Chapter 4 Section 1-‐ Egypt Under the Pharaohs Titles Notes QCIPL
... major role in the reason for mummification -‐Isis! his wife and mother goddess of Egypt represented love, caring, and protection -‐Horus! the son of the two gods above, according to legend he United ...
... major role in the reason for mummification -‐Isis! his wife and mother goddess of Egypt represented love, caring, and protection -‐Horus! the son of the two gods above, according to legend he United ...
Ancient Egypt
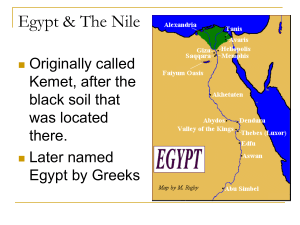
... Egypt & The Nile Originally called Kemet, after the black soil that was located there. Later named Egypt by Greeks ...
... Egypt & The Nile Originally called Kemet, after the black soil that was located there. Later named Egypt by Greeks ...
Early Egyptian Civilization
... • It is important to note that no type of writing would entirely replace another, but it would merely restrict the other writings to specific domains and be restricted itself to other domains. Thus demotic would become the writing of the administration from the 26th Dynasty on, but it did not entire ...
... • It is important to note that no type of writing would entirely replace another, but it would merely restrict the other writings to specific domains and be restricted itself to other domains. Thus demotic would become the writing of the administration from the 26th Dynasty on, but it did not entire ...
The History Ancient Egypt
... Daily life in ancient Egypt _____________ around the Nile and the fertile land along its banks. The yearly flooding of the Nile enriched the soil and brought good harvests and wealth to the land. The ancient Egyptians thought of Egypt as being divided into ...
... Daily life in ancient Egypt _____________ around the Nile and the fertile land along its banks. The yearly flooding of the Nile enriched the soil and brought good harvests and wealth to the land. The ancient Egyptians thought of Egypt as being divided into ...
Egyptian Civilization Fact Sheet
... the soul of Ptah.” (Ptah was an early Egyptian god). b. Egyptians called their land Kemet – “Black land”, or “Fertile land.” They called the land outside the Nile Deshret , the “Red land.” c. Series of kingdoms that developed along the Nile River Valley in present-day Egypt. d. Egypt flourished by m ...
... the soul of Ptah.” (Ptah was an early Egyptian god). b. Egyptians called their land Kemet – “Black land”, or “Fertile land.” They called the land outside the Nile Deshret , the “Red land.” c. Series of kingdoms that developed along the Nile River Valley in present-day Egypt. d. Egypt flourished by m ...
Study Guide: Egypt and Kush
... • Located along a river whose flood brought silt and fertile land to farm ( Nile) • Cataracts were natural barrier • Rose from farming villages • Diversification of labor ...
... • Located along a river whose flood brought silt and fertile land to farm ( Nile) • Cataracts were natural barrier • Rose from farming villages • Diversification of labor ...
Ancient Egyptian History: Mr. Hermansen
... • Centralized political authority embodied in the absolute ruler the pharaoh in Egypt and the person of the King in the region of Kush (Nubia) • Imperialist expansion in the second millennium B.C.E. as the Egyptian army pushed into Palestine, Syria, and north Africa and south into Nubia and as the K ...
... • Centralized political authority embodied in the absolute ruler the pharaoh in Egypt and the person of the King in the region of Kush (Nubia) • Imperialist expansion in the second millennium B.C.E. as the Egyptian army pushed into Palestine, Syria, and north Africa and south into Nubia and as the K ...
Ancient Egyptian History: Mr. Hermansen
... • Centralized political authority embodied in the absolute ruler the pharaoh in Egypt and the person of the King in the region of Kush (Nubia) • Imperialist expansion in the second millennium B.C.E. as the Egyptian army pushed into Palestine, Syria, and north Africa and south into Nubia and as the K ...
... • Centralized political authority embodied in the absolute ruler the pharaoh in Egypt and the person of the King in the region of Kush (Nubia) • Imperialist expansion in the second millennium B.C.E. as the Egyptian army pushed into Palestine, Syria, and north Africa and south into Nubia and as the K ...
The hallmarks of ancient Egyptian civilization, such as art
... were constructed of wood or sandstone. It was also during this period that the Egyptian writing system was further developed: initially composed of a few symbols, by the end of the 3rd dynasty it had been expanded to include more than 200 symbols, both phonograms and ideograms. While funeral practi ...
... were constructed of wood or sandstone. It was also during this period that the Egyptian writing system was further developed: initially composed of a few symbols, by the end of the 3rd dynasty it had been expanded to include more than 200 symbols, both phonograms and ideograms. While funeral practi ...
Government in Ancient Egypt
... Leadership/ Government- How a civilization creates an organized way of leadership. Around 3100 BC, there were two separate kingdoms in Egypt, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Soon a•erwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unifica•on happened, it became the world’s first e ...
... Leadership/ Government- How a civilization creates an organized way of leadership. Around 3100 BC, there were two separate kingdoms in Egypt, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Soon a•erwards, King Narmer (from Upper Egypt) united the two kingdoms. When the unifica•on happened, it became the world’s first e ...
The Later Middle Ages
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
First Age of Empires - Elizabeth School District C-1
... Had a genuine respect for other cultures and practiced tolerance of local customs ...
... Had a genuine respect for other cultures and practiced tolerance of local customs ...
Chapter 4 notes
... The Egyptian pharaohs wanted people to remember just how rich and powerful they were. Some had huge statues of themselves made. They also had their people build great teams for them. When the pharaohs died their bodies were placed in the tombs. Jewelry, food, clothing – all of the pharaoh’s favorite ...
... The Egyptian pharaohs wanted people to remember just how rich and powerful they were. Some had huge statues of themselves made. They also had their people build great teams for them. When the pharaohs died their bodies were placed in the tombs. Jewelry, food, clothing – all of the pharaoh’s favorite ...
The Ancient Egyptians - Sire`s Ancient History
... • “Ruler of Foreign Lands” • Came from Syria or Palestine • Egyptians learned the art of war from the Hyksos • Hyksos introduced horses, chariots, and bronzed weapons • Hyksos driven out of Egypt and pushed back to Asia Minor by 1570 B.C. ...
... • “Ruler of Foreign Lands” • Came from Syria or Palestine • Egyptians learned the art of war from the Hyksos • Hyksos introduced horses, chariots, and bronzed weapons • Hyksos driven out of Egypt and pushed back to Asia Minor by 1570 B.C. ...
Ancient Egypt
... – Mummifies Job was to rap a dead body in a huge towel. – They did this because they thought when their body dies there soul moves on. – To make these Mummies they put salt on their body's to preserve them. ...
... – Mummifies Job was to rap a dead body in a huge towel. – They did this because they thought when their body dies there soul moves on. – To make these Mummies they put salt on their body's to preserve them. ...
Mr. Hessel: Global History I: Ancient Egypt
... Mr. Hessel: Global History I: Ancient Egypt "Protected by nature from enemies and blessed with natural resources, the Ancient Egyptians were more self-contained than most have been, but the need for the cedars of Lebanon brought them into the stream of influences emanating from Mesopotamia." Charles ...
... Mr. Hessel: Global History I: Ancient Egypt "Protected by nature from enemies and blessed with natural resources, the Ancient Egyptians were more self-contained than most have been, but the need for the cedars of Lebanon brought them into the stream of influences emanating from Mesopotamia." Charles ...
Study sheet for Egypt summative with answers
... believed in more than one god; Both based their gods and goddesses off of things in nature; Both societies used their river/rivers to trade; Egyptians were located along the Nile River while the Mesopotamians were between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers; Egyptians mummified their dead, while the Mes ...
... believed in more than one god; Both based their gods and goddesses off of things in nature; Both societies used their river/rivers to trade; Egyptians were located along the Nile River while the Mesopotamians were between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers; Egyptians mummified their dead, while the Mes ...
Ancient Egypt - Ms. Byrne's Social Studies Class Website
... • Egyptians believed in life after death • Believed the good lived in happiness • Believed the dead needed to take the things they would need with them • Believed the earthly body is needed as a home for the soul • Preserved the bodies of the dead ...
... • Egyptians believed in life after death • Believed the good lived in happiness • Believed the dead needed to take the things they would need with them • Believed the earthly body is needed as a home for the soul • Preserved the bodies of the dead ...
Ch 4 Notes
... Besides providing a stable and varied food diet, what other advantages did Egypt’s location provide for early Egyptians? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Besides providing a stable and varied food diet, what other advantages did Egypt’s location provide for early Egyptians? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ...
World History Key Terms Ancient River Valley Civilizations
... Nile River - the river along which Ancient Egypt developed. Provided Egypt with protection, water and silt which fertilized the soil. Silt - left behind on the soil after the Nile River flooded made the soil highly fertile for farming. Gift of the Nile - the rich soil left behind after flooding and ...
... Nile River - the river along which Ancient Egypt developed. Provided Egypt with protection, water and silt which fertilized the soil. Silt - left behind on the soil after the Nile River flooded made the soil highly fertile for farming. Gift of the Nile - the rich soil left behind after flooding and ...
Egypt: Nordic Desert EmpireMARCH OF THE TITANS
... overwhelming to ordinary Egyptians at the time, who at best lived in two story mud brick houses, and it is no surprise that the builder was eventually deified. The Sphinx and pyramids of Giza, circa 2500 BC. The Cheops pyramids are impressive today - by the standards of the time of their constructio ...
... overwhelming to ordinary Egyptians at the time, who at best lived in two story mud brick houses, and it is no surprise that the builder was eventually deified. The Sphinx and pyramids of Giza, circa 2500 BC. The Cheops pyramids are impressive today - by the standards of the time of their constructio ...
The Middle Kingdom was a golden age of peace, prosperity, and
... and Egypt faced threats from outsiders known as the Hyksos from Western Asia. The Hyksos were mighty warriors who crossed the deserts on horse-drawn chariots and used weapons made of bronze and iron. Egyptians fought on foot with copper and stone weapons and were no match for the Hyksos. The H ...
... and Egypt faced threats from outsiders known as the Hyksos from Western Asia. The Hyksos were mighty warriors who crossed the deserts on horse-drawn chariots and used weapons made of bronze and iron. Egyptians fought on foot with copper and stone weapons and were no match for the Hyksos. The H ...
Blank Jeopardy
... The “Gift of the Nile” means if it was not for the longest river in the world the Ancient Egyptians would not have any means of work and travel. The Nile’s floods gave water to the crops so Egypt could flourish. ...
... The “Gift of the Nile” means if it was not for the longest river in the world the Ancient Egyptians would not have any means of work and travel. The Nile’s floods gave water to the crops so Egypt could flourish. ...
The Kingdoms of Egypt
... The New Kingdom Early pharaohs of the New Kingdom evicted the Hyksos. The New Kingdom is remembered as a time of renaissance in artistic creation, but also as the end of dynastic rule. This period was also marred by corrupt priests and tombrobbing by government officials. A famed pharaoh of the new ...
... The New Kingdom Early pharaohs of the New Kingdom evicted the Hyksos. The New Kingdom is remembered as a time of renaissance in artistic creation, but also as the end of dynastic rule. This period was also marred by corrupt priests and tombrobbing by government officials. A famed pharaoh of the new ...