Age of Pharaohs
... heirs and after his death there was a civil war and instability for about 100 years. The 7th and 8th dynasties ruled from Memphis, the 9th and 10th - from Herakleopolis, and the 11th – from Thebes. ...
... heirs and after his death there was a civil war and instability for about 100 years. The 7th and 8th dynasties ruled from Memphis, the 9th and 10th - from Herakleopolis, and the 11th – from Thebes. ...
Meroe Chapter_I - Les grandes énigmes de l`Antiquité
... 2. KUSH THE MILLENARY ENEMY OF EGYPT 2.1 The first people of Upper Nubia The Kingdom of Kush was one of the earliest civilizations to develop in the Nile Valley. Having also been referred to as Nubians, and as "Ethiopians" in ancient Greek and GrecoRoman records, the Kushites left their mark on vari ...
... 2. KUSH THE MILLENARY ENEMY OF EGYPT 2.1 The first people of Upper Nubia The Kingdom of Kush was one of the earliest civilizations to develop in the Nile Valley. Having also been referred to as Nubians, and as "Ethiopians" in ancient Greek and GrecoRoman records, the Kushites left their mark on vari ...
Websites and Books on Ancient Egypt - Anthropology
... Volume of the lithographs of David Roberts, who in 1838 set out for Egypt where he made countless sketches of the most remarkable sites and monuments. Bowman, Alan K. Egypt After the Pharaohs: 332 B.C. - A.D. 642 from Alexander to the Arab Conquest. Rev. ed. University of California Press, 1996. Bri ...
... Volume of the lithographs of David Roberts, who in 1838 set out for Egypt where he made countless sketches of the most remarkable sites and monuments. Bowman, Alan K. Egypt After the Pharaohs: 332 B.C. - A.D. 642 from Alexander to the Arab Conquest. Rev. ed. University of California Press, 1996. Bri ...
Websites and Books on Ancient Egypt
... Volume of the lithographs of David Roberts, who in 1838 set out for Egypt where he made countless sketches of the most remarkable sites and monuments. Bowman, Alan K. Egypt After the Pharaohs: 332 B.C. - A.D. 642 from Alexander to the Arab Conquest. Rev. ed. University of California Press, 1996. Bri ...
... Volume of the lithographs of David Roberts, who in 1838 set out for Egypt where he made countless sketches of the most remarkable sites and monuments. Bowman, Alan K. Egypt After the Pharaohs: 332 B.C. - A.D. 642 from Alexander to the Arab Conquest. Rev. ed. University of California Press, 1996. Bri ...
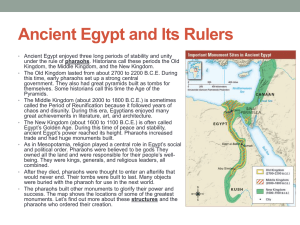
Ancient Egypt and Its Rulers
... ruled Egypt from about 1473 to 1458 B.C.E. Hatshepsut was Egypt’s first female pharaoh. Under her rule, Egyptian art and architecture flourished. Hatshepsut was also known for encouraging trade. One of her greatest accomplishments was her rise to power. Never before had a woman pharaoh ruled Egypt. ...
... ruled Egypt from about 1473 to 1458 B.C.E. Hatshepsut was Egypt’s first female pharaoh. Under her rule, Egyptian art and architecture flourished. Hatshepsut was also known for encouraging trade. One of her greatest accomplishments was her rise to power. Never before had a woman pharaoh ruled Egypt. ...
Chemistry in the Time of the Pharaohs
... not in Egypt. Indeed, the supremacy of iron weapons over the copper alloy ones has been seen as a major factor in the Persian conquest of Egypt in about 600 B.C.E. (8). After this time, iron smelting began in Egypt (4). From the 4th Dynasty onward (2500 B.C.E.), the pharaoh had the monopoly of metal ...
... not in Egypt. Indeed, the supremacy of iron weapons over the copper alloy ones has been seen as a major factor in the Persian conquest of Egypt in about 600 B.C.E. (8). After this time, iron smelting began in Egypt (4). From the 4th Dynasty onward (2500 B.C.E.), the pharaoh had the monopoly of metal ...
Reading Group - Hachette Book Group
... provide relative peace and provide opportunity to its citizens. What many take for granted is that these achievements rest on a foundation thousands of years old. Ancient Egypt, one of the world's first complex civilizations, played a vital role in the development of such aspects of our culture as a ...
... provide relative peace and provide opportunity to its citizens. What many take for granted is that these achievements rest on a foundation thousands of years old. Ancient Egypt, one of the world's first complex civilizations, played a vital role in the development of such aspects of our culture as a ...
WAS KHENT-KAWES HISTORY`S FIRST WOMAN KING
... unknown during Hassan’s excavation of the Giza tomb 44 years earlier. From 1976 to 1978 this small pyramid, sited between the pyramids of Neferirkare and Raneferef, was explored by archaeologists from the Czechoslovak Institute of Egyptology in Cairo under the leadership of Miroslav Verner. They cam ...
... unknown during Hassan’s excavation of the Giza tomb 44 years earlier. From 1976 to 1978 this small pyramid, sited between the pyramids of Neferirkare and Raneferef, was explored by archaeologists from the Czechoslovak Institute of Egyptology in Cairo under the leadership of Miroslav Verner. They cam ...
What are the gifts of the Nile?
... houses and lives were often destroyed. (Believed to be messages from the Gods). • However, once they figured out that the floods took place at the same time every year, they developed methods for using the mineral rich silt. Egyptian life was split into 3 seasons: flooding, planting and ...
... houses and lives were often destroyed. (Believed to be messages from the Gods). • However, once they figured out that the floods took place at the same time every year, they developed methods for using the mineral rich silt. Egyptian life was split into 3 seasons: flooding, planting and ...
Ancient Egyptians Activity Sheet
... What are the two basic kinds of temples in ancient Egypt? ___________________________________________________________________________ 23. Go to: Painting and Sculpture Sculptors used tools made of what two elements? ___________________________________________________________________________ 2 ...
... What are the two basic kinds of temples in ancient Egypt? ___________________________________________________________________________ 23. Go to: Painting and Sculpture Sculptors used tools made of what two elements? ___________________________________________________________________________ 2 ...
Winning Choices in Critical Moments, Part 5
... masters over them to oppress them with forced labor, and they built Pithom and Rameses as store cities for Pharaoh. 12 But the more they were oppressed, the more they multiplied and spread; so the Egyptians came to dread the Israelites 13 and worked them ruthlessly. 14 They made their lives bitter w ...
... masters over them to oppress them with forced labor, and they built Pithom and Rameses as store cities for Pharaoh. 12 But the more they were oppressed, the more they multiplied and spread; so the Egyptians came to dread the Israelites 13 and worked them ruthlessly. 14 They made their lives bitter w ...
File - Mrs. Sumner`s Social Science Course Website
... Pyramids were tombs for the mummified bodies of pharaohs. The largest and most magnificent of all pyramids was built under King Khufu. Constructed at Giza around 2540 B.C., the famous Great Pyramid of King Khufu covers 13 acres measure 756 ft at each side of its base and stands 481 ft high. Guardin ...
... Pyramids were tombs for the mummified bodies of pharaohs. The largest and most magnificent of all pyramids was built under King Khufu. Constructed at Giza around 2540 B.C., the famous Great Pyramid of King Khufu covers 13 acres measure 756 ft at each side of its base and stands 481 ft high. Guardin ...
A Journey Through Ancient Egypt: Teacher`s
... The goddess Maat was the personification of the basic laws of all existence; she embodied the concepts of law, truth, justice, and world order. In the Hall of Judgment at the “weighing of the heart,” the heart of the deceased was placed on the scales of justice balanced against the feather of Maat, ...
... The goddess Maat was the personification of the basic laws of all existence; she embodied the concepts of law, truth, justice, and world order. In the Hall of Judgment at the “weighing of the heart,” the heart of the deceased was placed on the scales of justice balanced against the feather of Maat, ...
5th Period - SMS Intranet
... What is the Old Kingdom? • The two kingdoms (Upper Egypt- south & Lower Egyptnorth) were unified by King Narmer, Menes • about 2664- 2180 B.C. • The pyramid age (3rd to 6th dynasties) of ancient Egypt – Ruling family (power passed one dynasty to another) ...
... What is the Old Kingdom? • The two kingdoms (Upper Egypt- south & Lower Egyptnorth) were unified by King Narmer, Menes • about 2664- 2180 B.C. • The pyramid age (3rd to 6th dynasties) of ancient Egypt – Ruling family (power passed one dynasty to another) ...
Rivard Rivard While the societies of Ancient Egypt and the Ottoman
... (Goggles1).” They had an ideal position, defended naturally by the geography and their people being cultural and ethnically united; the deserts from all around, Mediterranean from the north, Nile from the south with five cataracts protecting the southern border. Egyptian cities did not even need to ...
... (Goggles1).” They had an ideal position, defended naturally by the geography and their people being cultural and ethnically united; the deserts from all around, Mediterranean from the north, Nile from the south with five cataracts protecting the southern border. Egyptian cities did not even need to ...
Research Paper
... on coming to Argos took up his abode in the city of Inachos and throughout Greece [Hellas] he laid down the law that all people hitherto named Pelasgians were to be known as Danaans” (Bernal 79). In addition, Herodotus was of the belief that the Egyptian Danaids had taught the Pelasgians “the worshi ...
... on coming to Argos took up his abode in the city of Inachos and throughout Greece [Hellas] he laid down the law that all people hitherto named Pelasgians were to be known as Danaans” (Bernal 79). In addition, Herodotus was of the belief that the Egyptian Danaids had taught the Pelasgians “the worshi ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt and Kush
... neighbors? It’s not always easy—for individuals or countries. Read on to find out about the Egyptians’ neighbors to the south and the ways the two civilizations mixed. The Egyptians were not alone in settling along the Nile River. Farther south, in present-day Sudan, another strong civilization aros ...
... neighbors? It’s not always easy—for individuals or countries. Read on to find out about the Egyptians’ neighbors to the south and the ways the two civilizations mixed. The Egyptians were not alone in settling along the Nile River. Farther south, in present-day Sudan, another strong civilization aros ...
Ancient Mysteries - Sepulveda Middle School
... dated to this dynasty and furnish the details of the reigns of Amenhotep III and his son, Akhnaton. As Akhnaton neglected his rule in the pursuit of religion, letters from local rulers became increasingly urgent in begging help, especially against the Hittites. Of the rulers following Akhnaton in t ...
... dated to this dynasty and furnish the details of the reigns of Amenhotep III and his son, Akhnaton. As Akhnaton neglected his rule in the pursuit of religion, letters from local rulers became increasingly urgent in begging help, especially against the Hittites. Of the rulers following Akhnaton in t ...
Rulers of Egypt
... such a long, narrow nation. Only the strongest and wisest of rulers could keep the borders safe. So at times, people from other places took over some of Egypt’s land. About 1730 b.c., an army from Asia came into northern Egypt. The Hyksos (HIK-saws) conquered (KAHN-kuhrd) the Nile Delta at the Medit ...
... such a long, narrow nation. Only the strongest and wisest of rulers could keep the borders safe. So at times, people from other places took over some of Egypt’s land. About 1730 b.c., an army from Asia came into northern Egypt. The Hyksos (HIK-saws) conquered (KAHN-kuhrd) the Nile Delta at the Medit ...
Chapter 4.2 - Elmwood Park Public Schools
... Owned all land, often gave as a gift to the rich Maintained the land, kept up with it to make sure it could produce ...
... Owned all land, often gave as a gift to the rich Maintained the land, kept up with it to make sure it could produce ...
Egypt: The End of a Civilisation
... language in an augmented version of the Greek alphabet. The old art style was also tainted with paganism, and so was also replaced by a style derived from outside, thus further eating away at key parts of the ancient Egyptian civilisation. End of the old ways By the fourth century AD, the old ways w ...
... language in an augmented version of the Greek alphabet. The old art style was also tainted with paganism, and so was also replaced by a style derived from outside, thus further eating away at key parts of the ancient Egyptian civilisation. End of the old ways By the fourth century AD, the old ways w ...
The First Intermediate Period, the Seventh to Eleventh
... The founder of the Ninth Dynasty, Wahkare Khety I, is often described as an evil and violent ruler who caused much harm to the inhabitants of Egypt. He was seized with madness, and, as legend would have it, was eventually killed by a crocodile. Kheti I was succeeded by Kheti II, also known as Meryi ...
... The founder of the Ninth Dynasty, Wahkare Khety I, is often described as an evil and violent ruler who caused much harm to the inhabitants of Egypt. He was seized with madness, and, as legend would have it, was eventually killed by a crocodile. Kheti I was succeeded by Kheti II, also known as Meryi ...
Ancient Egypt Study Notes - Pineda Ancient History
... Egyptians considered the kings of the Old Kingdom to be living gods. The vizier (vuh-ZIR) or chief advisers, carried out the king’s orders. The Old Kingdom is known as the “The Pyramid Age” ….Pharaohs were buried in pyramids ONLY during this time in history. Pyramids were too easy to spot and much e ...
... Egyptians considered the kings of the Old Kingdom to be living gods. The vizier (vuh-ZIR) or chief advisers, carried out the king’s orders. The Old Kingdom is known as the “The Pyramid Age” ….Pharaohs were buried in pyramids ONLY during this time in history. Pyramids were too easy to spot and much e ...
paper topics - cloudfront.net
... 2. Egypt was traditionally divided into two areas: Upper Egypt, along the southern part of the Nile as far south as the First Cataract, and Lower Egypt, the northern delta area. The climate was good for agriculture, but with little or no rainfall, farmers had to depend on the river for irrigation. 3 ...
... 2. Egypt was traditionally divided into two areas: Upper Egypt, along the southern part of the Nile as far south as the First Cataract, and Lower Egypt, the northern delta area. The climate was good for agriculture, but with little or no rainfall, farmers had to depend on the river for irrigation. 3 ...