No Slide Title
... Sensation and Neural Integration. The all or none law is supplemented by the Rate law which states that the strength of a stimulus is represented by the firing rate of an axon, despite the fact that the action potential remains constant. The rate of firing of an axon is determined by whether th ...
... Sensation and Neural Integration. The all or none law is supplemented by the Rate law which states that the strength of a stimulus is represented by the firing rate of an axon, despite the fact that the action potential remains constant. The rate of firing of an axon is determined by whether th ...
KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural
... properties of the receptor and on the receptor’s location in the brain. The number of neurotransmitters that a neuron can manufacture varies. Some neurons manufacture only one type of neurotransmitter, whereas other neurons manufacture two or more. Although estimates vary depending on the source, re ...
... properties of the receptor and on the receptor’s location in the brain. The number of neurotransmitters that a neuron can manufacture varies. Some neurons manufacture only one type of neurotransmitter, whereas other neurons manufacture two or more. Although estimates vary depending on the source, re ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
A. Normal OD development - Molecular and Cell Biology
... But, each layer 4 cortical neuron receives inputs from many LGN axons representing the same eye, why don’t these axons compete with each other? If two presynaptic cells are correlated with each other, they do not compete! ...
... But, each layer 4 cortical neuron receives inputs from many LGN axons representing the same eye, why don’t these axons compete with each other? If two presynaptic cells are correlated with each other, they do not compete! ...
Physiology2 - Sheet#8 - Dr.Loai Alzgoul - Done By: Mais
... Norepinephrine (α and β family receptors) It's a slow neurotransmitter (neuromodulator) *The cell bodies of neurons that release norepinephrine are located in an area in the brain stem which is called "nucleus locus coeruleus", while their axons are distributed throughout the brain and the body . *A ...
... Norepinephrine (α and β family receptors) It's a slow neurotransmitter (neuromodulator) *The cell bodies of neurons that release norepinephrine are located in an area in the brain stem which is called "nucleus locus coeruleus", while their axons are distributed throughout the brain and the body . *A ...
Levetiracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsy
... hilus lead to mossy fiber sprouting in the inner and outer molecular layers. ...
... hilus lead to mossy fiber sprouting in the inner and outer molecular layers. ...
Real Neurons for Engineers
... their membranes. This changes ion concentrations and the potential across their membrane. The ions then function in various ways to cause changes in the neuron. • Bob will teach this. I will show you how to model it. ...
... their membranes. This changes ion concentrations and the potential across their membrane. The ions then function in various ways to cause changes in the neuron. • Bob will teach this. I will show you how to model it. ...
SChapter 12
... -Continuous propagation-Saltatory propagation▫Axon diameter affects propagation speed. -Type A fibers -Type B fibers -Type C fibers Synaptic Activity ▪Electric events of messages moving from one place to another are called nerve impulses. ▪General Properties of Synapses ▫Electrical synapse -Extremel ...
... -Continuous propagation-Saltatory propagation▫Axon diameter affects propagation speed. -Type A fibers -Type B fibers -Type C fibers Synaptic Activity ▪Electric events of messages moving from one place to another are called nerve impulses. ▪General Properties of Synapses ▫Electrical synapse -Extremel ...
Synaptic Transmission - Interactive Physiology
... • Thus the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscle is direct, fast, and excitatory. • The first of two neurons in the sympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is cholinergic. • The first of two neurons in the parasympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is also cholinergic. • The second n ...
... • Thus the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscle is direct, fast, and excitatory. • The first of two neurons in the sympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is cholinergic. • The first of two neurons in the parasympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is also cholinergic. • The second n ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... • Thus the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscle is direct, fast, and excitatory. • The first of two neurons in the sympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is cholinergic. • The first of two neurons in the parasympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is also cholinergic. • The second n ...
... • Thus the action of acetylcholine on skeletal muscle is direct, fast, and excitatory. • The first of two neurons in the sympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is cholinergic. • The first of two neurons in the parasympathetic chain, the preganglionic neuron, is also cholinergic. • The second n ...
Key Transmitters - Sinauer Associates
... current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (see below). The consequent entry of Ca2+ ions then induces a variety of downstream effect ...
... current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (see below). The consequent entry of Ca2+ ions then induces a variety of downstream effect ...
Synapse Formation in the Peripheral and Central Nervous System
... Clustering of ACh-R: A) Aggregation of existing receptors ...
... Clustering of ACh-R: A) Aggregation of existing receptors ...
Synapse formation
... • That is… that neurons which have been stimulated will have a greater ‘potential’ to fire when they are stimulated again. ...
... • That is… that neurons which have been stimulated will have a greater ‘potential’ to fire when they are stimulated again. ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
L23-Neurotransmitter
... Dopamine is transmitted via three major pathways: 1- The first extends from the substantia nigra to the caudate nucleus-putamen (neostriatum) and is concerned with sensory stimuli and movement. 2- The second pathway projects from the ventral tegmentum to the mesolimbic forebrain and is thought to be ...
... Dopamine is transmitted via three major pathways: 1- The first extends from the substantia nigra to the caudate nucleus-putamen (neostriatum) and is concerned with sensory stimuli and movement. 2- The second pathway projects from the ventral tegmentum to the mesolimbic forebrain and is thought to be ...
10synapse & neurotransmitter
... • EPSPs and IPSPs are graded potential [local]. They can be summated [added]. • Types of Summation 1. Temporal Summation 2. Spatial Summation ...
... • EPSPs and IPSPs are graded potential [local]. They can be summated [added]. • Types of Summation 1. Temporal Summation 2. Spatial Summation ...
Topic 5
... a connexon. However, as shown here, the term connexon can also be applied to the aggregate cluster of proteins. ...
... a connexon. However, as shown here, the term connexon can also be applied to the aggregate cluster of proteins. ...
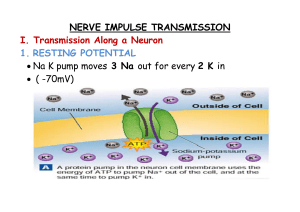
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
The Synapse - University of Toronto
... • Are associated with an ion channel • N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA): composed of 4 or 5 subunits (NR1 and NR2a,b,c,d) • -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA): composed of 4 or 5 subunits (GluR1-4) • Kainate receptors: GluR5-7, KA1-2 These receptors are presumed to have differen ...
... • Are associated with an ion channel • N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA): composed of 4 or 5 subunits (NR1 and NR2a,b,c,d) • -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA): composed of 4 or 5 subunits (GluR1-4) • Kainate receptors: GluR5-7, KA1-2 These receptors are presumed to have differen ...
Q24 Describe the mechanism of action of the
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
... Opioid receptors are serpentine structures which are linked to inhibitory G-‐proteins They are present both pre and post synaptically. o Presynaptically, activation causes closure of voltage gated calcium channel ...
3FA3M8-C-B4-Handout
... This eliminates any interindividual variability that may be present, such as age or motor threshold, because the individual acts as both the test subject and it’s own control. ...
... This eliminates any interindividual variability that may be present, such as age or motor threshold, because the individual acts as both the test subject and it’s own control. ...
How do neurotransmitters generate electrochemical signals in
... 1. binds to a ligand-activated ion (e.g., Na+) channel, causing the channel to open or close, producing an immediate change in potential (EPSP or IPSP) on the postsynaptic membrane (Figure A). 2. triggers the synthesis of a second messenger which: (a) binds to a ligand-activated ion channel, causing ...
... 1. binds to a ligand-activated ion (e.g., Na+) channel, causing the channel to open or close, producing an immediate change in potential (EPSP or IPSP) on the postsynaptic membrane (Figure A). 2. triggers the synthesis of a second messenger which: (a) binds to a ligand-activated ion channel, causing ...
Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... alter the membrane potentials of postsynaptic neurons. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter found in the end plates of many nerve cells. It acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter on many postsynaptic neurons by opening Sodium ion channels. ...
... alter the membrane potentials of postsynaptic neurons. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter found in the end plates of many nerve cells. It acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter on many postsynaptic neurons by opening Sodium ion channels. ...