Egyptian Economy - Colts Neck Township Schools
... Ancient Egypt: Economy, Innovation, Technology • Egyptian economy was based on agriculture – wheat ranked as the chief grain crop while cotton was raised to be woven into cloth • The Nile became filled w/farms and irrigation patterns, as well as water basins (large storage areas of water) • Ancient ...
... Ancient Egypt: Economy, Innovation, Technology • Egyptian economy was based on agriculture – wheat ranked as the chief grain crop while cotton was raised to be woven into cloth • The Nile became filled w/farms and irrigation patterns, as well as water basins (large storage areas of water) • Ancient ...
Powerpoint Slide
... Ununified Hellenic world with various citystates (polis) Aristocratic monarchies as political regimes The polis, the invention of the Greek alphabet: growth of trade and literacy ...
... Ununified Hellenic world with various citystates (polis) Aristocratic monarchies as political regimes The polis, the invention of the Greek alphabet: growth of trade and literacy ...
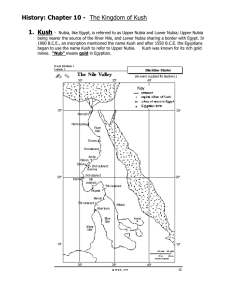
History: Chapter 10
... Once the ancient kingdom of Kush, Nubia is the stretch of land next to the Nile from Aswan down to Khartoum in the south. Nubians are depicted in many tomb paintings and reliefs, usually as mercenaries or traders. Nubians still have distinct traditions, architecture and languages, even though many ...
... Once the ancient kingdom of Kush, Nubia is the stretch of land next to the Nile from Aswan down to Khartoum in the south. Nubians are depicted in many tomb paintings and reliefs, usually as mercenaries or traders. Nubians still have distinct traditions, architecture and languages, even though many ...
Amber Myers, 2001-2002
... recovery of the texts (e.g. papyri, tablets, etc.) by European archaeologists in the nineteenth century C.E. Scholars have since studied the texts and published their translations, findings, and interpretations. It is the translations of the texts that form the core of my research. Translations of t ...
... recovery of the texts (e.g. papyri, tablets, etc.) by European archaeologists in the nineteenth century C.E. Scholars have since studied the texts and published their translations, findings, and interpretations. It is the translations of the texts that form the core of my research. Translations of t ...
egypt - The Learning Link
... ther Mycerinus, were built by farmers, who could be recruited when the floodwaters of the Nile covered their fields. Historians often describe the Old Kingdom as “the age of the pyramids” because these monumeii tal structures are one of the greatest achievements of the period. The Old Kingdom also w ...
... ther Mycerinus, were built by farmers, who could be recruited when the floodwaters of the Nile covered their fields. Historians often describe the Old Kingdom as “the age of the pyramids” because these monumeii tal structures are one of the greatest achievements of the period. The Old Kingdom also w ...
Woodward Academy Lower School Library
... Tomb of Perneb - 'Travel through space and time with the tomb of Perneb on its journey from ancient Egypt to its current home at the Met. Includes an animated reconstruction of the tomb, games, and more.' (THE METROPOLITAN MUSEUM OF ART) Treasures of Tutankhamun - 'In 1922 the discovery of the virtu ...
... Tomb of Perneb - 'Travel through space and time with the tomb of Perneb on its journey from ancient Egypt to its current home at the Met. Includes an animated reconstruction of the tomb, games, and more.' (THE METROPOLITAN MUSEUM OF ART) Treasures of Tutankhamun - 'In 1922 the discovery of the virtu ...
Nile—Egypt
... 3. New Kingdom (1551 – 1085 BCE)—the Empire Period; pharaohs expanded territory & power grew; new class emerged, the professional soldier; conflicts b/t pharaohs & priests a. Thebes (Luxor) made the capitol & wealth poured in giving funds to construct huge temple complexes b. Pharaohs (“Great Man” t ...
... 3. New Kingdom (1551 – 1085 BCE)—the Empire Period; pharaohs expanded territory & power grew; new class emerged, the professional soldier; conflicts b/t pharaohs & priests a. Thebes (Luxor) made the capitol & wealth poured in giving funds to construct huge temple complexes b. Pharaohs (“Great Man” t ...
Egypt, the Kingdom of Kush, and Mesopotamia
... 5. What is the main idea of this passage? A Ancient inventions made from iron ore were important to the success of the empires of Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Kingdom of Kush. B Ancient civilizations in the Fertile Crescent relied on rivers and harnessed their power to develop into strong and wealthy ...
... 5. What is the main idea of this passage? A Ancient inventions made from iron ore were important to the success of the empires of Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Kingdom of Kush. B Ancient civilizations in the Fertile Crescent relied on rivers and harnessed their power to develop into strong and wealthy ...
6th Grade Social Studies Ancient Egypt Museum Project
... questions from chapter 5: How does geography influence the way people live? What makes a culture unique? Why do civilizations rise and fall? 2. Must have a complimentary 1-page written piece explaining the visual project and informs the audience about your knowledge on the topic. This will be ...
... questions from chapter 5: How does geography influence the way people live? What makes a culture unique? Why do civilizations rise and fall? 2. Must have a complimentary 1-page written piece explaining the visual project and informs the audience about your knowledge on the topic. This will be ...
The Nile Valley
... • The Old Kingdom is known as the Age of Pyramids. • During this 500 year period, the Egyptians developed the technology to build the largest stone structures in the world. • In the 2,600’s B.C., King Zoser of Dynasty 3 became the first king to be buried in a stone pyramid. • This was the famous Ste ...
... • The Old Kingdom is known as the Age of Pyramids. • During this 500 year period, the Egyptians developed the technology to build the largest stone structures in the world. • In the 2,600’s B.C., King Zoser of Dynasty 3 became the first king to be buried in a stone pyramid. • This was the famous Ste ...
ancient egypt - WordPress.com
... Images could stand for perils or advantages, In the struggle getting to the kingdom of Osiris. 2. Ball games were a popular pastime for Egyptians. Leaping high in the air, ...
... Images could stand for perils or advantages, In the struggle getting to the kingdom of Osiris. 2. Ball games were a popular pastime for Egyptians. Leaping high in the air, ...
Daily Bellringer
... Khufu, called Cheops by the Greeks, was the son of King Snefru and Queen Hetepheres. Little is known about Khufu’s life. The contents of his tomb, which would have told more about his history, were stolen during ancient times. Instead, only a few clues remain about his life. The one major clue that ...
... Khufu, called Cheops by the Greeks, was the son of King Snefru and Queen Hetepheres. Little is known about Khufu’s life. The contents of his tomb, which would have told more about his history, were stolen during ancient times. Instead, only a few clues remain about his life. The one major clue that ...
The Ten Plagues of Egypt
... May have infected ponds and adjacent pools of water. Climate contributed to it. Sold commercially, thought to be a unique protein bound ...
... May have infected ponds and adjacent pools of water. Climate contributed to it. Sold commercially, thought to be a unique protein bound ...
File
... Egypt is often pictured as the world’s first civilization, but its cities got rolling a little later than Sumer, sometime after 4000 BCE. Still, a couple of hundred years is loose change at this point in human history - and if it’s a contest of size, Egypt wins hands down. Around 3100 BCE it became ...
... Egypt is often pictured as the world’s first civilization, but its cities got rolling a little later than Sumer, sometime after 4000 BCE. Still, a couple of hundred years is loose change at this point in human history - and if it’s a contest of size, Egypt wins hands down. Around 3100 BCE it became ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Middle East and Egypt 3200
... beliefs shaped the lives of ancient Egyptians Understand how Egyptians viewed the afterlife Explain hoe the Egyptians organized their society Outline the advances that the Egyptians made in learning the arts, science and ...
... beliefs shaped the lives of ancient Egyptians Understand how Egyptians viewed the afterlife Explain hoe the Egyptians organized their society Outline the advances that the Egyptians made in learning the arts, science and ...
Unit 3 — Ancient Middle East
... Having people available to work on different jobs meant that society could accomplish more. Large projects, such as constructing buildings and digging irrigations systems, required specialized workers, managers, and organization. To complete these projects, the Mesopotamians needed structure and ru ...
... Having people available to work on different jobs meant that society could accomplish more. Large projects, such as constructing buildings and digging irrigations systems, required specialized workers, managers, and organization. To complete these projects, the Mesopotamians needed structure and ru ...
Slide 1
... wheat. I must take care of my cattle too. I use oxen to help plough the fields. At Harvest time, we use sickles made of sharpened flint. The whole family must help. Although some years, Locusts may come and there might not be anything to harvest. ...
... wheat. I must take care of my cattle too. I use oxen to help plough the fields. At Harvest time, we use sickles made of sharpened flint. The whole family must help. Although some years, Locusts may come and there might not be anything to harvest. ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt and Kush
... body president or your sports team captain to have unlimited power? Think what it would be like to have such a leader as you read about the rulers of ancient Egypt. Around 2600 B.C., the period known as the Old Kingdom began in Egypt. The Old Kingdom lasted until about 2300 B.C. During those years, ...
... body president or your sports team captain to have unlimited power? Think what it would be like to have such a leader as you read about the rulers of ancient Egypt. Around 2600 B.C., the period known as the Old Kingdom began in Egypt. The Old Kingdom lasted until about 2300 B.C. During those years, ...
Ancient Egyptian Civilization
... with pre-state societies.You’ll recall that we defined these briefly in Assignment 3. It’s now time to look more closely at pre- state and state-organized societies. To refresh your memory. . . Pre-State societies are small scale societies based on the community, the band, or the village. They vary ...
... with pre-state societies.You’ll recall that we defined these briefly in Assignment 3. It’s now time to look more closely at pre- state and state-organized societies. To refresh your memory. . . Pre-State societies are small scale societies based on the community, the band, or the village. They vary ...
Discover Egypt
... The pyramid was considered a ladder to heaven, so the Pharaoh could ascend to the gods after his death. The Pyramids are located on the western bank of the Nile. Here, so the Egyptians believed, was the entrance to the netherworld because the sun goes down in the west. The largest Pyramid is the Che ...
... The pyramid was considered a ladder to heaven, so the Pharaoh could ascend to the gods after his death. The Pyramids are located on the western bank of the Nile. Here, so the Egyptians believed, was the entrance to the netherworld because the sun goes down in the west. The largest Pyramid is the Che ...
Mesopotamia River Valley Civilizations
... Egypt River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Origins Around 3,100 B.C., a king called Menes began to unite villages of the upper and lower Nile River in Northeastern Africa in an area not far from Mesopotamia. The Nile is the longest river in the world at over 4,000 miles. Its head waters are in the m ...
... Egypt River Valley Civilizations Egyptian Origins Around 3,100 B.C., a king called Menes began to unite villages of the upper and lower Nile River in Northeastern Africa in an area not far from Mesopotamia. The Nile is the longest river in the world at over 4,000 miles. Its head waters are in the m ...
Importance of the Nile River to Ancient Egypt
... The Libyans gained control of Egypt after 1100 B. C., and then the Assyrians took over. In 552 B. C., the Persians forced the Assyrians out of Egypt. In 332 B. C., the famous Macedonian, Alexander the Great, conquered Egypt. When he died, one of his generals assumed leadership. This general, King Pt ...
... The Libyans gained control of Egypt after 1100 B. C., and then the Assyrians took over. In 552 B. C., the Persians forced the Assyrians out of Egypt. In 332 B. C., the famous Macedonian, Alexander the Great, conquered Egypt. When he died, one of his generals assumed leadership. This general, King Pt ...
Menes - Net Texts
... Age". Pharaohs were buried in pyramids only during this time period in history. After building a few pyramids, at great expense to the state, it occurred to pharaohs that pyramids were rather easy to spot, and thus, much easier to rob than a hidden tomb. Things changed during the middle kingdom. The ...
... Age". Pharaohs were buried in pyramids only during this time period in history. After building a few pyramids, at great expense to the state, it occurred to pharaohs that pyramids were rather easy to spot, and thus, much easier to rob than a hidden tomb. Things changed during the middle kingdom. The ...
Ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt
... instead of funerary in nature, Predynastic period – some of the earliest hieroglyphic inscriptions and information about an Egyptian art ever found, thought by some to depict the unification of Upper and gyp under the king g Narmer.,. On Lower Egypt one side, the king is depicted with the red crown ...
... instead of funerary in nature, Predynastic period – some of the earliest hieroglyphic inscriptions and information about an Egyptian art ever found, thought by some to depict the unification of Upper and gyp under the king g Narmer.,. On Lower Egypt one side, the king is depicted with the red crown ...