1 - JustAnswer
... a. Increase the expected rate of return. b. Raise more debt capital. c. Offer stock at a higher price. d. Increase sales. 24. If an investor had a choice of receiving $1,000 today, or $1,000 in five years, which would the average investor prefer? B a. $1,000 in five years because they are not good a ...
... a. Increase the expected rate of return. b. Raise more debt capital. c. Offer stock at a higher price. d. Increase sales. 24. If an investor had a choice of receiving $1,000 today, or $1,000 in five years, which would the average investor prefer? B a. $1,000 in five years because they are not good a ...
November
... level of the nominal interest rate. The condition implies a monetary policy conducted in such a way that the effects of shocks due to the randomness of the money growth rate on private agents' optimal consumption are nullified. More... Optimal Investment Decisions When Time Horizon is Uncertain Many ...
... level of the nominal interest rate. The condition implies a monetary policy conducted in such a way that the effects of shocks due to the randomness of the money growth rate on private agents' optimal consumption are nullified. More... Optimal Investment Decisions When Time Horizon is Uncertain Many ...
An introduction to diversification by risk factor PORTFOLIO INSIGHTS
... example, the credit risk of an Australian government bond is significantly lower than the duration risk of a 100-year Irish government bond. But we’ve by no means exhausted the number of risk factors investors are exposed to. For example, those who outsource portfolio construction and investment man ...
... example, the credit risk of an Australian government bond is significantly lower than the duration risk of a 100-year Irish government bond. But we’ve by no means exhausted the number of risk factors investors are exposed to. For example, those who outsource portfolio construction and investment man ...
efficiency factor - Economic Regulation Authority
... Regulator-General, Victoria (ORGV) with respect to onshore gas reticulation and onshore gas transmission pipeline system tariff determination methodology including the cost of capital. The process of tariff determination during the course of 1997 and 1998 attracted submissions and commentary from so ...
... Regulator-General, Victoria (ORGV) with respect to onshore gas reticulation and onshore gas transmission pipeline system tariff determination methodology including the cost of capital. The process of tariff determination during the course of 1997 and 1998 attracted submissions and commentary from so ...
Ch10std
... Studies of stock returns indicate they are approximately normally distributed. Two statistics describe a normal distribution, the mean and the standard deviation (which is the square root of the variance). The standard deviation shows how spread out is the distribution. For stock returns, a more ...
... Studies of stock returns indicate they are approximately normally distributed. Two statistics describe a normal distribution, the mean and the standard deviation (which is the square root of the variance). The standard deviation shows how spread out is the distribution. For stock returns, a more ...
„unanimity” literature and the security market line criterion
... The “unanimity” literature, on the other hand, has demonstrated that the value maximization objective will be acceptable to all shareholders only under very restrictive conditions. In fact, it is now known that only in specific cases will there be any objective function at all which is unanimously s ...
... The “unanimity” literature, on the other hand, has demonstrated that the value maximization objective will be acceptable to all shareholders only under very restrictive conditions. In fact, it is now known that only in specific cases will there be any objective function at all which is unanimously s ...
Chapter 13 - Carlin Business
... some market volatility • What are Market Timers? Constant “shifters” – Hope to capture the upside of rising stock prices while avoiding most of the downside ...
... some market volatility • What are Market Timers? Constant “shifters” – Hope to capture the upside of rising stock prices while avoiding most of the downside ...
Risk and Rates of Return
... Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) … the relevant riskiness of an individual stock is its contribution to the riskiness of a well-diversified portfolio, since all investors can be well-diversified if they wish; the “market” offers no compensation for undertaking diversifiable risk … the risk that ...
... Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) … the relevant riskiness of an individual stock is its contribution to the riskiness of a well-diversified portfolio, since all investors can be well-diversified if they wish; the “market” offers no compensation for undertaking diversifiable risk … the risk that ...
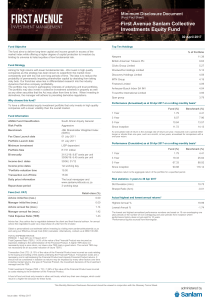
First Avenue Sanlam Collective Investments Equity Fund
... capital or the return of a portfolio. The performance of the portfolio depends on the underlying assets and variable market factors. Performance is based on NAV to NAV calculations with income reinvestments done on the ex-div date. Lump sum investment performances are quoted. The portfolio may inves ...
... capital or the return of a portfolio. The performance of the portfolio depends on the underlying assets and variable market factors. Performance is based on NAV to NAV calculations with income reinvestments done on the ex-div date. Lump sum investment performances are quoted. The portfolio may inves ...
Aberdeen Global – Select Euro High Yield Bond Fund
... It does not include any initial charges or the cost of buying and selling stocks for the Funds. The Ongoing Charges figure can help you compare the annual operating expenses of different Funds. ...
... It does not include any initial charges or the cost of buying and selling stocks for the Funds. The Ongoing Charges figure can help you compare the annual operating expenses of different Funds. ...
Diversification
... NAV = (Market value of fund securities – fund liabilities ÷ number of shares outstanding. NAV is usually calculated once per day at the close of trading except for EFTs. ...
... NAV = (Market value of fund securities – fund liabilities ÷ number of shares outstanding. NAV is usually calculated once per day at the close of trading except for EFTs. ...
Stocks
... NAV = (Market value of fund securities – fund liabilities ÷ number of shares outstanding. NAV is usually calculated once per day at the close of trading except for EFTs. ...
... NAV = (Market value of fund securities – fund liabilities ÷ number of shares outstanding. NAV is usually calculated once per day at the close of trading except for EFTs. ...
File
... Optimum portfolio and CML: Given the feasible set highest possible utility function gives us O.P. and the tangency is CML ...
... Optimum portfolio and CML: Given the feasible set highest possible utility function gives us O.P. and the tangency is CML ...
Dan diBartolomeo
... to be around very long, the economy is in a bad way • Low equity valuations and high leverage equate to short life expectancy – Higher leverage can be sustained with higher growth rates that cause higher equity valuations We propose “revenue weighted” expected average life as a measure of systemic s ...
... to be around very long, the economy is in a bad way • Low equity valuations and high leverage equate to short life expectancy – Higher leverage can be sustained with higher growth rates that cause higher equity valuations We propose “revenue weighted” expected average life as a measure of systemic s ...
KCR-Presentation-Final_a
... Long/Cash/Short – One needs the ability to make money in down markets Market Timing – There's a time to be long (bullish), short (bearish), and cash (neutral) as many asset classes as possible ...
... Long/Cash/Short – One needs the ability to make money in down markets Market Timing – There's a time to be long (bullish), short (bearish), and cash (neutral) as many asset classes as possible ...
Utility and Telecommunications Fund
... market and reduced liquidity for certain bonds held by the fund. In general, when interest rates rise, bond values fall and investors may lose principal value. Interest-rate changes and their impact on the fund and its share price can be sudden and unpredictable. The use of derivatives may reduce re ...
... market and reduced liquidity for certain bonds held by the fund. In general, when interest rates rise, bond values fall and investors may lose principal value. Interest-rate changes and their impact on the fund and its share price can be sudden and unpredictable. The use of derivatives may reduce re ...
Redefining Indexing Using Smart Beta Strategies
... Management”3 might also be terms that can be used. Smart Beta occupies the space between traditional passive and active investing4 by taking systematic rulesbased tilts from market capitalization-weighted indices with a focus on simplicity, transparency, large capacity, liquidity, diversification, a ...
... Management”3 might also be terms that can be used. Smart Beta occupies the space between traditional passive and active investing4 by taking systematic rulesbased tilts from market capitalization-weighted indices with a focus on simplicity, transparency, large capacity, liquidity, diversification, a ...
Download Document
... larger than the effect of the mean itself. As such, switching to computing variance around a conditional mean of zero has little effect. However, in cases where an asset return is consistently positive (or consistently negative for long periods), the use of a conditional mean will produce a higher e ...
... larger than the effect of the mean itself. As such, switching to computing variance around a conditional mean of zero has little effect. However, in cases where an asset return is consistently positive (or consistently negative for long periods), the use of a conditional mean will produce a higher e ...
The Case for a Concentrated Portfolio
... outperformance decreases. Further, a large number of different securities in a portfolio typically means the equity positions are so small (sometimes only 0.2% to 1%) that no individual stock can affect portfolio returns—negatively or positively—with any real degree of significance. The result is of ...
... outperformance decreases. Further, a large number of different securities in a portfolio typically means the equity positions are so small (sometimes only 0.2% to 1%) that no individual stock can affect portfolio returns—negatively or positively—with any real degree of significance. The result is of ...
Finance&ExcelCh10
... • Efficient Markets = new information is assimilated quickly & correctly into financial asset prices. The correctly priced assets help to efficiently allocate resources in the capitalist system. • Financial Markets are efficient in that when new information becomes available, people buying and selli ...
... • Efficient Markets = new information is assimilated quickly & correctly into financial asset prices. The correctly priced assets help to efficiently allocate resources in the capitalist system. • Financial Markets are efficient in that when new information becomes available, people buying and selli ...
EMBA Corporate Finance - Home Page of Dr. Rodney Boehme
... The CAPM is relatively simple. Firm specific risk is diversifiable and irrelevant. Market (macroeconomic) risk is not diversifiable and is therefore relevant. Required returns are a function of the risk-free rate, market risk premium, and the Beta. The CAPM is very difficult to test empirically. It’ ...
... The CAPM is relatively simple. Firm specific risk is diversifiable and irrelevant. Market (macroeconomic) risk is not diversifiable and is therefore relevant. Required returns are a function of the risk-free rate, market risk premium, and the Beta. The CAPM is very difficult to test empirically. It’ ...
the full document
... if so, are subject to the relevant FAIS disclosure requirements. A fund of funds is a portfolio that invests in portfolios of CISs that levy their own charges which could result in a higher fee structure for the fund of funds. A feeder fund is a portfolio that invests in a single portfolio of a CIS, ...
... if so, are subject to the relevant FAIS disclosure requirements. A fund of funds is a portfolio that invests in portfolios of CISs that levy their own charges which could result in a higher fee structure for the fund of funds. A feeder fund is a portfolio that invests in a single portfolio of a CIS, ...
Lower Returns Likely in the Years Ahead
... are on sale.” Six years later, we think circumstances are much different. In fact, we expect returns from both bond and stock portfolios will likely be much more modest in the years just ahead. The outlook for bonds: It is easy to see why we expect modest returns from bonds over the next several yea ...
... are on sale.” Six years later, we think circumstances are much different. In fact, we expect returns from both bond and stock portfolios will likely be much more modest in the years just ahead. The outlook for bonds: It is easy to see why we expect modest returns from bonds over the next several yea ...
Traditional insurance products will not go out of vogue - Sa-Dhan
... ULIPs by design are long-term in nature where customers enjoy flexibility (to switch between debt and equity) and transparency (charge structure). They are products that have been chosen by the customer because of these characteristics and also because they help the customers meet the need of enjoyi ...
... ULIPs by design are long-term in nature where customers enjoy flexibility (to switch between debt and equity) and transparency (charge structure). They are products that have been chosen by the customer because of these characteristics and also because they help the customers meet the need of enjoyi ...
Collective Investments
... underlying assets. Their price can therefore be above or below the value of all the assets in the fund. This is called trading at a ‘premium’ or ‘discount’. In addition to the money invested by shareholders, the investment trust can borrow to make additional ...
... underlying assets. Their price can therefore be above or below the value of all the assets in the fund. This is called trading at a ‘premium’ or ‘discount’. In addition to the money invested by shareholders, the investment trust can borrow to make additional ...
Beta (finance)

In finance, the beta (β) of an investment is a measure of the risk arising from exposure to general market movements as opposed to idiosyncratic factors. The market portfolio of all investable assets has a beta of exactly 1. A beta below 1 can indicate either an investment with lower volatility than the market, or a volatile investment whose price movements are not highly correlated with the market. An example of the first is a treasury bill: the price does not go up or down a lot, so it has a low beta. An example of the second is gold. The price of gold does go up and down a lot, but not in the same direction or at the same time as the market.A beta greater than one generally means that the asset both is volatile and tends to move up and down with the market. An example is a stock in a big technology company. Negative betas are possible for investments that tend to go down when the market goes up, and vice versa. There are few fundamental investments with consistent and significant negative betas, but some derivatives like equity put options can have large negative betas.Beta is important because it measures the risk of an investment that cannot be reduced by diversification. It does not measure the risk of an investment held on a stand-alone basis, but the amount of risk the investment adds to an already-diversified portfolio. In the capital asset pricing model, beta risk is the only kind of risk for which investors should receive an expected return higher than the risk-free rate of interest.The definition above covers only theoretical beta. The term is used in many related ways in finance. For example, the betas commonly quoted in mutual fund analyses generally measure the risk of the fund arising from exposure to a benchmark for the fund, rather than from exposure to the entire market portfolio. Thus they measure the amount of risk the fund adds to a diversified portfolio of funds of the same type, rather than to a portfolio diversified among all fund types.Beta decay refers to the tendency for a company with a high beta coefficient (β > 1) to have its beta coefficient decline to the market beta. It is an example of regression toward the mean.