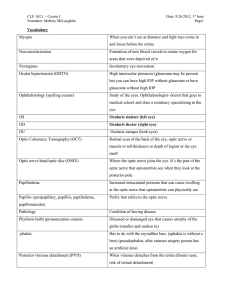
Acute visual loss
... Otherwise: later treatment or surgery (vitrectomy) depending on aetiology of the vitreous haemorrhage ...
... Otherwise: later treatment or surgery (vitrectomy) depending on aetiology of the vitreous haemorrhage ...
Dear Notetaker:
... When your retina detaches from the back part of your eye (flashes and floaters, can cause permanent loss of vision) ...
... When your retina detaches from the back part of your eye (flashes and floaters, can cause permanent loss of vision) ...
PYRAMIDS AND CONES
... height, altitude and base length given two of the others. • You can use them in the Pythagorean theorem to find them. ...
... height, altitude and base length given two of the others. • You can use them in the Pythagorean theorem to find them. ...
C onference 20 - The Joint Pathology Center (JPC)
... autoimmune disease process, as well as the partial response to immunosuppressive therapy in dogs.1,2,5 Most cases reported appear to be localized to the eye, with rare reports that have evidence for other systemic immune-mediated disease, which is the case for humans with necrotizing scleritis.1 The ...
... autoimmune disease process, as well as the partial response to immunosuppressive therapy in dogs.1,2,5 Most cases reported appear to be localized to the eye, with rare reports that have evidence for other systemic immune-mediated disease, which is the case for humans with necrotizing scleritis.1 The ...
GO-08 Outline
... b) Intra-canalicular portion extends through the optic canal c) Intra-cranial section extends from the posterior optic canal to the anterior chiasm 2. Field defects based upon optic nerve anatomy C. Chiasm 1. Optic nerves converge over the sella turcica to form the chiasm 2. Left and right visual wo ...
... b) Intra-canalicular portion extends through the optic canal c) Intra-cranial section extends from the posterior optic canal to the anterior chiasm 2. Field defects based upon optic nerve anatomy C. Chiasm 1. Optic nerves converge over the sella turcica to form the chiasm 2. Left and right visual wo ...
Visual fields and eye morphology support color vision in a color
... The AM eye in longitudinal section is pyriform (Fig. 2C, E), while it is almost circular in transverse section (Fig. 3BeE). The lens is biconvex and almost spherical, of approximately 70 mm in diameter (Fig. 2A). Beneath the lens, the cells of the vitreous body are arranged to form a flattened sphero ...
... The AM eye in longitudinal section is pyriform (Fig. 2C, E), while it is almost circular in transverse section (Fig. 3BeE). The lens is biconvex and almost spherical, of approximately 70 mm in diameter (Fig. 2A). Beneath the lens, the cells of the vitreous body are arranged to form a flattened sphero ...
DOC - The Foundation Fighting Blindness
... Wallace’s lab aimed specifically at cone cell transplants. Only 5% of the retina’s light-sensing cells are cone cells, but they are responsible for our precious central and colour vision. Transplants of these cells would provide a brighter future for people living with central vision loss, such as t ...
... Wallace’s lab aimed specifically at cone cell transplants. Only 5% of the retina’s light-sensing cells are cone cells, but they are responsible for our precious central and colour vision. Transplants of these cells would provide a brighter future for people living with central vision loss, such as t ...
Week 2 of development
... It also occurs in somatic mesoderm of the body wall and to form the pelvic and shoulder girdles and long bones of the limbs ...
... It also occurs in somatic mesoderm of the body wall and to form the pelvic and shoulder girdles and long bones of the limbs ...
Treatment and Management of Posterior Segment Trauma
... • Direct contusive injury to the globe: coup versus countercoup • Often multiple • Commonly found inferotemporal and supranasal • Contusion injury may cause large equatorial breaks, dialysis, or MH ...
... • Direct contusive injury to the globe: coup versus countercoup • Often multiple • Commonly found inferotemporal and supranasal • Contusion injury may cause large equatorial breaks, dialysis, or MH ...
25-autonomic supply of head & neck
... • Sympathetic fibers from deep petrosal nerve → ganglion (without relay) → orbital branches → orbitalis muscle ...
... • Sympathetic fibers from deep petrosal nerve → ganglion (without relay) → orbital branches → orbitalis muscle ...
acute monocular blindness & basic neuro ophthalmology
... • Usually some degree of permanent loss if not corrected immediately • ICA -> ophthalmic artery -> retinal artery • Occasional additional supply by the cilioretinal art. ...
... • Usually some degree of permanent loss if not corrected immediately • ICA -> ophthalmic artery -> retinal artery • Occasional additional supply by the cilioretinal art. ...
107308 ECFA Ocular Outlook.indd
... the lens (e.g., lenticular sclerosis), or changes in corneal or lens curvature. Hyperopia (or farsightedness) occurs when light focuses behind the retina due to a shortened globe or changes in corneal or lens curvature. Studies have shown that certain breeds are predisposed to myopia, and myopia oft ...
... the lens (e.g., lenticular sclerosis), or changes in corneal or lens curvature. Hyperopia (or farsightedness) occurs when light focuses behind the retina due to a shortened globe or changes in corneal or lens curvature. Studies have shown that certain breeds are predisposed to myopia, and myopia oft ...
visual reflexes
... SYMPATHETIC TONE – improves distant vision Suspensory ligaments attach radially around the lens, pulling the lens toward the outer surface of the eyeball. Suspensory ligaments are constantly tensed by their attachments at the anterior border of the choroid and retina. This tension keeps the lens rel ...
... SYMPATHETIC TONE – improves distant vision Suspensory ligaments attach radially around the lens, pulling the lens toward the outer surface of the eyeball. Suspensory ligaments are constantly tensed by their attachments at the anterior border of the choroid and retina. This tension keeps the lens rel ...
The inner ear The inner ear can be divided into
... sensitivities to such deformation of the hairs. Thus, a sound that produces a particular frequency of vibration will excite certain receptor cells, while a sound involving another frequency will stimulate a different set of cells. The cells act very like Neurons in that when it is stimulated appropr ...
... sensitivities to such deformation of the hairs. Thus, a sound that produces a particular frequency of vibration will excite certain receptor cells, while a sound involving another frequency will stimulate a different set of cells. The cells act very like Neurons in that when it is stimulated appropr ...
Lens - Anatomy and Physiology
... • Originates as outpocketing of brain • Delicate two-layered membrane – Outer Pigmented layer ...
... • Originates as outpocketing of brain • Delicate two-layered membrane – Outer Pigmented layer ...
Cochlear labyrinth (pars auditiva labyrinthi)
... The columnar cells contact the basilar membrane with one end, while the other end is extended to form plates, which provide stability to the receptor cells of the organ of Corti. The columnar cells are assisted by the phalangeal cells, which also support the receptor cells. The receptor cells are ar ...
... The columnar cells contact the basilar membrane with one end, while the other end is extended to form plates, which provide stability to the receptor cells of the organ of Corti. The columnar cells are assisted by the phalangeal cells, which also support the receptor cells. The receptor cells are ar ...
ANS = general visceral motor portion of PNS sympathetic division
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
Chapter 15 ()
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
... a. synapse with postganglionic neuron in paravertebral ganglion; return to spinal nerve in gray ramus same segment inferior or superior segment ...
EMBRYOLOGY
... When a motor axon and a muscle fiber meet, a series of changes occurs that mark the formation of a functional synapse or neuromuscular junction. The early changes consist of (1) cessation of outgrowth of the axon, (2) the preparation of the nerve terminal for the release of the appropriate neurotran ...
... When a motor axon and a muscle fiber meet, a series of changes occurs that mark the formation of a functional synapse or neuromuscular junction. The early changes consist of (1) cessation of outgrowth of the axon, (2) the preparation of the nerve terminal for the release of the appropriate neurotran ...
Aud & Equil
... • Auditory ossicles conduct the vibration into the inner ear – Tensor tympani and stapedius muscles contract to reduce the amount of movement when loud sounds arrive • Movement at the oval window applies pressure to the perilymph of the cochlear duct • Pressure waves distort basilar membrane • Hair ...
... • Auditory ossicles conduct the vibration into the inner ear – Tensor tympani and stapedius muscles contract to reduce the amount of movement when loud sounds arrive • Movement at the oval window applies pressure to the perilymph of the cochlear duct • Pressure waves distort basilar membrane • Hair ...
Unit 7
... It is also a chemical sense. To be detected, molecules must be dissolved. Taste stimuli classes include sour, sweet, bitter, salty, and umami (savory). Gustation is closely linked to olfaction, without the sense of smell, you cannot taste. We have 10,000 taste buds, which decline with age ...
... It is also a chemical sense. To be detected, molecules must be dissolved. Taste stimuli classes include sour, sweet, bitter, salty, and umami (savory). Gustation is closely linked to olfaction, without the sense of smell, you cannot taste. We have 10,000 taste buds, which decline with age ...
After Images
... spreads nerve fibers onto the back of the eye to make up there retina. • The small round spot where this cable enters the back of your eye is called the optic nerve head or optic disc. There are no light-detecting cells on this disc. As a result, you have a very small gap in the visual field of each ...
... spreads nerve fibers onto the back of the eye to make up there retina. • The small round spot where this cable enters the back of your eye is called the optic nerve head or optic disc. There are no light-detecting cells on this disc. As a result, you have a very small gap in the visual field of each ...
Photoreceptor cell

A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuron found in the retina that is capable of phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form a representation of the visual world, sight. The rods are narrower than the cones and distributed differently across the retina, but the chemical process in each that supports phototransduction is similar. A third class of photoreceptor cells was discovered during the 1990s: the photosensitive ganglion cells. These cells do not contribute to sight directly, but are thought to support circadian rhythms and pupillary reflex.There are major functional differences between the rods and cones. Rods are extremely sensitive, and can be triggered by a single photon. At very low light levels, visual experience is based solely on the rod signal. This explains why colors cannot be seen at low light levels: only one type of photoreceptor cell is active.Cones require significantly brighter light (i.e., a larger numbers of photons) in order to produce a signal. In humans, there are three different types of cone cell, distinguished by their pattern of response to different wavelengths of light. Color experience is calculated from these three distinct signals, perhaps via an opponent process. The three types of cone cell respond (roughly) to light of short, medium, and long wavelengths. Note that, due to the principle of univariance, the firing of the cell depends upon only the number of photons absorbed. The different responses of the three types of cone cells are determined by the likelihoods that their respective photoreceptor proteins will absorb photons of different wavelengths. So, for example, an L cone cell contains a photoreceptor protein that more readily absorbs long wavelengths of light (i.e., more ""red""). Light of a shorter wavelength can also produce the same response, but it must be much brighter to do so.The human retina contains about 120 million rod cells and 6 million cone cells. The number and ratio of rods to cones varies among species, dependent on whether an animal is primarily diurnal or nocturnal. Certain owls, such as the tawny owl, have a tremendous number of rods in their retinae. In addition, there are about 2.4 million to 3 million ganglion cells in the human visual system, the axons of these cells form the 2 optic nerves, 1 to 2% of them photosensitive.The pineal and parapineal glands are photoreceptive in non-mammalian vertebrates, but not in mammals. Birds have photoactive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons within the paraventricular organ that respond to light in the absence of input from the eyes or neurotransmitters. Invertebrate photoreceptors in organisms such as insects and molluscs are different in both their morphological organization and their underlying biochemical pathways. Described here are human photoreceptors.