... of blood vessels. The innermost tissue is the retina, which contains two major types of cells: an external layer one cell thick, the retinal pigment epithelium Citation: Valle D, Beaudet AL, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW,with Antonarakis SE,humor. BallabioLight A, Gibson G. Thethe Online Metabolic and Mo ...
Chapter 12
... – Rods: 100 million, 100X more sensitive to light, best in dim light, more convergence: less detail, peripheral – Cones: 3 million, color, sharp detail, less convergence, only cones in fovea (no convergence) ...
... – Rods: 100 million, 100X more sensitive to light, best in dim light, more convergence: less detail, peripheral – Cones: 3 million, color, sharp detail, less convergence, only cones in fovea (no convergence) ...
Relation types used in CL
... class switched memory B cell is_a: “memory B cell” has_completed “isotype switching” ...
... class switched memory B cell is_a: “memory B cell” has_completed “isotype switching” ...
Human Visual System
... element) and the value f (x, y) as the grayvalue (or graylevel) of image f at (x, y). • Images are of two types: continuous and discrete. • A continuous image is a function of two independent variables, that take values in a continuum. Example: The intensity of a photographic image recorded on a fil ...
... element) and the value f (x, y) as the grayvalue (or graylevel) of image f at (x, y). • Images are of two types: continuous and discrete. • A continuous image is a function of two independent variables, that take values in a continuum. Example: The intensity of a photographic image recorded on a fil ...
Notes
... A) Refraction (bending) of light rays by the cornea and lens causes the light rays to come into exact focus onto the retina B) Once the light stimulates the rods and cones of the retina, nerve impulses are generated and sent to the brain via the optic nerve C) All images are inverted (upside down an ...
... A) Refraction (bending) of light rays by the cornea and lens causes the light rays to come into exact focus onto the retina B) Once the light stimulates the rods and cones of the retina, nerve impulses are generated and sent to the brain via the optic nerve C) All images are inverted (upside down an ...
ReNeuron Group plc ReNeuron files application to commence
... Pre-clinical studies carried out in disease models by the Company’s academic collaborators have demonstrated that, when transplanted into the retina, ReNeuron’s retinal progenitor cell technology has the potential to preserve existing photoreceptors, potentially reducing or halting further deteriora ...
... Pre-clinical studies carried out in disease models by the Company’s academic collaborators have demonstrated that, when transplanted into the retina, ReNeuron’s retinal progenitor cell technology has the potential to preserve existing photoreceptors, potentially reducing or halting further deteriora ...
Chapter 15
... – Divergence: Light striking a concave surface – Convergence: Light striking a convex surface ...
... – Divergence: Light striking a concave surface – Convergence: Light striking a convex surface ...
Chapter 16
... • Sensitive to dim light and best suited for night vision • Absorb all wavelengths of visible light • Perceived input is in gray tones only • Sum visual input from many rods feed into a single ganglion cell • Results in fuzzy and indistinct images ...
... • Sensitive to dim light and best suited for night vision • Absorb all wavelengths of visible light • Perceived input is in gray tones only • Sum visual input from many rods feed into a single ganglion cell • Results in fuzzy and indistinct images ...
Photoreceptor cell

A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuron found in the retina that is capable of phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form a representation of the visual world, sight. The rods are narrower than the cones and distributed differently across the retina, but the chemical process in each that supports phototransduction is similar. A third class of photoreceptor cells was discovered during the 1990s: the photosensitive ganglion cells. These cells do not contribute to sight directly, but are thought to support circadian rhythms and pupillary reflex.There are major functional differences between the rods and cones. Rods are extremely sensitive, and can be triggered by a single photon. At very low light levels, visual experience is based solely on the rod signal. This explains why colors cannot be seen at low light levels: only one type of photoreceptor cell is active.Cones require significantly brighter light (i.e., a larger numbers of photons) in order to produce a signal. In humans, there are three different types of cone cell, distinguished by their pattern of response to different wavelengths of light. Color experience is calculated from these three distinct signals, perhaps via an opponent process. The three types of cone cell respond (roughly) to light of short, medium, and long wavelengths. Note that, due to the principle of univariance, the firing of the cell depends upon only the number of photons absorbed. The different responses of the three types of cone cells are determined by the likelihoods that their respective photoreceptor proteins will absorb photons of different wavelengths. So, for example, an L cone cell contains a photoreceptor protein that more readily absorbs long wavelengths of light (i.e., more ""red""). Light of a shorter wavelength can also produce the same response, but it must be much brighter to do so.The human retina contains about 120 million rod cells and 6 million cone cells. The number and ratio of rods to cones varies among species, dependent on whether an animal is primarily diurnal or nocturnal. Certain owls, such as the tawny owl, have a tremendous number of rods in their retinae. In addition, there are about 2.4 million to 3 million ganglion cells in the human visual system, the axons of these cells form the 2 optic nerves, 1 to 2% of them photosensitive.The pineal and parapineal glands are photoreceptive in non-mammalian vertebrates, but not in mammals. Birds have photoactive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons within the paraventricular organ that respond to light in the absence of input from the eyes or neurotransmitters. Invertebrate photoreceptors in organisms such as insects and molluscs are different in both their morphological organization and their underlying biochemical pathways. Described here are human photoreceptors.