Ancient Egypt
... Step Pyramid Saqqara is the earliest pyramid that is still there today. The Step Pyramid was built in 2630 B.C. The architect of the Step pyramid was Imhotep. The Egyptians later worshipped Imhotep as a god.The pyramid rose in six giant steps. It was the burial place of King Djoser. These steps ...
... Step Pyramid Saqqara is the earliest pyramid that is still there today. The Step Pyramid was built in 2630 B.C. The architect of the Step pyramid was Imhotep. The Egyptians later worshipped Imhotep as a god.The pyramid rose in six giant steps. It was the burial place of King Djoser. These steps ...
The First River Valley Civilizations, 3500 – 1500 B.C.E.
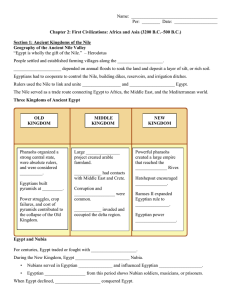
... history into thirty dynasties (kings from the same family) identified by Manetho, and Egyptian from the 3rd century B.C.E. 5. From a much broader point of view, scholars also refer Egyptian history as the “Old”, “Middle”, and “New Kingdoms”. 6. The central figure in the Egyptian state was the King a ...
... history into thirty dynasties (kings from the same family) identified by Manetho, and Egyptian from the 3rd century B.C.E. 5. From a much broader point of view, scholars also refer Egyptian history as the “Old”, “Middle”, and “New Kingdoms”. 6. The central figure in the Egyptian state was the King a ...
Food and Farming - The Fitzwilliam Museum
... a raising agent forming the basis of the next day's baking. There is also evidence that yeast was used in Egypt for baking and brewing as early as 1500 BC. To makes beer, loaves, partly baked so as not to destroy the enzymes needed for fermentation, were sieved into large vats, mixed with water and ...
... a raising agent forming the basis of the next day's baking. There is also evidence that yeast was used in Egypt for baking and brewing as early as 1500 BC. To makes beer, loaves, partly baked so as not to destroy the enzymes needed for fermentation, were sieved into large vats, mixed with water and ...
egypt test - BC Learning Network
... 1. How was the ability to interpret hieroglyphics regained with the Rosetta Stone? 2. Why was the person's heart left in the body when it was mummified? 3. Explain the mystery surrounding Tutenkhamen's death. 4. Compare the Egyptian idea ofKa with the Biblical idea of a spirit or soul. 5. Describe a ...
... 1. How was the ability to interpret hieroglyphics regained with the Rosetta Stone? 2. Why was the person's heart left in the body when it was mummified? 3. Explain the mystery surrounding Tutenkhamen's death. 4. Compare the Egyptian idea ofKa with the Biblical idea of a spirit or soul. 5. Describe a ...
Chapter 2 First civilizations Africa and Asia
... Queen Hatshepsut was the first female ruler. She encouraged trade with the eastern Mediterranean and expanded the empire as far as Africa. One of the greatest most influential pharaohs was Ramses II. Gained fame for the wars he led agaist the Hittites until a treaty was finally signed between the tw ...
... Queen Hatshepsut was the first female ruler. She encouraged trade with the eastern Mediterranean and expanded the empire as far as Africa. One of the greatest most influential pharaohs was Ramses II. Gained fame for the wars he led agaist the Hittites until a treaty was finally signed between the tw ...
Directions - Circle USD 375
... ______ 1) During the Old Kingdom, Egyptian cities became centers of business. ______ 2) Historians do not know if Menes was a real person. ______ 3) Egyptian pharaohs were kings, but not priests. ______ 4) The ancient Egyptians believed that life after death was very different from life on Earth. __ ...
... ______ 1) During the Old Kingdom, Egyptian cities became centers of business. ______ 2) Historians do not know if Menes was a real person. ______ 3) Egyptian pharaohs were kings, but not priests. ______ 4) The ancient Egyptians believed that life after death was very different from life on Earth. __ ...
Name - My CCSD
... project created arable farmland. ____________ had contacts with Middle East and Crete. Corruption and __________________ were common. ____________ invaded and occupied the delta region. ...
... project created arable farmland. ____________ had contacts with Middle East and Crete. Corruption and __________________ were common. ____________ invaded and occupied the delta region. ...
ancient egypt travel brochure
... _____________________________________________. This allowed for ________________________. They also used the Nile to ___________________________________. This helped with __________________. Finally, the Nile was the Egyptian’s primary source of/for ____________________________________. This allowed ...
... _____________________________________________. This allowed for ________________________. They also used the Nile to ___________________________________. This helped with __________________. Finally, the Nile was the Egyptian’s primary source of/for ____________________________________. This allowed ...
Ancient Civilizations Mr. Hanover Egypt Student Study Guide Egypt
... 54) What did Inhotep invent? What kind of material did he build with? 55) What figure of speech was used to describe the accuracy of Cheop’s pyramid? 56) In Egypt, was inheritance through the mother or the father? 57) How far away can you be and still see the pyramids? 58) What kind of calendar did ...
... 54) What did Inhotep invent? What kind of material did he build with? 55) What figure of speech was used to describe the accuracy of Cheop’s pyramid? 56) In Egypt, was inheritance through the mother or the father? 57) How far away can you be and still see the pyramids? 58) What kind of calendar did ...
Egypt Notes 2015 - Hewlett
... Narmer/Menes was king of Upper Egypt; he led armies to take over lower Egypt Rules from Memphis, wore a double crown United Egypt became a dynasty; was ruled by Narmrer’s descendants for 31 dynasties (2,800 years) ...
... Narmer/Menes was king of Upper Egypt; he led armies to take over lower Egypt Rules from Memphis, wore a double crown United Egypt became a dynasty; was ruled by Narmrer’s descendants for 31 dynasties (2,800 years) ...
Egypt – Nile River Valley River Valley Project Cornell notes
... The Vizier reported to the Pharaoh every day on what was happening all over Egypt The Vizier was also the judge of the high court. If you had a problem and it was not solved in the local courts, or in the provincial courts, you could bring your problem in front of the Vizier on a first come, first s ...
... The Vizier reported to the Pharaoh every day on what was happening all over Egypt The Vizier was also the judge of the high court. If you had a problem and it was not solved in the local courts, or in the provincial courts, you could bring your problem in front of the Vizier on a first come, first s ...
Ancient Egypt*s Daily Life
... When was the Rosetta Stone found? • The Rosetta Stone was found in 1799 by French soldiers who were rebuilding a fort in Egypt (in a small village in Delta called Rosetta (Rashid) What does the Rosetta Stone say? • The Rosetta Stone is a text written by a group of priests in Egypt to honour the Egyp ...
... When was the Rosetta Stone found? • The Rosetta Stone was found in 1799 by French soldiers who were rebuilding a fort in Egypt (in a small village in Delta called Rosetta (Rashid) What does the Rosetta Stone say? • The Rosetta Stone is a text written by a group of priests in Egypt to honour the Egyp ...
Focus Question: What were the characteristics of the world`s first
... Power passed from one dynasty, or ruling family, to another, but Egypt generally stayed united for over 2,000 years. During the Old Kingdom, pharaohs, or Egyptian kings, created a strong central government. They set up a bureaucracy, with a vizier, or chief minister of government. The Great Pyramids ...
... Power passed from one dynasty, or ruling family, to another, but Egypt generally stayed united for over 2,000 years. During the Old Kingdom, pharaohs, or Egyptian kings, created a strong central government. They set up a bureaucracy, with a vizier, or chief minister of government. The Great Pyramids ...
Egypt-Geography-Notes-Outline
... D. Protected from invades, the villages along the Nile grew. a. By 3200 BCE, the villages banded together and developed into two kingdoms: Lower Egypt and Upper Egypt. Kings Unify Egypt A. Lower Egypt – capital was Pe and the king wore a red crown. B. Upper Egypt – capital was Nekhen and the king wo ...
... D. Protected from invades, the villages along the Nile grew. a. By 3200 BCE, the villages banded together and developed into two kingdoms: Lower Egypt and Upper Egypt. Kings Unify Egypt A. Lower Egypt – capital was Pe and the king wore a red crown. B. Upper Egypt – capital was Nekhen and the king wo ...
This is Jeopardy - Town of Mansfield, CT
... Egypt, Etc. for 500 • The opening of the mouth ceremony was for these 2 purposes. • What is allowing deceased person to speak and eat in the afterlife? ...
... Egypt, Etc. for 500 • The opening of the mouth ceremony was for these 2 purposes. • What is allowing deceased person to speak and eat in the afterlife? ...
Old Kingdom - Construction Technology Many temples from Ancient
... Obelisks were a prominent part of the architecture of the ancient Egyptians, who placed them in pairs at the entrances of temples. In 1911, Encyclopædia Britannica wrote, "The earliest temple obelisk still in position is that of Senwosri I. of the XIIth Dynasty at Heliopolis (68 feet high)". The wor ...
... Obelisks were a prominent part of the architecture of the ancient Egyptians, who placed them in pairs at the entrances of temples. In 1911, Encyclopædia Britannica wrote, "The earliest temple obelisk still in position is that of Senwosri I. of the XIIth Dynasty at Heliopolis (68 feet high)". The wor ...
Western Asia and Egypt
... How did Nebuchadnezzar defend his city? What happened to Babylon in 539 B.C.? How did the Persians treat the various groups they incorporated into their empire? Who was responsible for the unification of the Persian empire? When did this occur? What is a satrap and how does it differ from a satrapy? ...
... How did Nebuchadnezzar defend his city? What happened to Babylon in 539 B.C.? How did the Persians treat the various groups they incorporated into their empire? Who was responsible for the unification of the Persian empire? When did this occur? What is a satrap and how does it differ from a satrapy? ...
Ancient Egyptian Social Structure
... lives. Horus was the son of Isis and Osiris. Then the pharaohs would become the god Osiris when they died, people believed. The pharaohs had complete power over the people. After pharaohs died, huge stone pyramids were built as their graves. Pharaohs were buried in rooms inside the pyramids. ...
... lives. Horus was the son of Isis and Osiris. Then the pharaohs would become the god Osiris when they died, people believed. The pharaohs had complete power over the people. After pharaohs died, huge stone pyramids were built as their graves. Pharaohs were buried in rooms inside the pyramids. ...
Egypt Powerpoint
... • Unlike Sumer, Egypt moved (fairly directly) from pre-civilization to large government units. • Egypt had a strong Pharoah (king), and had fewer problems with political unity than in Mesopotamia • This unification was partly due to the unifying influence of the Nile River ...
... • Unlike Sumer, Egypt moved (fairly directly) from pre-civilization to large government units. • Egypt had a strong Pharoah (king), and had fewer problems with political unity than in Mesopotamia • This unification was partly due to the unifying influence of the Nile River ...
SECTION_3_TEXT__egypt
... Finally, around 2050 BC, a powerful pharaoh named Mentuhotep II defeated his rivals. Once again all of Egypt was united. Mentuhotep’s rule began the Middle Kingdom, a period of order and stability that lasted until about 1750 BC. Toward the end of the Middle Kingdom, however, Egypt again experienced ...
... Finally, around 2050 BC, a powerful pharaoh named Mentuhotep II defeated his rivals. Once again all of Egypt was united. Mentuhotep’s rule began the Middle Kingdom, a period of order and stability that lasted until about 1750 BC. Toward the end of the Middle Kingdom, however, Egypt again experienced ...
Treasures of Egypt
... Temple of Queen Hatshepsut • 17) Temple of Queen Hatshepsut, located in Luxor, built of limestone. She became a 5-m pharaoh of the 18 th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt and the rules for longer than any other woman of the Egyptian dynasties. ...
... Temple of Queen Hatshepsut • 17) Temple of Queen Hatshepsut, located in Luxor, built of limestone. She became a 5-m pharaoh of the 18 th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt and the rules for longer than any other woman of the Egyptian dynasties. ...
What was the “SOUL” of Ancient Egypt?
... • Each hieroglyph found in pyramids and tombs often symbolized more than one consonant. Not only that, but actual Egyptian hieroglyphs were a combination of sound-signs, pictograms, and ideograms. No wonder it was so hard to decode them! ...
... • Each hieroglyph found in pyramids and tombs often symbolized more than one consonant. Not only that, but actual Egyptian hieroglyphs were a combination of sound-signs, pictograms, and ideograms. No wonder it was so hard to decode them! ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.