Chapter 5.1
... • The last of the three seasons was the “drought” season. During the drought, the harvest took place. ...
... • The last of the three seasons was the “drought” season. During the drought, the harvest took place. ...
The Nile River Valley
... • The last of the three seasons was the “drought” season. During the drought, the harvest took place. ...
... • The last of the three seasons was the “drought” season. During the drought, the harvest took place. ...
The Nile River Valley - Rutherford County Schools
... • The last of the three seasons was the “drought” season. During the drought, the harvest took place. ...
... • The last of the three seasons was the “drought” season. During the drought, the harvest took place. ...
Untitled 3
... title used by the rulers of Egypt. The title pharaoh means “great house.” Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Menes built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile Delta. The city was later named Memphis. For centuries, Memphis was the pol ...
... title used by the rulers of Egypt. The title pharaoh means “great house.” Menes also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. Menes built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile Delta. The city was later named Memphis. For centuries, Memphis was the pol ...
Ancient Egypt - Northside Middle School
... • The Nile forms branches near the Mediterranean Sea. These branches fan out over an area of fertile soil called a delta. ...
... • The Nile forms branches near the Mediterranean Sea. These branches fan out over an area of fertile soil called a delta. ...
Ancient Egypt - Allenwood BNS
... depended on the waters of the Nile for its survival. The rivers yearly floods left its regular gift of silt That made fertile land for crops. The river provided Water for drinking and irrigation and was Egypt's main transport route ...
... depended on the waters of the Nile for its survival. The rivers yearly floods left its regular gift of silt That made fertile land for crops. The river provided Water for drinking and irrigation and was Egypt's main transport route ...
Test 5 Key - Ms. Anderson`s Science and Social Studies Page
... 18. Describe Egypt’s invasion of Nubia. Egyptian armies invaded in 1400 BC--the was lasted 50 years. Egyptians ruled for the next 700 years. 19. How did the Nubians and Egyptians influence one another? Nubians adopted Egyptian beliefs and customs. They learned to make tools out of copper and bronze ...
... 18. Describe Egypt’s invasion of Nubia. Egyptian armies invaded in 1400 BC--the was lasted 50 years. Egyptians ruled for the next 700 years. 19. How did the Nubians and Egyptians influence one another? Nubians adopted Egyptian beliefs and customs. They learned to make tools out of copper and bronze ...
Review sheet 2017
... in the fertile Nile River valley. The Nile River provided fresh water in an area that was mostly desert. The topography of the Nile River valley made the land good for farming. The valley also supported useful vegetation like reeds and papyrus. The Nile flows from South to North. The end of the Nile ...
... in the fertile Nile River valley. The Nile River provided fresh water in an area that was mostly desert. The topography of the Nile River valley made the land good for farming. The valley also supported useful vegetation like reeds and papyrus. The Nile flows from South to North. The end of the Nile ...
Chapter 4 Egypt Outline - Methacton School District
... finally new pharaohs brought peace and a new period pharaohs had less power, buried in cliffs in hillsides, began trading with other countries 1786 BC the Hyksos from western Asia invaded crossed the desert in horsedrawn chariots and used weapons made of iron and bronze. ruled Egypt for ab ...
... finally new pharaohs brought peace and a new period pharaohs had less power, buried in cliffs in hillsides, began trading with other countries 1786 BC the Hyksos from western Asia invaded crossed the desert in horsedrawn chariots and used weapons made of iron and bronze. ruled Egypt for ab ...
Module 2 - Travel Biz Monitor
... more than 40,000 years. An amazing example of that period is the swimmers cave in WadiSura “Valley of Pictures” in Western Desert with fantastic paintings estimated to be produced around 7000 BC. As from 5000 BC, archaeologists can easily recognize a real human cultural production, namely the Baradi ...
... more than 40,000 years. An amazing example of that period is the swimmers cave in WadiSura “Valley of Pictures” in Western Desert with fantastic paintings estimated to be produced around 7000 BC. As from 5000 BC, archaeologists can easily recognize a real human cultural production, namely the Baradi ...
Egypt
... • Menes was probably Egypt’s first pharaoh, the title used by the rulers of Egypt. • He also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. • The First Dynasty lasted for about 200 years and extended Egyptian territory southward along the Nile. ...
... • Menes was probably Egypt’s first pharaoh, the title used by the rulers of Egypt. • He also founded Egypt’s first dynasty, or series of rulers from the same family. • The First Dynasty lasted for about 200 years and extended Egyptian territory southward along the Nile. ...
File
... He was considered to be Egypt’s first Pharaoh. He founded Egypt’s first dynasty. He built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile delta, later named Memphis. He invaded Lower Egypt, unifying Upper and Lower Egypt. 11. Tell how the words pharaoh and dynasty are related. Pg. 281 Pharaoh is ...
... He was considered to be Egypt’s first Pharaoh. He founded Egypt’s first dynasty. He built a new capital city at the southern tip of the Nile delta, later named Memphis. He invaded Lower Egypt, unifying Upper and Lower Egypt. 11. Tell how the words pharaoh and dynasty are related. Pg. 281 Pharaoh is ...
TODAY*s OBJECTIVES:
... Lower Egypt = Delta Where most of Egypt’s history focused Upper Egypt developed later upstream Nile provided reliable transportation to go north, drift with the current toward the sea to go south, sail catching the Mediterranean breeze ...
... Lower Egypt = Delta Where most of Egypt’s history focused Upper Egypt developed later upstream Nile provided reliable transportation to go north, drift with the current toward the sea to go south, sail catching the Mediterranean breeze ...
Chapter 2, Section 2
... • Egyptians thought their pharaoh was a god on earth who controlled Egypt’s welfare. ...
... • Egyptians thought their pharaoh was a god on earth who controlled Egypt’s welfare. ...
Chapter 5 Lesson 3 Egypt`s Empire A Golden Age
... -‐Egyptians traded with Phoenicians for wood -‐Hatshepsut used some of this wealth to build monuments ...
... -‐Egyptians traded with Phoenicians for wood -‐Hatshepsut used some of this wealth to build monuments ...
Pyramids on the Nile - mrs
... • If floodwaters were few feet lower than usual, amount of silt, crops, and food was reduced • If waters were higher, water could spread beyond fields to the mud-brick villages nearby and destroy homes ...
... • If floodwaters were few feet lower than usual, amount of silt, crops, and food was reduced • If waters were higher, water could spread beyond fields to the mud-brick villages nearby and destroy homes ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... • If floodwaters were few feet lower than usual, amount of silt, crops, and food was reduced • If waters were higher, water could spread beyond fields to the mud-brick villages nearby and destroy homes ...
... • If floodwaters were few feet lower than usual, amount of silt, crops, and food was reduced • If waters were higher, water could spread beyond fields to the mud-brick villages nearby and destroy homes ...
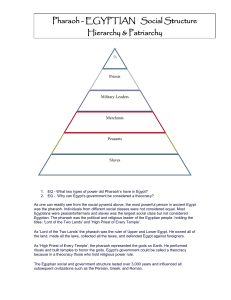
r EQ - What two types of power did Pharaoh`s have in Egypt? EQ
... As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh represented the gods on Earth. He performed rituals and built temples to honor the gods. Egypt’s government could be called a theocracy because in a theocracy those who hold religious power rule. The Egyptian social and government structure lasted over 3 ...
... As 'High Priest of Every Temple', the pharaoh represented the gods on Earth. He performed rituals and built temples to honor the gods. Egypt’s government could be called a theocracy because in a theocracy those who hold religious power rule. The Egyptian social and government structure lasted over 3 ...
Ancient Egypt - Saugerties Central Schools
... settled along the Nile River. • The Nile was the lifeblood of ancient Egypt because of its fertile soil for farming. • It made life possible in the otherwise hot, dry desert of Egypt. • It was the major source of water for bathing, drinking, cooking, and irrigation. ...
... settled along the Nile River. • The Nile was the lifeblood of ancient Egypt because of its fertile soil for farming. • It made life possible in the otherwise hot, dry desert of Egypt. • It was the major source of water for bathing, drinking, cooking, and irrigation. ...
Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death
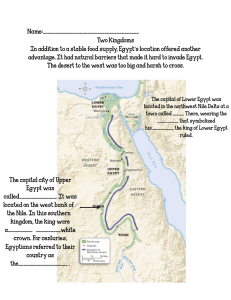
... The Beginnings of Ancient Egypt 6,000 B.C.--The first inhabitants begin to settle around the Nile River. 3,100 B.C.--The King of Upper Egypt named Menes, united Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes makes the city of Memphis his capital city. ...
... The Beginnings of Ancient Egypt 6,000 B.C.--The first inhabitants begin to settle around the Nile River. 3,100 B.C.--The King of Upper Egypt named Menes, united Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes makes the city of Memphis his capital city. ...
Lesson 5.3 Egypt*s Empire
... Mediterranean Sea where present day Lebanon is located. • People in that region were called Phoenicians, and culturally had a large impact on other societies with their invention of an alphabet and a system of writing different from other regions. ...
... Mediterranean Sea where present day Lebanon is located. • People in that region were called Phoenicians, and culturally had a large impact on other societies with their invention of an alphabet and a system of writing different from other regions. ...
Document
... • The Nile was the source of life and path to immortality • Egyptians lived on Eastern side but buried on Western side – River was symbol of passage of one life to next ...
... • The Nile was the source of life and path to immortality • Egyptians lived on Eastern side but buried on Western side – River was symbol of passage of one life to next ...