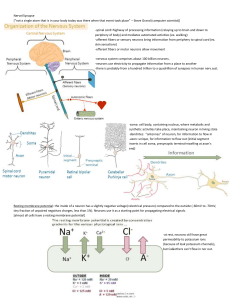
Synaptic Transmission
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
23Neurotransmitter22012-09
... Dopamine is transmitted via three major pathways: 1- The first extends from the substantia nigra to the caudate nucleus-putamen (neostriatum) and is concerned with sensory stimuli and movement. 2- The second pathway projects from the ventral tegmentum to the mesolimbic forebrain and is thought to be ...
... Dopamine is transmitted via three major pathways: 1- The first extends from the substantia nigra to the caudate nucleus-putamen (neostriatum) and is concerned with sensory stimuli and movement. 2- The second pathway projects from the ventral tegmentum to the mesolimbic forebrain and is thought to be ...
Neuroscience in PT: Introduction and Review
... of presynaptic facilitation and inhibition? • Describe the structure of a chemical synapse and the events of signal transmission at the synapse. • Compare and contrast neurotransmitters versus neuromodulators. • Discuss the functions of neurotransmitters and the associated clinical implications. ...
... of presynaptic facilitation and inhibition? • Describe the structure of a chemical synapse and the events of signal transmission at the synapse. • Compare and contrast neurotransmitters versus neuromodulators. • Discuss the functions of neurotransmitters and the associated clinical implications. ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -The main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain is glutamate (amino acid), the most prevalent neurotransmitter in nervous system. -The EPSP is a small, transient depolarization of the postsynaptic spine (1 to 2 mV and about 20 msec). -From 50 to 100 EPSPs must sum at the initial segment to initia ...
... -The main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain is glutamate (amino acid), the most prevalent neurotransmitter in nervous system. -The EPSP is a small, transient depolarization of the postsynaptic spine (1 to 2 mV and about 20 msec). -From 50 to 100 EPSPs must sum at the initial segment to initia ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... ‘Classical’ neurotransmitters that possess ligand-gated ion channel receptors and operate in this manner include acetylcholine (ACh, an excitatory transmitter used at the neuromuscular junction and in the cerebral cortex), glutamate (the main excitatory transmitter in the brain) and GABA (γ-aminobut ...
... ‘Classical’ neurotransmitters that possess ligand-gated ion channel receptors and operate in this manner include acetylcholine (ACh, an excitatory transmitter used at the neuromuscular junction and in the cerebral cortex), glutamate (the main excitatory transmitter in the brain) and GABA (γ-aminobut ...
overview of neural f..
... When a neurotransmitter and receptor combine together two possibilities: 1. The resting potential may become less negative (an excitatory post-synaptic potential - E.P.S.P). Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
... When a neurotransmitter and receptor combine together two possibilities: 1. The resting potential may become less negative (an excitatory post-synaptic potential - E.P.S.P). Effect of E.P.S.P is to INCREASE probability that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
Ca 2+
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
Brainsignals, Synaptic Transmission and Short
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
... describe the observation that synaptic strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a f ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
... Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term… Psychology 2617 ...
IV. Conduction Across Synapses
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
... neurotransmitter transported back into pre-synaptic neuron for re-use ex: norepinephrine dopamine serotonin D. Neurotransmitters chemical messengers at synapses most are excitatory – depolarize post-synaptic membrane some are inhibitory – hyperpolarize post-synaptic membrane effect of neurotransmitt ...
Molecular basis of learning in the hippocampus and the amygdala
... Some parts of these two types pathways are probably common. However, there is a need of determination of theirs cascades, especially on their nuclear level. It is only known that eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (EEF2) can be nuclear activator. Some researchers claim that its effect is a translation o ...
... Some parts of these two types pathways are probably common. However, there is a need of determination of theirs cascades, especially on their nuclear level. It is only known that eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (EEF2) can be nuclear activator. Some researchers claim that its effect is a translation o ...
Diapositive 1
... Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-like NT (Cannabis effects) Vigorous firing of action potentials in the postsynaptic neuron causes voltage-gated calcium channels to open, Ca2+ enters the cell in large quantities, and intracellular [Ca2+] rises. ...
... Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-like NT (Cannabis effects) Vigorous firing of action potentials in the postsynaptic neuron causes voltage-gated calcium channels to open, Ca2+ enters the cell in large quantities, and intracellular [Ca2+] rises. ...
Slide ()
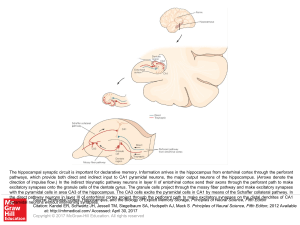
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
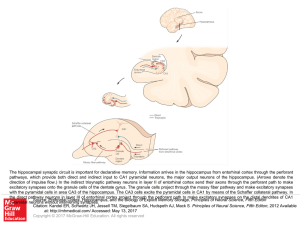
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Neurotransmitters
... Glutamate/learning and memory Long term Potentiation LTP Biochemical reactions Drugs and Neurotransmitters (look at good info) ...
... Glutamate/learning and memory Long term Potentiation LTP Biochemical reactions Drugs and Neurotransmitters (look at good info) ...
Slide ()
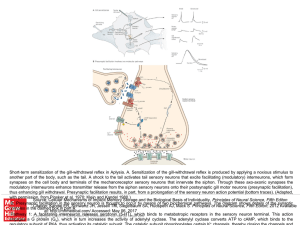
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... calculation. This project proved an abortion, but it brought another climax to AI research and NN research. ...
... calculation. This project proved an abortion, but it brought another climax to AI research and NN research. ...
neuroplasticity 2016
... – In people with upper extremity amputations, much of the region of the cortex that use to correspond to the U/E becomes reorganized. The area can then provide a presentation of the face. ...
... – In people with upper extremity amputations, much of the region of the cortex that use to correspond to the U/E becomes reorganized. The area can then provide a presentation of the face. ...
(580.422) Lecture 7, Synaptic Transmission
... On the postsynaptic side, neurotransmitter binds to a receptor (9). Ionotropic receptors open an ion channel (10) for some ion, allowing a current to flow. The effect of the synapse depends on which ion the channel conducts. Metabotropic receptors are coupled to G-proteins and/or kinases which prod ...
... On the postsynaptic side, neurotransmitter binds to a receptor (9). Ionotropic receptors open an ion channel (10) for some ion, allowing a current to flow. The effect of the synapse depends on which ion the channel conducts. Metabotropic receptors are coupled to G-proteins and/or kinases which prod ...
Postsynaptic Potential
... glutamine by glutamine synthetase • Released from the glia, • taken up by the nerve terminal, • converted back to glutamate by the enzyme glutaminase. ...
... glutamine by glutamine synthetase • Released from the glia, • taken up by the nerve terminal, • converted back to glutamate by the enzyme glutaminase. ...
Toxicology of the Nervous System
... • Organic mercury from fish is the most significant source of human exposure • Brain and nervous system toxicity ...
... • Organic mercury from fish is the most significant source of human exposure • Brain and nervous system toxicity ...
Lecture 5 Transmitters and receptors lecture 2015
... AMPA: a-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate Kainate: Kainic acid ...
... AMPA: a-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate Kainate: Kainic acid ...